As industries continue to expand their operations, the pressing question arises: How can the industrial sector conserve energy without compromising production efficiency or growth? With the increasing awareness of climate change and its ramifications, the necessity for energy conservation has become paramount. But is it possible to balance sustainability with operational demands? This query presents not only a challenge but also an opportunity for innovation and transformation.
Energy conservation in the industrial sector is multifaceted and requires a sophisticated approach. To tackle this challenge, industries can adopt a variety of strategies that prioritize efficiency while minimizing environmental impact. Understanding the nuances of these strategies is vital for long-term sustainability.
Firstly, conducting an energy audit is an essential first step. An energy audit involves a systematic assessment of energy usage within an industrial facility. By identifying areas of inefficiency, industries can develop targeted actions to reduce energy consumption. This process involves evaluating energy systems, analyzing energy bills, and inspecting equipment performance. The result is a comprehensive understanding of energy flow, which can guide subsequent conservation efforts. Moreover, engaging employees in this audit process fosters a culture of energy consciousness in the workplace.
Once potential inefficiencies are identified, the implementation of energy-efficient technologies becomes imperative. The adoption of advanced manufacturing techniques, including automation and robotics, can significantly enhance productivity while minimizing energy expenditure. For instance, using smart sensors can optimize machinery performance by ensuring that equipment operates only when necessary, thereby reducing idle energy consumption. This method not only conserves energy but also lowers operational costs, creating a win-win scenario for businesses.
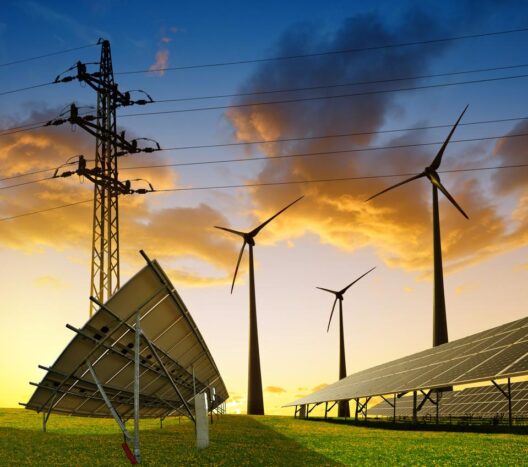
Furthermore, industries should explore the integration of renewable energy sources into their operations. Solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal heating can provide renewable energy that reduces reliance on fossil fuels. By harnessing natural energy resources, industries can significantly diminish their carbon footprint while ensuring a steady power supply. The intersection of renewable energy and industrial processes catalyzes a shift towards sustainable practices, fostering a more resilient energy grid.
Another promising avenue is the practice of cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) systems, which maximize energy utility by concurrently producing electricity and useful heat from the same energy source. These systems improve overall efficiency, drastically reducing fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. By generating power on-site, industries not only lower energy costs but also enhance energy security, further mitigating the risks associated with energy price volatility.
Moreover, investing in employee training and awareness programs can significantly bolster energy conservation efforts. Engaging the workforce in sustainability initiatives cultivates a proactive mentality toward energy management. Employees who understand the importance of energy conservation are more likely to participate in initiatives such as reducing waste, switching off unnecessary equipment, and promoting energy-efficient practices. Creating an inclusive atmosphere for dialogue about energy conservation also brings forth innovative ideas from diverse perspectives.
In terms of energy management systems, the implementation of intelligent software can revolutionize energy conservation strategies within industries. These systems utilize real-time data analytics to monitor energy consumption patterns and optimize usage. By analyzing historical usage data, industries can forecast energy needs and implement strategies to avoid peak demand times, ultimately reducing costs and energy waste. The integration of machine learning algorithms can further enhance predictive capabilities, allowing for exhaustive measures that continually adapt to changing energy landscapes.
Another critical element is to embrace circular economy principles. By rethinking product design with energy efficiency in mind, industries can create products that require less energy throughout their lifecycle, from manufacture to disposal. The circular economy model emphasizes reducing waste, reusing materials, and recycling, which inherently aligns with energy conservation. For example, using lightweight materials in manufacturing processes not only conserves energy during production but also enhances fuel efficiency during transportation.
Additionally, establishing robust partnerships with other organizations can facilitate knowledge-sharing and collaborative energy reduction initiatives. Industries can benefit greatly from participating in forums where successful strategies and experiences are exchanged. By working together, sectors can develop industry-wide standards for energy efficiency that challenge each entity to push for innovation and improvement.
Ultimately, navigating the intricate balance between energy conservation and industrial productivity requires a combination of strategies tailored to specific operational needs. Adopting a holistic approach that integrates technology, workforce engagement, renewable resources, and collaborative efforts will define the future of the industrial sector. The road ahead is rife with challenges, but the potential to advance towards a sustainable energy landscape presents an exhilarating opportunity for transformation.
As industries embark on this journey, it is essential to ask: Are we ready to embrace the change necessary for a sustainable future? The path towards energy conservation without compromise demands innovation, resilience, and unwavering commitment. With the groundwork laid through audits, technology adoption, and employee engagement, the industrial sector stands poised to tackle the energy challenges ahead. The time to act is now; let us harness our collective ingenuity to forge a future that respects both productivity and the planet.