As global temperatures continue to rise, the urgency to combat climate change has become more critical than ever. One of the most promising solutions to mitigating the effects of global warming lies in harnessing solar energy. This clean and renewable energy source presents a compelling case for its ability to substantially decrease greenhouse gas emissions, thus contributing significantly to the preservation of our planet.
The fascination with solar energy stems from its omnipresence: sunlight is available almost everywhere and in abundant supply. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and polluting, solar energy harnesses the potential of an inexhaustible resource. With the proliferation of climate change evidence, the transition toward sustainable energy sources is not merely a choice; it is an imperative.
Solar energy systems convert sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic (PV) cells, thermal energy through solar thermal systems, and concentrated solar power (CSP) technology. Each of these methods capitalizes on the sun’s unrivaled ability to produce energy, which can power homes, businesses, and entire cities. This shift to renewable energy curtails the reliance on carbon-intensive energy sources, such as coal and natural gas, directly impacting overall greenhouse gas emissions.
One of the primary reasons solar energy helps in reducing global warming is its role in displacing fossil fuels. Conventional forms of energy generation largely involve burning fossil fuels, a process that emits significant quantities of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases. These emissions trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to climate change. Solar power, however, produces electricity without emitting CO2 during operation, making it a cleaner alternative. In fact, estimates suggest that for every megawatt-hour of solar electricity produced, approximately 900 kilograms of carbon dioxide emissions can be avoided.
Not only does solar energy minimize emissions during electricity generation, but it also promotes energy independence. By investing in solar infrastructure, countries can decrease their reliance on imported fuels, thereby enhancing their energy security. This transition towards localized energy production diminishes the geopolitical tensions often associated with fossil fuel dependence, ultimately contributing to a more stable global climate. A diversified energy portfolio bolsters resilience against price fluctuations in global fossil fuel markets.
Moreover, the proliferation of solar technology has catalyzed innovation in energy storage solutions. As solar energy production is intermittent, especially during cloudy days or at night, effective storage systems are crucial for maximizing its potential. Advancements in battery technologies, such as lithium-ion and flow batteries, allow for the efficient capture and retention of solar energy. This capability provides a reliable energy supply while simultaneously leveling out demand on the grid, allowing for smoother integration of solar power.
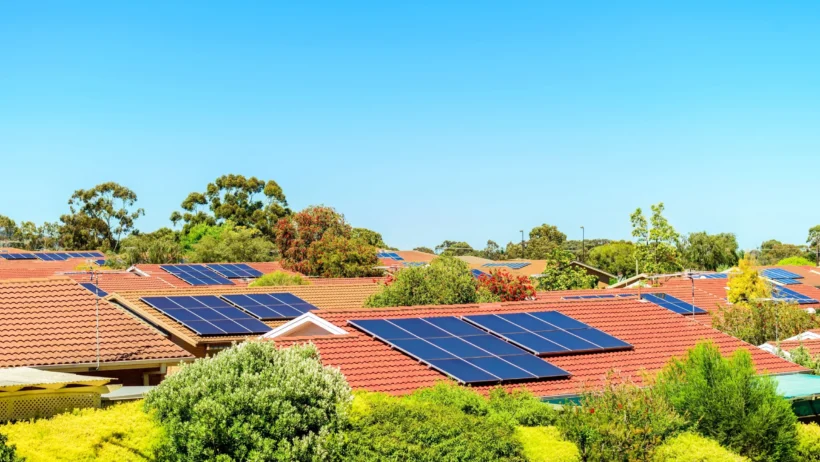
Furthermore, the scalability of solar energy solutions is highly advantageous. Solar panels can be installed on rooftops, commercial buildings, and large solar farms. This flexibility aids in generating power at various scales, from single households to vast utility-scale projects. In urban settings, where land is often scarce, rooftop installations can mitigate the urban heat island effect and reduce energy demand. As communities embrace solar energy, they not only capitalize on its environmental benefits but also stimulate local economies through job creation within the renewable energy sector.
Solar energy also holds immense potential for electrifying developing regions. Areas lacking infrastructure often remain reliant on kerosene or other polluting fossil fuels for energy, exacerbating health issues and environmental degradation. Solar power can deliver clean energy quickly and efficiently to remote communities, vastly improving living conditions. In various parts of sub-Saharan Africa, solar microgrids have emerged as viable solutions, offering light and electricity to locales without access to the traditional power grid. This energy transition is not just about reducing global warming; it is also about fostering social equity and improving quality of life.
The environmental ramifications of solar energy extend beyond greenhouse gas reductions. Traditional energy extraction processes, such as coal mining and oil drilling, often lead to catastrophic damage to ecosystems. Waterways, forests, and wildlife habitats become collateral victims in the pursuit of fossil fuel resources. In contrast, solar power installations have a much lower ecological footprint. While solar farms require land, careful site selection and environmental planning can minimize impacts on natural landscapes and biodiversity.
Of great significance is the role of government regulation and policy in promoting solar energy adoption. To unlock the full potential of solar technologies, supportive incentives, such as tax credits, rebates, and feed-in tariffs, create a conducive environment for investment. By establishing ambitious renewable energy targets, nations can accelerate the transition to a sustainable energy economy, galvanizing public and private sector collaboration to drive innovation and scalability in solar technologies.
In advocating for solar energy, it is vital to recognize the challenges that remain. Intermittency, initial installation costs, and the need for sustainable production of solar panels are key issues that require continuous attention. However, ongoing research and development can address many of these concerns, enhancing the efficiency and lifespan of solar technologies while minimizing their environmental impacts.
In conclusion, solar energy represents one of humanity’s greatest allies in the battle against climate change. By transitioning to this abundant, clean, and renewable resource, we can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enhance energy independence, and support social progress. The transition toward solar energy is not merely an alternative but an essential strategy in safeguarding our planet for future generations. Embracing this inexhaustible power source is tantamount to securing a sustainable and resilient world amidst the escalating challenges posed by global warming.