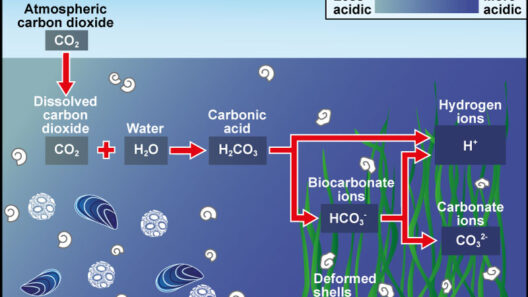
Climate change is an exigent reality confronting humanity, precipitated largely by anthropogenic activities that emit greenhouse gases. As global temperatures continue to escalate, it becomes imperative for individuals to understand how their actions can mitigate their impact on global warming. This discourse delineates actionable strategies that each person can adopt to contribute to a more sustainable future.
At the heart of combating climate change lies the principle of carbon footprint minimization. The carbon footprint quantifies the total greenhouse gas emissions that result directly and indirectly from an individual’s lifestyle. A holistic understanding of this concept facilitates more conscientious decisions. One foundational approach involves re-evaluating the means of transportation employed in daily life. Opting for public transportation, carpooling, cycling, or simply walking when feasible can substantially curtail fossil fuel consumption.
In addition to transportation methods, another significant contributor to individual carbon footprints is energy consumption in households. Appliances, lighting, and heating systems can exhaust considerable amounts of energy. Transitioning to energy-efficient appliances and integrating smart technologies can lower energy bills and minimize carbon emissions. For instance, utilizing LED bulbs instead of incandescent ones can reduce electricity use by up to 75% over their lifespan. Furthermore, implementing smart thermostats enables better regulation of heating and cooling, leading to decreased energy consumption.
A pertinent observation within the realm of global warming relates to dietary choices. The production of food, particularly animal products, is a formidable source of greenhouse gas emissions. The extensive resources required for livestock farming, including land, water, and feed, contribute to deforestation and methane production. Thus, reducing meat consumption or exploring plant-based alternatives can have a substantial impact on one’s carbon footprint. Initiatives like “Meatless Mondays” can serve as a simple yet effective starting point.
It is also worth noting the significance of local food sourcing. By purchasing from local farmers’ markets or participating in community-supported agriculture (CSA), individuals can diminish emissions associated with food transportation. This collective shift not only supports local economies but enhances the sustainability of food systems. Additionally, growing one’s own vegetables can further solidify one’s commitment to reducing environmental impact.
Waste management represents another critical facet of reducing global warming. Landfills are notorious for producing methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Implementing a robust recycling and composting system minimizes waste and fosters a material culture that prioritizes reuse and repurposing. Adopting the principles of the circular economy can transform societal consumption patterns, shifting towards sustainability rather than disposability.
Moreover, understanding the significance of water conservation is essential. Water treatment and delivery consume energy; thus, inefficiencies in water use contribute indirectly to greenhouse gas emissions. Simple adjustments in daily habits—such as taking shorter showers, fixing leaks, and using water-efficient fixtures—can lead to significant conservation outcomes. Additionally, being mindful of water-intensive products, like cotton, can mitigate unnecessary water waste in agriculture.
Education plays a pivotal role in fostering an environmentally-conscious community. Raising awareness about climate change and its intricate ties to daily actions encourages collective responsibility. Engaging in community discussions, attending workshops, or even initiating a blog can disseminate valuable information and galvanize action among peers. Being informed cultivates a sense of urgency about the climate crisis, motivating individuals to adopt more sustainable practices.
Furthermore, advocating for policy changes is vital. Individuals can advocate for local and national policies that prioritize renewable energy, carbon emissions reductions, and sensible environmental practices. This may involve contacting legislators, participating in protests, or supporting organizations dedicated to environmental issues. Collective action often leads to monumental shifts in how societies prioritize climate issues, rendering individual efforts substantially impactful.
It is equally important to recognize the interconnectedness of global cultures with environmental sustainability. Engaging in international dialogues, whether virtually or through travel, exposes individuals to diverse perspectives on environmental stewardship. By learning from the practices of other communities, one can adopt innovative solutions that resonate on a global scale.
Individuals should also be cognizant of the role that technology can play in environmental sustainability. The rise of electric vehicles, solar panels, and wind turbines signifies a pivotal transition towards cleaner energy sources. Investing in renewable energy technologies—whether through personal choices or by supporting companies that prioritize sustainability—can drive further advancements in reducing carbon emissions. Organizations and individuals alike are harnessing technology for environmental monitoring, leading to data-driven decisions that promote a healthier planet.
In conclusion, the journey toward reducing the impact of global warming hinges on the convergence of individual actions, community engagement, and global awareness. From reimagining transportation and energy consumption to advocating for policy reforms, there exist myriad avenues for meaningful contributions. Each choice has the potential to influence decades of climate health ahead. By fostering a culture of sustainability, individuals can collectively mitigate their ecological impact and navigate toward a more resilient, thriving planet.