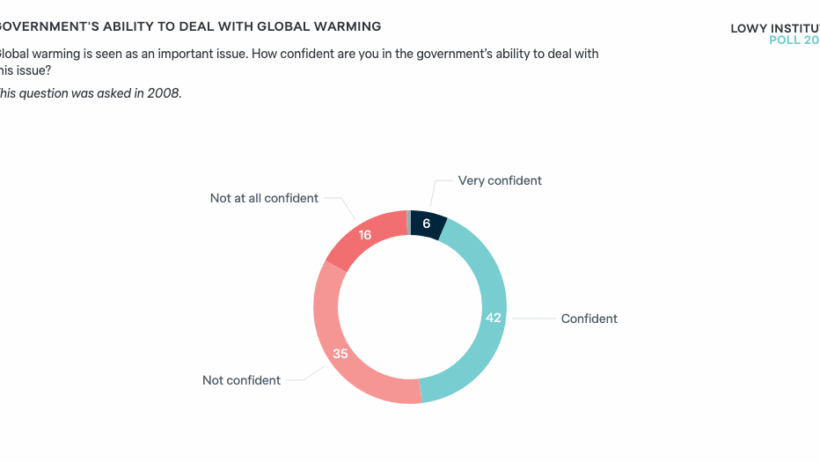
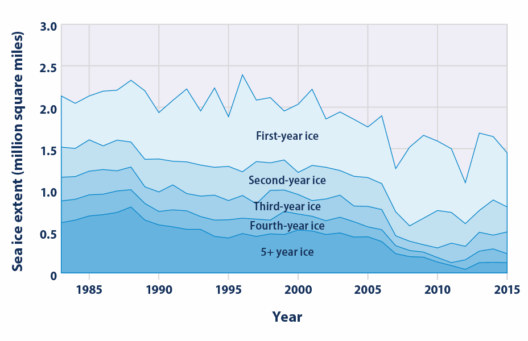
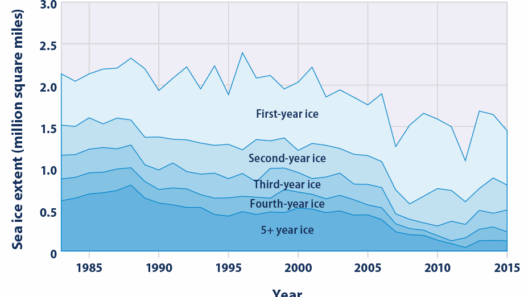
Climate change constitutes one of the most formidable challenges of our era. Its implications permeate every aspect of our existence, from socio-political stability to economic viability and public health. As temperatures rise and extreme weather events become more common, the need for concerted efforts from governments worldwide becomes increasingly urgent. Central to this endeavor are the roles of leadership and legislation. This article will explore how these elements can be harnessed to prevent global warming, focusing on various strategies that governments can implement.
Leadership in environmental policy is not merely about setting goals but also about inspiring a collective commitment to action. Effective leaders must prioritize climate change and communicate its significance to the populace. This entails utilizing a language that resonates and transcends scientific jargon. The art of persuasion, therefore, is essential. By fostering an emotional connection to the issue, leaders can engage citizens, galvanizing them to participate in sustainable practices and support legislative frameworks aimed at combating climate change.
Effective leadership must also include a multidisciplinary approach. Governments should consider the expertise of scientists, economists, social scientists, and grassroots activists. Bridging these diverse perspectives ensures that policies are well-informed and holistic. A practical example can be seen in the integration of climate change adaptation strategies into urban planning. This approach requires collaboration between urban planners, environmental experts, and community members to design cities that are resilient to climate impacts while also reducing their carbon footprint.
In tandem with leadership, robust legislation is a critical component of preventing global warming. Governments have the power to enact laws that can foster significant shifts in societal behavior and industrial practices. This legislative apparatus can target several pivotal areas, such as energy, transportation, industrial emissions, and waste management. For instance, implementing stringent emissions regulations for industries compels companies to innovate and adopt cleaner technologies.
Furthermore, one of the most effective legislative measures is the introduction of carbon pricing. This economic strategy assigns a cost to carbon emissions, effectively incentivizing businesses and individuals to reduce their carbon output. Countries that have adopted carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems illustrate the profound potential of such legislation. These mechanisms not only disincentivize harmful practices but also generate revenue that can be funneled into renewable energy initiatives and public transportation systems.
The transportation sector represents another significant focal point for legislation aimed at curbing global warming. Governments can promote the transition to electric vehicles (EVs) through subsidies, grants, and the establishment of comprehensive charging infrastructure. Additionally, investment in public transportation systems reduces reliance on personal vehicles, minimizing congestion and emissions. This multifaceted approach enables a systemic shift toward a more sustainable transportation paradigm.
Another area where leadership and legislation intersect is in fostering innovation in renewable energy technologies. Governments can facilitate research and development by providing grants and tax incentives for clean energy projects. This not only stimulates economic growth but also positions countries as leaders in the burgeoning green economy. The shift toward wind, solar, and geothermal energy sources can be accelerated through government-backed initiatives that promote public-private partnerships.
In terms of renewable energy, legislation requiring a certain percentage of energy production from renewable sources can create a stable market demand. For instance, renewable portfolio standards can ensure that utilities are held accountable for diversifying their energy sources. Investments in grid infrastructure further bolster this transition, ensuring that renewable energy can be efficiently integrated into existing systems.
Moreover, education and public awareness are critical components in this fight against global warming. Governments should invest in educational campaigns that elucidate the science of climate change and its impacts on daily life. By fostering environmental literacy from an early age, societies can cultivate a generation of informed citizens who are equipped to make sustainable choices. Schools, community centers, and digital platforms can serve as conduits for disseminating this vital information.
The role of international cooperation cannot be underestimated in the fight against climate change. Established agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, underscore the necessity for unified action. Governments must engage in meaningful dialogue, sharing best practices and technologies that can facilitate global warming mitigation. Initiatives that foster collaboration across borders can result in a more comprehensive approach to environmental challenges, enriching the efforts of individual nations.
In addition, governments must also consider social justice implications in their climate policies. Environmental issues often disproportionately affect marginalized communities. Therefore, inclusive climate action—that engages diverse stakeholders—is paramount. Legislation that prioritizes equity ensures that solutions are accessible to all citizens, fostering a united front in the battle against climate change.
The private sector plays a pivotal role in implementing climate solutions. Governments can encourage corporate accountability through regulations that require businesses to report their environmental impact. Publicly available sustainability reports can drive transparency and consumer awareness, leading to informed purchasing decisions. Furthermore, ethical consumerism can be amplified through legislative measures that endorse sustainable business practices and facilitate certifications for eco-friendly products.
In conclusion, the prevention of global warming is a multidimensional challenge that necessitates a robust synergy between leadership and legislation. By embracing a comprehensive approach that includes technological innovation, economic incentives, public education, and international cooperation, governments can spearhead the transition to a sustainable future. Every policy decision not only has immediate implications but also resonates through generations, making it imperative for today’s leaders to act decisively in the face of climate change.