Global warming constitutes one of the most formidable challenges of our time, catalyzing profound shifts in weather patterns, elevating sea levels, and wreaking havoc on biodiversity. Tackling this multifaceted phenomenon requires a concerted global effort, one grounded in scientific rationale and ambitious innovation. This exploration delves into actionable, science-backed solutions that promise to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and foster resilience against climate change.
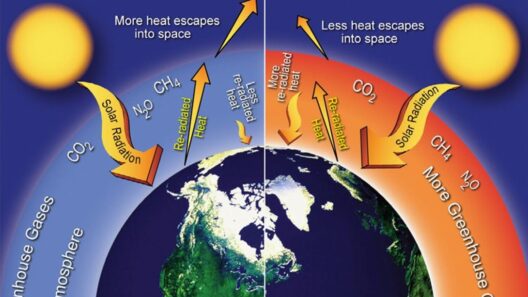
At the nucleus of global warming is the unabated release of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4). These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to rising global temperatures. Reversing this trend necessitates a drastic reduction in emissions through diverse strategies. Transitioning to renewable energy sources represents a foundational solution. Solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy harness natural processes that emit little to no greenhouse gases compared to fossil fuels.
Significantly, solar energy exemplifies this transition. The price of photovoltaic cells has plummeted over the past decade, making solar power more accessible. Harnessing solar energy on a larger scale can fundamentally transform energy consumption in households and industries alike. Wind energy, meanwhile, is another powerhouse alternative, with wind farms gaining traction globally. The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that both solar and wind could together supply over half of the world’s electricity by 2040 if given the proper policy support.
Beyond adopting renewable energy, enhancing energy efficiency looms large as an effective strategy. Energy-efficient appliances, LED lighting, and improved building designs result in significant reductions in energy consumption. The implementation of stringent standards for energy efficiency can catalyze widespread adoption, enabling consumers to reduce both their carbon footprints and their energy bills. Smart technologies, including home automation systems that optimize energy use, also present a fascinating opportunity for energy conservation.
However, merely converting to renewable energy and improving efficiency will not suffice without addressing the transportation sector, a significant contributor to fossil fuel emissions. Electrifying transportation through electric vehicles (EVs) and expanding public transport systems can dramatically curtail emissions. EVs have advanced considerably, offering longer ranges and faster charging times, rendering them more practical for daily use. Coupled with the establishment of charging infrastructure and incentives for EV purchases, this transition could spark a major reduction in reliance on conventional combustion engines.
Moreover, an innovative perspective lies in the burgeoning field of carbon capture and storage (CCS). CCS technology captures carbon dioxide emissions produced from the use of fossil fuels in electricity generation and industrial processes, preventing CO2 from entering the atmosphere. Captured carbon can be stored underground or utilized in various industrial processes, creating a closed-loop system that may fundamentally alter the landscape of emissions management.
The role of reforestation and afforestation cannot be underestimated in the climate mitigation arsenal. Forests act as vital carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Initiatives aimed at restoring degraded ecosystems or planting new forests not only sequester carbon but also enhance biodiversity and improve local climatic conditions. Engaging communities in tree-planting efforts fosters a sense of stewardship and can bolster local economies through eco-tourism and sustainable forestry practices.
This brings us to another critical component: sustainable agriculture practices. Conventional agricultural methods often exacerbate climate change through methane emissions from livestock and nitrous oxide from fertilizers. Techniques such as regenerative agriculture, permaculture, and agroforestry can significantly reduce emissions. These methods enhance soil health, improve water retention, and optimize resource use, aligning economic and environmental goals. Additionally, supporting local food systems bolsters food security while minimizing carbon footprints associated with food transportation.
Public policy plays an indispensable role in all these initiatives. Governments must enact robust regulations geared towards emissions reduction, such as carbon pricing mechanisms, which could incentivize businesses to limit their emissions. Transitioning subsidies from fossil fuels to renewable energies reflects a commitment to sustainable development, ensuring that economic investments align with climate goals. Nurturing international collaborations, such as the Paris Agreement, catalyzes combined efforts toward a low-carbon future.
Education and awareness also cannot be overlooked. Empowering individuals with knowledge about climate change and its impacts encourages responsible consumption patterns. Grassroots movements have shown that collective action can lead to meaningful change. People are motivated to make a difference; however, they require the tools and understanding to navigate the complexities of sustainability.
In essence, combating global warming mandates an integrated approach, where renewable energy, energy efficiency, cleaner transportation, innovative technologies, sustainable practices, policy advocacy, and public awareness converge. Each solution, while distinct, operates interdependently, creating a synergistic effect that amplifies progress against climate change.
As we contemplate the diverse pathways to curtail global warming, a fundamental shift in perspective is essential. Viewing climate solutions not solely as burdens but as avenues for innovation, job creation, and improved public health can pique curiosity and attract stakeholders from all walks of life. The era of climate awareness is not merely a scientific endeavor; it is an opportunity to redefine our societal values and priorities for a sustainable future.