Global warming represents one of the most pressing challenges of our time, with profound implications for the polar regions, particularly Antarctica. The rapid melting of ice sheets and glaciers not only contributes to rising sea levels but also disrupts global weather patterns and ecosystems. As stewards of our planet, it is imperative to explore viable strategies to mitigate global warming in Antarctica and safeguard these majestic, critical habitats.
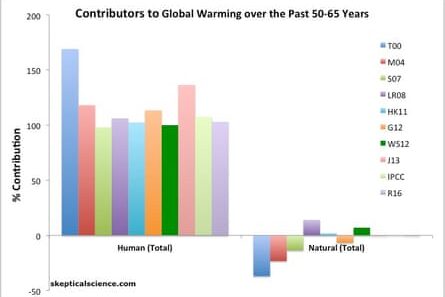
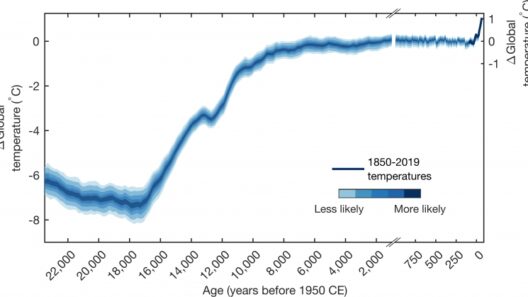
To initiate our discussion, we must comprehend the factors driving temperature increases in polar regions. Anthropogenic influences, particularly the emission of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane, are significant contributors to global warming. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to elevated global temperatures. Understanding this causative relationship allows us to formulate effective responses.
One of the foremost strategies in combating global warming lies in reducing carbon emissions. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, is vital. These alternatives present a sustainable avenue to decrease our dependence on fossil fuels, which are the predominant source of greenhouse gas emissions. As communities invest in renewable technologies, we inevitably catalyze a broader shift towards a low-carbon economy. Innovations in energy efficiency also play a crucial role. For instance, enhancing the thermal performance of buildings and optimizing industrial processes can substantially lower energy consumption.
In addition to transitioning to renewable energy, advocating for stronger international agreements is essential. The Paris Agreement, forged in 2015, represents a critical framework for global climate action. Encouraging nations to commit to more ambitious targets significantly influences global temperature trends. Active participation in international dialogues fosters collaboration and innovation. By pooling resources and sharing best practices, we can amplify our collective impact on global warming prevention.
Equally important is the need for rigorous research and monitoring programs focused on polar ecosystems. Enhanced scientific inquiry into the effects of climate change on Antarctic ice dynamics, wildlife, and oceanography will provide invaluable data. This information can guide policymakers in making informed decisions rooted in concrete evidence. Moreover, increased funding for scientific research allows for the development of adaptive strategies that can be deployed in response to observed changes.
Another critical aspect of ameliorating the impact of climate change on Antarctica is to foster public awareness and advocacy. Educating the public on the interconnectedness of the global climate system and the significance of polar regions can mobilize grassroots support for climate action. Outreach initiatives that resonate with diverse audiences can pique curiosity and inspire action. For instance, engaging storytelling that illustrates the effects of climate change on local communities can bridge the gap between scientific discourse and public understanding.
Furthermore, promoting sustainable practices within industries that have a direct impact on polar regions is crucial. Tourism, fishing, and shipping industries must adopt environmentally responsible practices. Regulations that limit carbon footprints, protect marine biodiversity, and enforce sustainable quotas are vital. Emphasizing the importance of responsible tourism, for instance, can help preserve fragile ecosystems while providing economic benefits to local communities.
Land management, particularly in terms of conservation, cannot be understated. The establishment of marine protected areas (MPAs) around Antarctica is essential for safeguarding biodiversity. These sanctuaries help mitigate human impacts on marine ecosystems and bolster their resilience to climate change. Legislative frameworks that facilitate the creation and enforcement of MPAs should be prioritized to ensure their effectiveness in achieving long-term ecological health.
Efforts to combat climate change cannot overlook the significance of reforestation and afforestation in other parts of the world. While Antarctica itself may not be conducive to forest growth, trees play a pivotal role in sequestering carbon dioxide, thus helping to mitigate global warming effects everywhere, including polar regions. Global initiatives aimed at planting trees can aggregate substantial reductions in atmospheric carbon levels, fostering a healthier planet overall.
Technology serves as a powerful ally in our quest to prevent global warming. Innovations like carbon capture and storage (CCS) offer the potential to directly address emissions from industrial sources. By capturing carbon dioxide before it enters the atmosphere, CCS could serve as a stopgap measure while we transition to more sustainable energy sources. In addition, advancements in climate modeling technology enable a better understanding of potential future scenarios and guide adaptive planning for both local and global systems.
Lastly, fostering intergenerational responsibility is crucial. Engaging youth and educating the next generation about environmental stewardship is an investment in the future. Initiatives that promote environmental education in schools and community programs empower young people to advocate for change and support sustainability efforts. Youth leadership in climate action can catalyze a cultural shift towards prioritizing planetary health.
In conclusion, there is a multiplicity of strategies that can be employed to prevent global warming in Antarctica and protect our polar regions. A comprehensive approach that encompasses reducing carbon emissions, fostering international collaboration, enhancing scientific research, and promoting sustainable practices is essential. Every effort counts, and by embracing innovative solutions and fostering a culture of accountability, we can rewrite the narrative of climate change and secure a thriving future for our planet and its polar regions.