The interdependence of water conservation and energy efficiency is an intrinsic aspect of sustainable living. As global populations burgeon, the strain on our finite natural resources intensifies. Thus, the imperative to judiciously manage water and energy consumption becomes paramount. Herein, we delve into multifaceted approaches to concurrently conserve these essential resources.
To begin, one must appreciate the nexus between water and energy. The water-energy nexus highlights that the production and distribution of energy often require substantial water inputs. For instance, thermoelectric power plants, which generate electricity from steam, consume vast quantities of water for cooling processes. Conversely, energy is also required for water extraction, treatment, and distribution. Therefore, initiatives aimed at conserving one often yield profound benefits for the other.
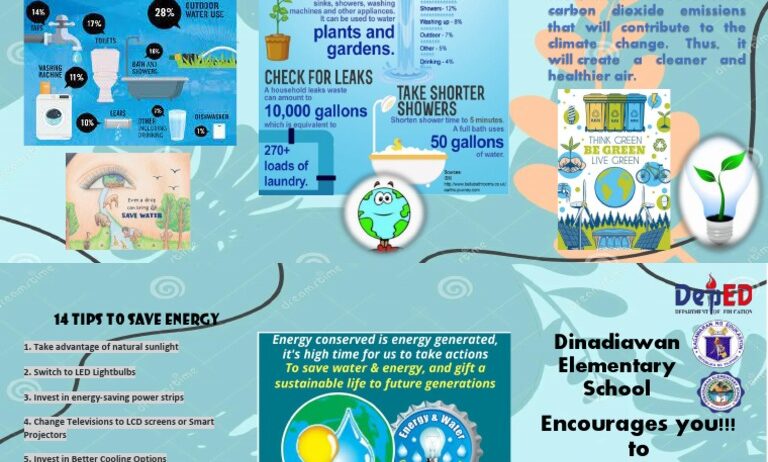
In domestic settings, the implementation of water-efficient appliances is a foundational step. Toilets with dual-flush mechanisms, for instance, can drastically reduce water usage without compromising on effectiveness. Similarly, energy-efficient dishwashers and washing machines often employ sophisticated water-saving technologies. Opting for appliances that are both ENERGY STAR-rated and designed to minimize water consumption can significantly lower one’s environmental footprint.
Beyond individual appliances, one can adopt lifestyle changes that promote both water and energy conservation. Shortening shower times or turning off the tap while brushing teeth can substantially decrease water wastage. This act inevitably leads to energy savings as well, as less hot water usage translates to reduced energy demand for heating water. In arid regions, where both water scarcity and energy consumption for irrigation pose challenges, the implementation of xeriscaping—landscaping that reduces or eliminates the need for irrigation—proves advantageous.
Incorporating renewable energy solutions into residential ecosystems offers a dual advantage. Solar panels harness the sun’s energy, not only supplying organic electricity but also enabling efficient water heating systems. Innovations such as solar water heaters utilize sunlight to heat water directly, consequently decreasing energy bills and lowering the carbon footprint associated with traditional heating methods.
Commercial settings have an equally significant role in the synergy of water and energy conservation. Businesses can conduct thorough audits to identify inefficiencies in water and energy usage. Implementing demand response programs can optimize energy use during peak hours while simultaneously reducing water consumption in cooling systems. Additionally, green building certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), encourage businesses to construct environments that are resource-efficient through advanced conservation methodologies.
Further extending the conversation to agricultural practices, farmers are increasingly adopting technologies that conserve both water and energy. Precision irrigation methods, such as drip irrigation, deliver water directly to the roots of plants, thereby maximizing efficiency and minimizing evaporation. This targeted approach not only conserves water but also curtails energy use associated with pumping and distributing water across fields. Coupled with energy-efficient machinery, farmers can sustain crop yields while reducing their overall environmental impact.
Public awareness campaigns also play a crucial role in fostering a culture of conservation. Educational initiatives that elucidate the water-energy nexus can galvanize communities to adopt more sustainable practices. Informative workshops, distribution of educational materials, and community challenges can inspire individuals to commit to conservation efforts. An informed populace is more equipped to recognize the impact of their choices and the benefits of adopting water and energy-efficient habits.
Furthermore, policy measures can precipitate large-scale changes. Governments can incentivize the installation of water-efficient technologies and renewable energy systems through tax rebates and subsidies. Regulatory frameworks that mandate energy audits and performance benchmarks in various sectors can stimulate systemic investment in conservation practices. By integrating water and energy policies, a more cohesive approach can facilitate the development of infrastructure that supports sustainable resource management.
Additionally, rainwater harvesting systems provide an innovative solution to the conservation dilemma. These systems collect and store rainwater for irrigation, washing, and even potable use after appropriate treatment. By harnessing a natural resource, one can significantly reduce reliance on municipal water systems, thereby conserving both water and the energy expended in its treatment and transportation.
Moreover, smart technology integration can enhance water and energy conservation efforts. Smart meters enable households and businesses to monitor real-time water and energy consumption, encouraging proactive behavior towards resource management. These technologies provide invaluable data that can inform better usage patterns, leading to more informed decision-making that aligns with conservation objectives.
In conclusion, the duality of conserving water and energy is not merely a coincidental pursuit; it is a critical strategy in combatting climate change and promoting sustainability. Through a holistic approach encompassing innovative technologies, lifestyle changes, agriculture, community engagement, and sound policy frameworks, individuals and organizations can effectively mitigate environmental degradation. The convergence of water and energy conservation is indeed a clarion call for all—ensuring a resilient future for generations to come.