In the ongoing struggle against global warming and climate change, trees emerge as nature’s exceptional climate warriors. Their role transcends mere aesthetics; they are integral to maintaining ecological equilibrium. An examination of how trees can save the Earth from escalating temperatures reveals their multifaceted contributions to global health and sustainability.
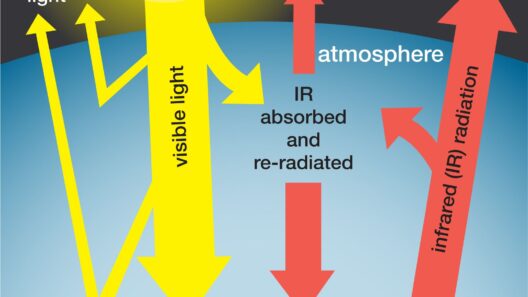
To grasp the significance of trees, one must first understand the carbon cycle. Trees act as carbon sinks, a critical process where they absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. During photosynthesis, trees utilize sunlight to convert CO2 into glucose, storing carbon in their biomass. This remarkable ability helps mitigate the greenhouse effect, which is primarily caused by excessive amounts of CO2 and other greenhouse gases trapping heat in the atmosphere. With deforestation and land-use change contributing to rising CO2 levels, trees become indispensable allies in the fight against climate change.
Additionally, trees play a pivotal role in reducing air pollution. Urban areas often struggle with high levels of pollutants, which can impact residents’ health and exacerbate climate-related crises. Trees act as natural filters. Their leaves trap dust, soot, and other harmful particles, facilitating cleaner air and a healthier environment. Through photosynthesis, they also release oxygen, a vital component of the Earth’s atmosphere, thus enhancing the air quality for all living organisms.
Moreover, trees contribute to temperature regulation. Urban heat islands, where city areas experience significantly higher temperatures than their rural counterparts, are often exacerbated by a lack of vegetation. Trees provide shade and release moisture through a process known as transpiration, which cools the surrounding air. This cooling effect can lower energy costs by reducing the need for air conditioning during scorching summers, presenting a dual benefit: energy savings and temperature moderation.
Another, often overlooked benefit of trees is their capacity to enhance biodiversity. Forests and woodlands serve as habitats for a myriad of species. Biodiversity contributes to ecosystem resilience, allowing communities to adapt to the vicissitudes of climate change. When species thrive, they fulfil essential roles, such as pollination and soil fertilization, which are crucial for agriculture, further underlining the interdependence of environmental systems.
The preservation of tree species is vital, particularly in the face of invasive species and environmental degradation. By promoting sustainable forestry practices, we can ensure the longevity and health of forests, maintaining their role as carbon sinks and biodiversity reservoirs. Initiatives focused on reforestation and afforestation are essential to replenish tree populations and reclaim deforested areas, fostering a robust response to climate change.
Community-driven tree planting initiatives have gained traction across the globe, highlighting the human aspect of this environmental issue. Engaging local populations fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards their environment. In many cases, these initiatives provide educational opportunities, making community members acutely aware of the intrinsic value of trees. Empowering individuals with knowledge about their vital contributions to mitigating climate change leads to a more educated citizenry dedicated to protecting the planet.
Additionally, trees have significant hydrological benefits. They play a crucial role in the water cycle by absorbing rainwater and facilitating groundwater recharge. This process minimizes runoff, reduces erosion, and enhances the quality of nearby waterways. By maintaining healthy tree populations, communities can mitigate the impact of flooding and combat drought conditions, showcasing trees as pivotal players in managing water resources in a changing climate.
Furthermore, trees offer substantial economic benefits. Timber, fruits, and other forest products provide livelihoods for millions, demonstrating that sustainable practices can correlate with economic prosperity. By investing in green technologies and sustainable forestry, economies can not only protect their environments but also reap financial rewards. This economic lens underscores the practicality of tree conservation and promotes a holistic view of forest management.
However, the relationship between humans and trees requires a conscious effort to foster sustainability. This includes reducing dependence on single-use plastics, advocating for responsible consumption, and supporting policies aimed at conservation and reforestation. It is imperative to understand that every individual can contribute to this collective goal. Simple actions, such as planting trees or advocating for local environmental policies, can ripple outward, creating a profound impact.
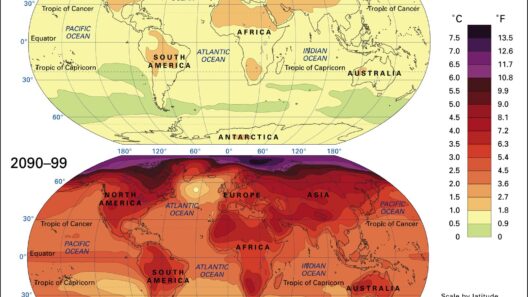
As urbanization and industrialization continue to encroach upon natural landscapes, the need for trees has never been more urgent. Their myriad benefits—including carbon sequestration, air filtration, temperature moderation, and biodiversity support—render them essential in combating climate change. Cultivating a deeper appreciation for trees not only enhances our understanding of their ecological role but also fortifies our commitment to safeguard these guardians of the planet.
In conclusion, trees stand as the silent sentinels of our Earth, embodying resilience, strength, and potential against the backdrop of climate adversity. Their multifaceted contributions illuminate their significance, urging us all to recognize and champion their preservation. As we grapple with the inexorable challenges posed by climate change, it is evident that trees are more than mere flora; they are vital components of our environmental future.