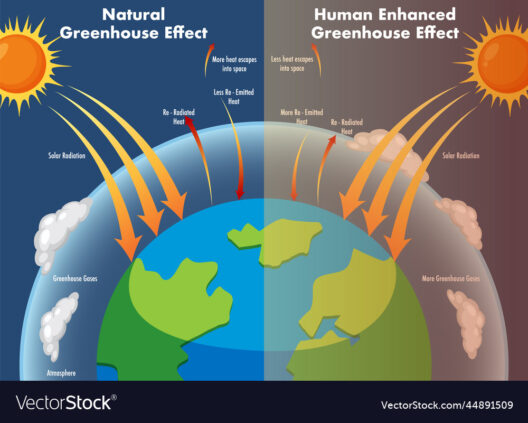
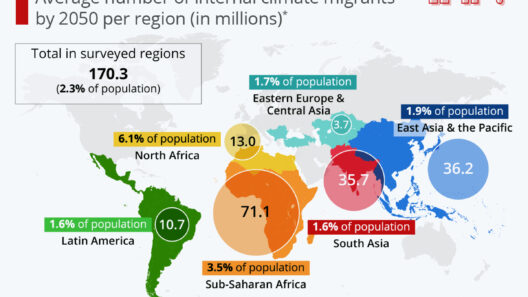
The nexus of artificial intelligence (AI) and climate change presents an intricate tapestry of potential benefits and considerable challenges. Deploying AI in the realm of environmentalism can instigate transformative changes, optimizing processes while also augmenting our understanding of climate dynamics. This article delves into how AI can serve as both a formidable ally in combating climate change and, conversely, as a contributor to the problem if mismanaged. The duality of technology necessitates a discerning examination of its applications and implications.
One primary avenue by which AI contributes to climate change mitigation is through enhanced predictive analytics. Machine learning algorithms can process vast quantities of climate data—ranging from weather patterns to greenhouse gas emissions—thereby yielding insights that enable more accurate forecasts. For instance, AI models can assess historical climate data and identify trends, facilitating early warnings for extreme weather events. This predictive capability can empower governments and organizations to devise timely responses and allocate resources more effectively, ultimately saving lives and minimizing economic losses.
Additionally, AI is instrumental in optimizing energy systems. The energy sector, particularly when transitioning to renewable sources, stands to benefit immensely from AI-driven analytics. Algorithms can optimize energy consumption, predict power demands, and manage distribution networks more efficiently. This is particularly evident in smart grids, which leverage AI to balance load and forecast energy production from renewable sources like solar and wind. By maximizing the efficacy of these systems, AI enables a significant reduction in reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to a decrease in overall carbon emissions.
Moreover, AI finds application in precision agriculture, a transformative approach to food production that significantly lessens environmental impacts. Drones equipped with AI can monitor crop health, soil conditions, and water usage. By employing data analytics, farmers can tailor their input usage—such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides—far more accurately than traditional methods allow. This not only boosts crop yields but also minimizes the ecological footprint of agricultural practices, addressing one of the leading drivers of climate change.
AI also plays a pivotal role in biodiversity conservation efforts. Algorithms can analyze data from satellite imagery and sensor networks to monitor wildlife populations and their habitats. Conservationists can utilize predictive models to address threats such as poaching, habitat loss, and climate-induced shifts in ecosystems. The integration of AI in these scenarios not only aids in the protection of endangered species but also contributes to broader ecological stability, critical in mitigating the effects of climate change.
However, it is crucial to recognize the potential perils of AI in the context of climate change. One significant concern lies in the energy consumption associated with training large AI models. The computational power required for deep learning algorithms often leads to substantial carbon footprints, particularly if the electricity used originates from fossil fuels. The paradox here is that while AI has the potential to optimize energy usage, its own operational demands can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions if not managed responsibly. This calls for an urgent conversation about sustainable AI practices and the need for green computing initiatives.
Furthermore, the implementation of AI systems can inadvertently exacerbate social inequalities. Vulnerable communities frequently bear the brunt of climate impacts, yet they may have limited access to AI technologies meant to mitigate those crises. If AI-driven solutions are developed without considering equitable access, the digital divide may amplify existing disparities. Hence, it is imperative that stakeholders prioritize inclusivity in the deployment of AI in environmental strategies.
Addressing the question of governance and ethical concerns surrounding AI in climate action is equally vital. As AI continues to evolve, questions surrounding accountability and transparency become more pertinent. Decisions made by algorithms can sometimes appear opaque, leading to mistrust among stakeholders. Establishing robust ethical frameworks will be crucial in ensuring that AI-based climate solutions are deployed responsibly and effectively. Stakeholders must engage in comprehensive dialogues to create guidelines that ensure AI is employed in ways that align with environmental and social justice principles.
In terms of content readers can expect on this topic, a blend of case studies, expert interviews, and analytical reports can provide a well-rounded understanding of AI’s role in climate change. Case studies highlighting successful AI applications in climate initiatives can serve as inspiring blueprints for future projects. Expert interviews with leading researchers and practitioners offer insights into emerging trends and best practices. Lastly, analytical reports dissecting climate data through the lens of AI trends will furnish readers with actionable knowledge and awareness of ongoing developments in this field.
In conclusion, the interplay between AI and climate change is characterized by immense promise and significant risk. Harnessing the power of AI can propel humanity towards more effective climate strategies, optimizing energy use, conserving biodiversity, and enhancing predictive capabilities. However, mindful implementation is crucial to mitigate unintended consequences. As society grapples with the sprawling implications of this technology, fostering collaborative frameworks and equitable access will be essential in ensuring that AI acts as a robust ally in the collective fight against climate change.