Climate change operates like a maestro, conducting an orchestra of atmospheric phenomena, modulating the symphony of weather patterns that shape our planet. With each passing decade, the crescendos of storms grow more ferocious while the subtler harmonies of droughts resonate deeper into the earth, altering the intricate balance of ecosystems worldwide. This transformation, unequivocally fueled by human activity, is not merely a gradual evolution; it is an unequivocal upheaval, signaling a critical turning point in Earth’s climatic narrative.
To understand how climate change modifies weather, we must first examine its influence on storm activity. An increase in global temperatures has led to heightened humidity levels in the atmosphere, providing storms with an abundant source of energy. This phenomenon is akin to adding fuel to a fire, creating a ferocious blaze wherein storms are amplified in intensity and frequency. The statistics are compelling: a study by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration revealed that hurricanes have become more powerful, with the proportion of Category 4 and 5 storms surging by over 30% in just a few decades. As these storms escalate, so too do the threats to human life, infrastructure, and natural habitats.
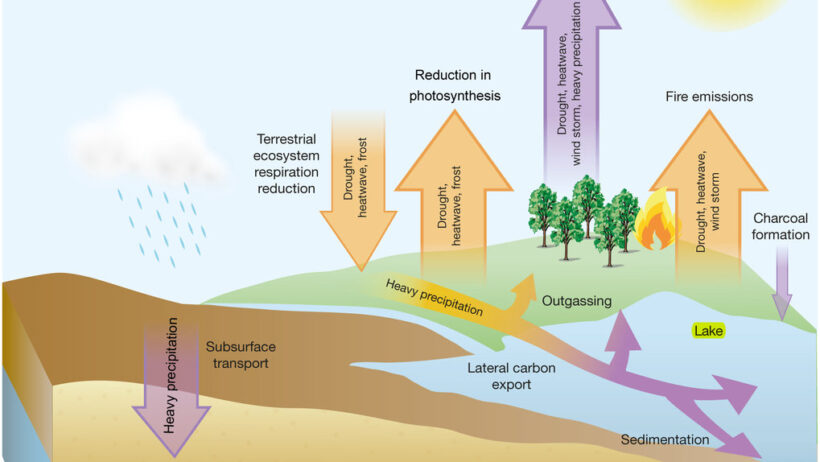
Moreover, climate change manipulates the jet streams—those fast-flowing air currents that dictate weather patterns. With warming polar regions, these streams exhibit erratic behavior, spiraling into unexpected configurations that give rise to prolonged droughts or unanticipated deluges. Picture the jet stream as a river. When the banks of this river are tampered with, the waters spill into floodplains or recede into parched lands, wreaking havoc on agricultural practices and ecosystems alike. The recent droughts across the American West serve as a glaring exemplification of this alteration. Prolonged dry spells not only resonate with the farmers struggling to nourish their crops but also threaten the livelihood of countless species that depend on these vital water sources.
The juxtaposition of storms and droughts illuminates the paradoxical nature of climate change. While certain regions endure the relentless battering of torrential rain and winds, others find themselves parched and stripped of resources. This tug-of-war within the atmosphere could be viewed as nature’s foreboding reminder of our environmental transgressions. As the Great Plains experience devastating tornadoes, entire ecosystems in regions such as the Mediterranean basin face stark water scarcity. Aquifers drain, rivers dwindle, and habitats crumble, unable to cope with the increase in temperature that is acting like a double-edged sword.
Furthermore, the implications of these climatic disturbances resonate across borders, illustrating that climate change is not a discrete local affair. It is an intricate web of global interconnectedness where one region’s climate crises precipitate repercussions felt miles away. The energy harnessed during our relentless pursuit of industrial growth has inadvertently unleashed a series of responses, with emergent climate refugees fleeing their desiccated lands in search of survival. This migration can amplify socio-political tensions, as nations grapple with their capacities to accommodate these displaced populations while confronting their climate responsibilities.
As we delve deeper into the ramifications of climate change, the impact on agriculture becomes glaringly evident. With the volatility of weather patterns, farmers are left to navigate an unpredictable landscape where the traditional wisdom of planting seasons becomes obsolete. The Continental Divide, once a steadfast divider between weather systems, seems blurred, as the boundaries that dictated climatic behaviors shift, leading to uncertainties about crop viability. As a result, food security finds itself on a precipice, teetering between abundance and scarcity, entailing severe implications for economies reliant on agriculture.
Moreover, the ecology of our planet suffers dramatically. Biodiversity, a crucial pillar for a resilient ecosystem, is increasingly strained as species fail to adapt to rapidly changing weather conditions. With the temperature increasing, many species find themselves either forging into new territories or facing extinction. The phenomenon of ‘climate mismatching’ emerges, wherein seasons that dictate breeding and migration are no longer in sync with climatic signals. Such ecological discord favors invasive species, amplifying the decline of native flora and fauna and disrupting intricate relationships within food webs.
Mitigating the consequences of climate change remains imperative. One approach is to transition towards renewable energy sources—venturing beyond the archaic mega fossil fuel projects that have long fueled this crisis. The shift to solar, wind, and hydroelectric power can ultimately curtail our carbon emissions, recalibrating the atmospheric balance. Furthermore, investing in research on sustainable agricultural practices allows us to cultivate food with an eye toward resilience, enabling future generations to thrive amidst climatic upheaval.
Ultimately, the narrative of climate change is complex and multifaceted, affording us the opportunity to understand the delicate balance of our ecosystems and the ramifications of our choices. As we grapple with the reality of a warming planet, awareness and action must converge. The storms and droughts that characterize our climate are not mere happenstance; they are a siren call for a collective awakening. Humanity stands at a crossroads, with the power to redefine its relationship with nature—an opportunity that must not be squandered.