Wind is nature’s breath, a vast and invisible force that dances through the air, shaping weather patterns and moving clouds across the horizon. This mesmerizing phenomenon has captivated humanity for centuries, whispering tales of energy that lies in the hands of the elements. It has now emerged as a formidable ally in the quest for renewable energy, transforming from an ethereal visual into a powerful means to drive our modern world. Understanding how wind can produce energy unravels not just the mechanics of turbines, but also the larger narrative of innovation aligned with nature.
The Mechanics of Wind Power Generation
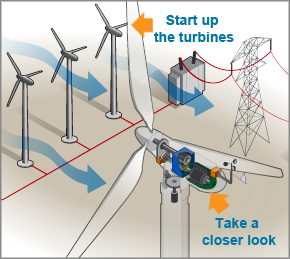
At its core, wind power generation is about harnessing the kinetic energy of moving air. When we observe the majestic blades of a wind turbine spinning against the cerulean sky, we should remind ourselves that they are not merely decorative. These blades are engineered to convert the wind’s energy into usable electrical power through a series of intricate systems. The process begins with the wind itself, which possesses kinetic energy based on its speed and mass. As air molecules collide and flow, they create zones of varying pressure, generating wind currents that can travel long distances.
As breezes transform into gusts, they meet the turbine’s blades, which catch the wind much like a bird spreads its wings. This encounter initiates a mechanical ballet wherein the rotor blades turn, swinging around a hub connected to a gearbox. The gearbox is essential; it translates the slow rotational speed of the blades into a higher speed capable of energizing a generator. Envision a delicate gear mechanism, where cogs elegantly interact, each oscillation further amplifying the wind’s initial force. The generator then converts this rotational motion into electrical energy, ready to be transported through power lines and into homes and businesses.
Dynamic Components: An Intricate Tapestry
Each component of a wind turbine plays a pivotal role in this energy transformation. The turbine’s tower, often majestic and towering above the landscape, serves not just as a support structure. It elevates the rotor blades to an optimal height, where wind speeds are greater and more consistent. Imagine planting a seed in fertile ground; height is crucial for it to flourish. Similarly, the higher the turbine, the more reliable and potent the wind resource becomes.
Moreover, modern turbines are equipped with advanced technology that allows for nimbleness in wind direction and speed. This adaptability is akin to a dancer adjusting their moves in response to the rhythm of music. The turbine’s yaw mechanism enables it to rotate and face the wind, ensuring that it captures the maximum energy possible. Additionally, the pitch control adjusts the angle of the blades, optimizing performance and safeguarding the turbine from damage during exceptionally high winds—an elegant pivot in the choreography of energy production.
Sustaining the Wind: Environmental and Economic Advantages
Harnessing wind energy offers numerous environmental advantages, rendering it a pivotal element of our sustainable future. The transition from fossil fuels to renewable sources significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, thereby mitigating climate change. Wind power is inherently clean; it consumes no water during operation, preserving this vital resource for communities and ecosystems alike. Visualize a landscape where turbines flourish alongside crops and wildlife, yielding energy without depleting nature’s bounty—a perfect symbiosis.
Economically, investing in wind energy is akin to sowing seeds in fertile soil; the returns can be substantial. The cost of wind technology has plummeted over the past decade, making it one of the most cost-effective forms of energy generation available today. This accessibility fuels job growth in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of wind farms, invigorating local economies and creating a durable market for skilled labor. Each wind farm erected symbolizes more than just electricity production; it epitomizes a commitment to progress and resilience.
Unlocking the Future: Challenges and Innovations
Despite its myriad benefits, wind power is not without challenges. The intermittent nature of wind means that energy production is variable, creating a need for efficient energy storage solutions and grid management strategies. The inherent unpredictability of wind patterns can lead to surplus generation during windy days and scarcity during lulls, reminiscent of the ebb and flow of tides. Here lies an opportunity for innovation: the development of cutting-edge energy storage technologies—think of batteries that will hold onto the wind’s whisper long after it has passed.
Furthermore, the ecological impact of wind farms must be thoughtfully addressed. The placement of turbines requires careful consideration of migratory bird patterns and local wildlife habitats to minimize disruptions. Striking a balance between energy production and environmental stewardship is akin to walking a tightrope, requiring continual adjustments and commitment to sustainability.
Wind as the Silent Contributor to a Sustainable Future
To encapsulate the essence of wind power generation is to appreciate not only the engineering marvel of turbines but also the harmonious relationship between humanity and nature. Each gust of wind carries the potential to illuminate our spaces, power our devices, and sustain our lives. This dance of air and technology is a testament to human ingenuity in harnessing the universe’s elemental forces. The future of energy lies in such synergies—innovative solutions that respect and echo the rhythms of the natural world. As we journey towards a sustainable tomorrow, let us embrace wind power as a pivotal ally in our quest for a cleaner, greener world.