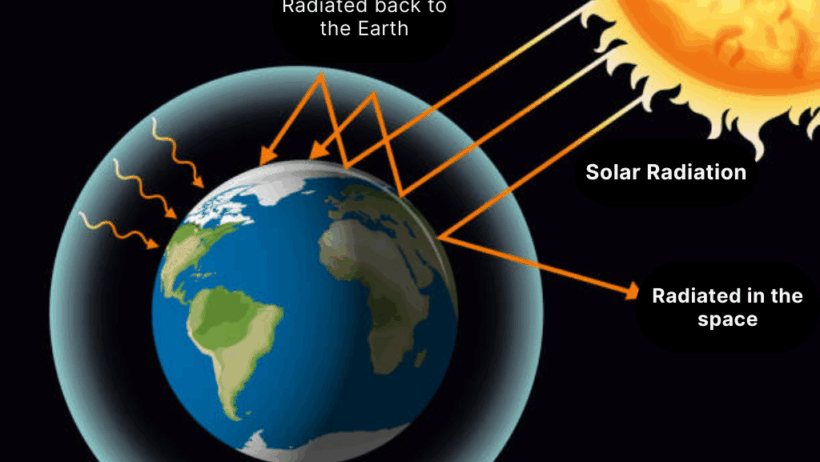
The greenhouse effect, a natural phenomenon essential for sustaining life on Earth, has seen an alarming intensification due to anthropogenic activities. This elevation in greenhouse gases leads to global warming, wreaking havoc on ecosystems and human societies alike. In response to this pressing issue, it is imperative to explore effective methodologies that can be deployed to mitigate the greenhouse effect. Below, we delineate numerous strategies, ranging from individual lifestyle changes to systemic reforms, aimed at reducing the impact of greenhouse gases.
Understanding the Greenhouse Effect and Its Implications
Before delving into strategies to minimize the greenhouse phenomenon, it is vital to grasp its underlying mechanics. Greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, maintaining temperatures conducive for life. However, excessive emissions have resulted in climatic aberrations, exemplified by rising sea levels, extreme weather patterns, and biodiversity loss. Such drastic changes demand immediate action to correct our trajectory toward a more sustainable future.
Adopting Renewable Energy Sources
Transitioning to renewable energy stands as one of the most effective approaches to curtail greenhouse gas emissions. Fossil fuel combustion for power generation has been a primary contributor to greenhouse gases, necessitating a paradigm shift toward alternatives such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power.
Solar energy, harnessed through photovoltaic cells, converts sunlight directly into electricity. Investment in solar technology not only aids in emissions reduction but also promotes energy independence. Furthermore, advancements in battery technologies are enhancing the viability of solar energy, enabling its integration into various applications.
Wind energy presents another sustainable avenue. Wind turbines convert kinetic energy from wind into power, offering a clean alternative to traditional energy sources. Expanding wind farms, especially in regions with favorable wind patterns, can significantly lower carbon footprints while providing jobs and economic growth.
Moreover, hydroelectric power, generated from flowing water, remains a stalwart in renewable energy solutions. Careful management and innovative approaches can mitigate ecological impacts, ensuring that biodiversity thrives alongside energy generation.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Improving energy efficiency represents a more localized yet impactful strategy to curb emissions. This can be achieved through retrofitting buildings, upgrading appliances, and adopting energy-efficient practices. Insulation improvements in homes can lead to substantial energy savings by minimizing heating and cooling demands.
In commercial settings, implementing smart technologies can optimize energy use, reducing unnecessary consumption without sacrificing productivity. Investing in energy-efficient lighting solutions, such as LEDs, also warrants consideration as it leads to prolonged lifespan and significant energy savings.
Automobiles constitute another pivotal aspect of energy efficiency. The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly gaining traction as technological advancements improve battery life and charging capabilities. Encouraging public transportation and carpooling reduces reliance on individual car use, further diminishing emissions from transport.
Altering Agricultural Practices
The agricultural sector plays a crucial role in both contributing to and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. Traditional farming practices often result in high levels of methane and nitrous oxide emissions due to livestock production and the application of synthetic fertilizers. Transitioning to sustainable agricultural practices can ameliorate these issues.
Implementing regenerative agriculture techniques, such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced tillage, enhances soil health while sequestering carbon. By improving soil structure and biodiversity, these practices not only contribute to climate change mitigation but also bolster food security and resilience to climate-related impacts.
Moreover, adopting plant-based diets can significantly decrease greenhouse gas emissions associated with meat production. Moving towards more plant-centric diets encourages sustainable food systems while promoting health. Local sourcing further reduces transportation emissions, emphasizing the importance of community-supported agriculture (CSA).
Promoting Sustainable Transportation
The transportation sector remains a formidable contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, underscoring the necessity for comprehensive reforms in this area. Promoting public transport, cycling, and walking as viable alternatives can reduce vehicular emissions significantly. Urban planning should prioritize the development of pedestrian-friendly infrastructure and efficient public transport systems.
Moreover, the adoption of low-carbon fuels, such as biodiesel and ethanol, offers potential pathways for reducing carbon footprints in transportation. Governments should incentivize research and development in alternative fuel technologies, propelling us toward a sustainable transport future.
Furthermore, integrating electric and hybrid vehicles into fleets—whether public transport, delivery services, or private ownership—will accelerate the transition to a lower-emission transport system.
Legislative Action and Policy Reform
For systemic change, robust legislative frameworks are essential. Governments must take the initiative to enact policies that support renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable practices. Financial incentives, such as tax credits for energy-efficient home renovations and subsidies for renewable energy projects, can catalyze widespread adoption of sustainable practices.
Moreover, imposing stricter regulations on emissions from industries encourages organizations to innovate and reduce their ecological footprints. International cooperation remains pivotal, necessitating a unified global response to climate change challenges.
In conclusion, addressing the greenhouse effect involves a multifaceted strategy incorporating technological innovation, shifts in consumer behavior, sustainable agriculture, and decisive government actions. Every small step taken towards sustainability contributes to a more viable planet, emphasizing the collective responsibility we bear in combating climate change. By embracing these effective methods, we can collectively minimize the greenhouse phenomenon, ensuring a healthier and more resilient environment for generations to come.