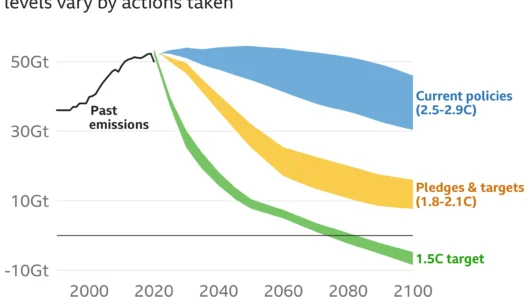
The phenomenon of global warming is no longer a distant concern; it is a pressing reality evidenced by fluctuating weather patterns, rising sea levels, and increasingly severe natural disasters. To effectively slow the process of global warming, a multifaceted approach is necessary—one that combines science-backed strategies with collective action. Addressing the underlying causes of carbon emissions while promoting sustainable practices can significantly mitigate the impact on our environment.
At the core of global warming lies an increase in greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2) resulting from fossil fuel combustion. Transitioning to renewable energy sources is pivotal in combating this issue. Solar, wind, and hydroelectric power offer a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. The implementation of these technologies requires substantial investment; however, long-term benefits include reduced air pollution, job creation in the green sector, and enhanced energy security. Countries around the globe are beginning to embrace these energy sources through subsidies and incentives aimed at promoting clean energy adoption.
Moreover, energy efficiency plays a crucial role in reducing carbon footprints. Enhancing the efficiency of buildings, appliances, and transportation systems can lead to substantial reductions in energy consumption. The use of energy-efficient appliances, alongside better insulation and window technologies in residential and commercial buildings, can diminish energy demand. The automotive industry is also advancing toward electric and hybrid vehicles, which are not only more environmentally friendly but can significantly decrease reliance on coal and oil.
Another significant contributor to carbon emissions is deforestation. Trees act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 and releasing oxygen. Thus, preserving existing forests and promoting reforestation efforts are essential components in the battle against global warming. Not only do trees sequester carbon, but they also provide habitat for countless species, thus maintaining biodiversity. Initiatives to engage local communities in forest conservation can foster a sense of stewardship that encourages sustainable land management practices.
Additionally, adopting sustainable agricultural practices can make a remarkable difference. The agriculture sector is responsible for a considerable share of global greenhouse gas emissions. By incorporating techniques such as crop rotation, reduced tillage, and organic farming, farmers can enhance soil health while simultaneously reducing carbon emissions. The introduction of permaculture principles can also promote agricultural systems that work harmoniously with natural ecosystems, which is crucial in mitigating climate change impacts.
Waste management is another area ripe for improvement. Organic waste decomposing in landfills emits methane, a potent greenhouse gas that contributes significantly to global warming. Transitioning to a circular economy model—where waste is minimized, and materials are reused or recycled—can substantially lower emissions. Composting organic waste, reducing single-use plastics, and promoting recycling are all practical measures that can lead to significant environmental benefits. Furthermore, educating communities about responsible waste disposal and the consequences of excess waste generation is vital for long-term change.
Transportation is a major contributor to carbon emissions as well. Encouraging the use of public transportation, cycling, and walking can help alleviate the reliance on personal vehicles, thus reducing emissions. Government investments in public transport infrastructure and the promotion of carpooling initiatives serve as effective strategies to decrease the number of cars on the roads. Moreover, incentivizing the use of electric vehicles through tax credits and deploying charging stations can facilitate a transition towards a greener transportation mandate.
Public awareness and education are foundational to fostering meaningful change. Campaigns aimed at informing citizens about their carbon footprints and encouraging Conscious consumer choices can drive collective action. By instigating discussions about the significance of individual actions—like reducing energy consumption, choosing sustainable products, and supporting local businesses—people can be empowered to make choices that collectively contribute to a healthier planet.
Innovation also plays a transformative role in mitigating climate change. Investing in research and development of new technologies, such as carbon capture and storage (CCS), can significantly curtail emissions from industrial processes. CCS involves capturing CO2 emissions at their source and storing them underground to prevent their release into the atmosphere. While CCS technology is still in its nascent stages, its potential for significantly reducing atmospheric CO2 levels merits continued research and investment.
International cooperation is imperative for an effective global response to climate change. Agreements such as the Paris Accord signify an acknowledgment of the shared responsibility among nations to curtail greenhouse gas emissions. Such treaties establish frameworks for accountability, setting reduction targets and implementing measures to achieve them. Countries must work collaboratively, sharing technology and resources, to create a unified front against the climate crisis.
Lastly, engaging in local grassroots initiatives can ignite passion for climate action. Community-led projects, such as urban gardening or local clean-up efforts, foster a spirit of cooperation and shared responsibility. These initiatives not only contribute to environmental health but also empower communities to effectuate change at a grassroots level.
Through a comprehensive strategy integrating renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, waste management, public transportation, education, technological innovation, and international cooperation, we can make remarkable strides in slowing the process of global warming. It requires a concerted effort, but the potential benefits for our planet and future generations are immeasurable. Each individual has a role to play in this collective endeavor; through informed actions and community engagement, we can cultivate a resilient world that thrives in harmony with nature.