Global warming represents one of the most pressing issues our planet faces today, with consequences that ripple across ecosystems, economies, and communities worldwide. Addressing this challenge necessitates a multifaceted and long-term plan. To gradually reduce global warming, we must focus on a combination of innovative technologies, policy changes, and individual actions that collectively create a sustainable future.
Understanding Global Warming
Global warming is primarily driven by the increase in greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4), released into the atmosphere through human activities. These gases trap heat, resulting in a rise in Earth’s average temperature. This phenomenon leads to more severe weather events, rising sea levels, and disruptions to biodiversity. A comprehensive understanding of the causes and effects of global warming is crucial for devising effective strategies to combat it.
Transitioning to Renewable Energy
One of the most critical steps in mitigating global warming is the transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. Solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy provide environmentally friendly alternatives that significantly reduce carbon emissions. Governments and businesses should invest in renewable energy infrastructure, incentivizing the development of solar farms, wind turbines, and hydropower plants.
This shift will not only minimize greenhouse gas emissions but also promote energy independence and employment in the green sector. The gradual implementation of renewable technologies should involve collaboration between public and private sectors, ensuring that energy transitions are equitable and accessible to all communities.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Improving energy efficiency across various sectors is another vital component of a long-term plan. This includes optimizing energy consumption in residential homes, commercial buildings, and industrial processes. The adoption of smart technology, better insulation materials, and energy-efficient appliances can drastically reduce energy demand.
Moreover, retrofitting existing structures with energy-efficient systems can generate significant savings and reduce overall carbon output. Encouraging legislatures to implement energy efficiency standards and offering incentives for businesses and homeowners are essential strategies for achieving significant reductions in energy use.
Promoting Sustainable Transportation
Transportation is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. Transitioning to sustainable transportation options is paramount in addressing global warming. This can be achieved by investing in public transport, promoting electric and hybrid vehicles, and improving infrastructure for cycling and walking.
Incentives for using public transportation and the establishment of carpooling programs can encourage a cultural shift away from reliance on single-occupancy vehicles. Additionally, ongoing research and development in alternative fuels such as hydrogen and biofuels should be supported to create a more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
Reforestation and Afforestation
Forests play a crucial role in absorbing CO2, thus acting as significant carbon sinks. Reforestation and afforestation efforts should be prioritized as part of a holistic global warming reduction strategy. Collaborating with local communities to restore degraded lands and expand forest cover can significantly contribute to the mitigation of climate change.
Incorporating agroforestry practices, where agricultural activities are combined with tree planting, can enhance both food security and carbon sequestration. Supporting policies that protect existing forests and promote biodiversity conservation is equally essential to ensure these vital ecosystems continue to function effectively.
Reducing Waste and Promoting Circular Economy
The modern world has seen a rise in consumerism, leading to a dramatic increase in waste production and landfill usage. Implementing waste reduction initiatives is crucial for decreasing greenhouse gas emissions associated with waste management. Promoting a circular economy model encourages the reuse and recycling of materials, thereby minimizing the demand for new resources.
Encouraging consumers to embrace sustainable practices, such as composting and reducing single-use plastics, fosters a culture of responsibility. Legislating policies that reduce packaging waste and promote recycling will help shift societies towards more sustainable consumption patterns.
Supporting Climate Education and Advocacy
Education is a foundational element in the fight against global warming. By fostering awareness about climate change and its impacts, individuals are equipped to make informed decisions. Schools, governments, and non-governmental organizations must prioritize climate education, promoting initiatives that engage communities in discussions about sustainability and ecological stewardship.
Moreover, advocacy plays a pivotal role in catalyzing change. Mobilizing citizens to support climate-friendly policies at local, national, and international levels can lead to meaningful legislative reforms aimed at reducing carbon emissions and enhancing environmental protections.
Collaboration on a Global Scale
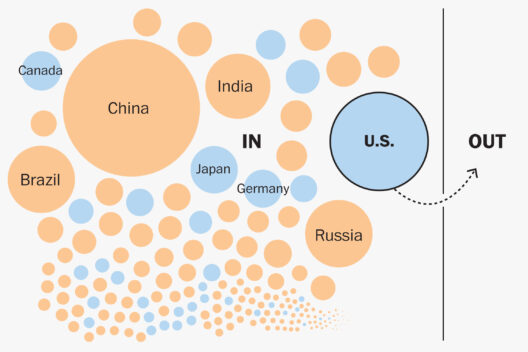
Climate change is a global challenge that necessitates cooperation among nations. International accords, such as the Paris Agreement, are essential frameworks for encouraging countries to commit to reducing their emissions. These collaborative efforts must include developed and developing nations, ensuring that everyone plays a part in combating climate change.
Sharing resources, technology, and knowledge can facilitate a more effective global response. Adequate funding for climate initiatives, particularly in vulnerable communities and developing countries, ensures that all nations can achieve sustainable development goals.
Conclusion
Reducing global warming is not an instantaneous process; it requires comprehensive, long-term planning and execution. By embracing renewable energy, enhancing energy efficiency, promoting sustainable transportation, supporting reforestation, advocating for waste reduction, and prioritizing education, we can foster a collective movement toward a more sustainable future. With concerted effort, collaboration, and unwavering commitment, we can work towards minimizing global warming and protecting our planet for generations to come.