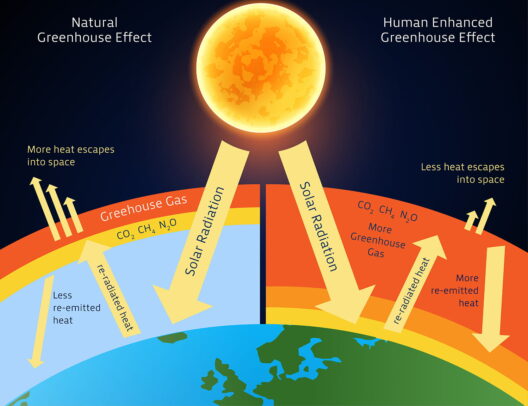
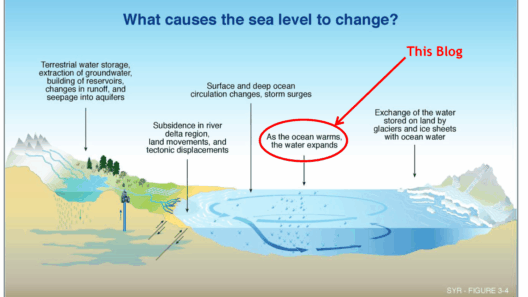
The phenomenon of rising sea levels is one of the most pressing issues in the context of climate change, with profound and multifaceted implications for human society. As the Earth’s temperature continues to rise, polar ice caps and glaciers are melting, leading to an increase in ocean volumes. This occurrence not only threatens coastal ecosystems but also presents significant social and economic challenges. Understanding the ramifications of rising seas is crucial for policymakers, urban planners, and individuals alike. This article delves into how rising sea levels can affect human life—from displacement to economic ramifications—and what this means for our global community.
Environmental Effects of Rising Sea Levels
Rising sea levels primarily affect the physical environment, particularly in coastal regions. One of the most immediate effects is the inundation of low-lying areas. Flooding becomes more frequent and severe, putting coastal cities and agriculture at risk. This phenomenon leads to not just environmental degradation but also significant changes in land use patterns. As saltwater encroaches upon freshwater sources, the quality of drinking water diminishes, making it increasingly challenging to meet basic human needs. Moreover, coastal ecosystems, including wetlands and mangroves, face existential threats, with habitat loss leading to declines in biodiversity. The ecological balance is severely threatened, with ripple effects on fish and wildlife populations crucial for human sustenance.
Human Displacement and Migration
One of the most alarming consequences of rising sea levels is the potential for widespread human displacement. As coastal regions become untenable, communities are forced to migrate inland, a process often referred to as “climate migration.” This upheaval affects millions globally, particularly in developing nations where populations are more vulnerable. The mass movement of people can lead to overcrowding in urban centers, straining infrastructure and resources.
The social dynamics of such migration can be complicated. Upon relocating, climate migrants often encounter xenophobia and resentment from established populations, which can exacerbate social tensions. Moreover, the resulting changes in demographics can impact local economies and cultural identities, leading to further conflict over scarce resources. Nations that are ill-equipped to handle these displacements may find themselves facing humanitarian crises, ultimately requiring international assistance and collaboration.
Economic Ramifications: A Multi-Pronged Dilemma
The economic impact of rising sea levels is another critical concern that cannot be overlooked. Coastal industries, particularly fishing and tourism, are at great risk. As marine ecosystems deteriorate, fish stocks decline, threatening livelihoods and food security for millions who depend on these industries. Additionally, beach erosion and flooding could deter tourists, an essential revenue source for many coastal communities.
Insurance markets are also affected, as increased flooding leads to higher payouts and higher premiums, further straining homeowners. As a result, some regions may even become uninsurable, leading to a decline in property values. This financial domino effect impacts local economies and can lead to increased taxes or changes in municipal funding priorities—factors that directly affect quality of life for residents. In summary, rising sea levels introduce a cascade of economic challenges that can influence everything from individual wealth to national policies.
Infrastructure and Urban Planning: The Challenges Ahead
The impact of rising seas necessitates urgent reconsideration of infrastructure and urban planning in vulnerable regions. As flooding becomes a predictable threat, cities must rethink their designs and adaptability strategies.
Innovative solutions have emerged in response to these challenges, including the development of floating buildings and improved drainage systems designed to cope with heavy rainfall and storm surges. Urban planners must balance environmental sustainability with the needs of growing populations, making thoughtful decisions regarding land usage.
Moreover, investment in renewable energy and green technologies can offer pathways for resilience. By transitioning to more sustainable practices, communities can better equip themselves for a changing climate, potentially mitigating some of the adverse effects associated with rising oceans.
Policy Implications: The Need for Global Collaboration
As nations grapple with the challenges of rising sea levels, effective policy frameworks will be essential. International cooperation is critical, as climate change is a global issue that transcends borders. Countries need to work together to devise comprehensive strategies for adaptation and mitigation.
Funding mechanisms for climate adaptation projects must be established, particularly aimed at helping vulnerable populations. Initiatives focusing on environmental conservation and restoration can also play a vital role in fortifying coastal communities against flooding. Grassroots movements must also be empowered, ensuring that local knowledge and concerns inform broader policy decisions.
Climate education is paramount, enabling individuals and communities to understand the implications of rising sea levels and actively participate in solutions. In essence, acknowledging the multifaceted impacts of rising sea levels sets the stage for informed action, fostering resilience in communities globally.
In conclusion, the rising tide of our oceans is not merely an environmental issue—it is an existential challenge for humanity. From ecological disaster to economic loss and social upheaval, the ramifications of rising sea levels are far-reaching. By understanding these issues, communities can better prepare for the challenges ahead, advocating for effective policies, innovative solutions, and collective global action that prioritizes sustainability and resilience.