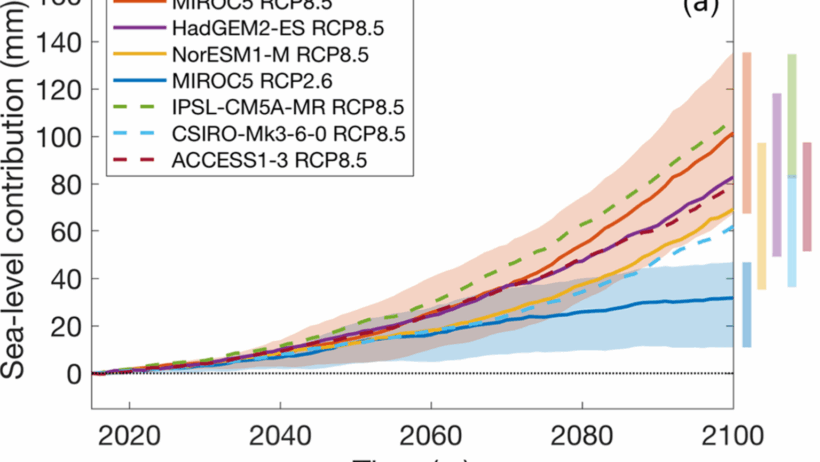
The phenomenon of rising sea levels serves as a stark indicator of the multifaceted impacts of global warming. As temperatures steadily rise, a critical relationship unfolds between warming atmospheric conditions and the consequent rise in ocean levels. Understanding this connection is pivotal, not only for coastal communities but for the entire planet, as it foreshadows sweeping ecological shifts and socio-economic challenges. This article delves into the intricacies of how global warming exacerbates sea level rise, illuminating the mechanisms at work and the wider implications for our environment.
The warming of the Earth’s atmosphere is predominantly driven by anthropogenic activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and other practices that amplify the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. As global temperatures soar, two primary processes contribute to the rise in sea levels: thermal expansion of seawater and the melting of land-based ice, including glaciers and polar ice sheets.
Thermal Expansion: The Heat Is On
One primary process contributing to rising sea levels is thermal expansion—the tendency of water to occupy more space as it warms. As ocean temperatures increase due to the accumulation of heat in the atmosphere, the water molecules expand, leading to a measurable rise in sea level. Sea surface temperatures have already escalated by approximately 1.5°C since the late 1800s, resulting in significant expansion. This process may seem subtle, but its cumulative effects translate into considerable increases in overall ocean levels over time.
This means that every incremental rise in temperature leads to a corresponding rise in sea levels. Estimates suggest that thermal expansion contributes nearly half of the observed increase in sea levels. As ocean waters continue to absorb heat, the risk of exceeding critical thresholds grows, potentially resulting in catastrophic consequences for coastal environments and ecosystems.
The Melting of Ice: A Ticking Time Bomb
In tandem with thermal expansion, the melting of glaciers and polar ice sheets contributes substantially to rising sea levels. The Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets hold vast reservoirs of freshwater, and their ongoing deterioration poses an imminent threat to global sea levels. Research indicates that these ice sheets have shown a pronounced acceleration in loss, primarily due to higher surface temperatures dipping below freezing, which creates conditions conducive to accelerated melting.
For instance, the Greenland ice sheet is currently losing an estimated 250 billion tons of ice annually, significantly contributing to global sea level rise. Meanwhile, the expansive Antarctic ice sheets, increasingly unstable, release colossal icebergs into ocean waters, further exacerbating the situation. The breaking apart of these massive structures introduces new water into the ocean, culminating in elevated sea levels while also altering oceanic currents and weather patterns.
Glacier retreat, another salient aspect in this equation, cannot be overlooked. From the Himalayas to the Andes, glaciers are dwindling, and as they vanish, runoff adds to the volume of surrounding water bodies. This situation not only threatens freshwater supplies but also contributes directly to the rising tide affecting coastal cities worldwide.
Future Projections: An Alarming Trajectory
The trajectory of global warming and its implications for sea level rise are deeply concerning. Projections suggest that, without substantial intervention to curb greenhouse gas emissions, sea levels could rise by as much as three feet by the end of the century. Such increases could inundate coastal cities, displace millions, and irreversibly devastate natural habitats through increased salinity and erosion. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has warned that the worst-case scenarios could see even higher sea level rises, further compounding the urgency of addressing climate change.
Coastal Adaptation: Strategies for Resilience
The impending challenge posed by rising sea levels necessitates strategic, adaptive responses from policymakers, scientists, and communities alike. One key approach to tackling the crisis entails enhancing the resilience of coastal infrastructure through innovative urban planning and landscape architecture. Initiatives such as constructing sea walls, restoring wetlands, and implementing sustainable drainage systems can mitigate flood risks and safeguard vulnerable areas.
Moreover, ecosystems like mangroves and coral reefs play a critical role in coastal protection. By preserving these natural barriers, communities can enhance their defenses against the encroaching sea while also fostering biodiversity. The nexus between conservation and adaptation is vital, as it promotes ecological integrity while addressing the human-centric challenges posed by climate change.
Public awareness of the gravity of rising sea levels is integral to galvanizing action. Engaging local communities in climate preparedness programs, emphasizing the importance of sustainable practices, and advocating for renewable energy sources can collectively steer societal behavior towards a more sustainable trajectory. Educating individuals on their carbon footprint and its implications is crucial for affecting change at the grassroots level.
Conclusion: The Call to Action
As we navigate the complexities of global warming and its ramifications, comprehending how rising sea levels intertwine with the phenomenon becomes imperative. Climate change isn’t a distant threat; it’s a pressing reality that demands immediate attention. The interplay between thermal expansion and ice melt vividly illustrates the urgency of our situation. Failure to take decisive actions now could lead to irreversible damage to our ecosystems and the communities that depend on them. Thus, it is not merely a matter of survival, but a clarion call for resilience, innovation, and collective responsibility to safeguard our planet for future generations.