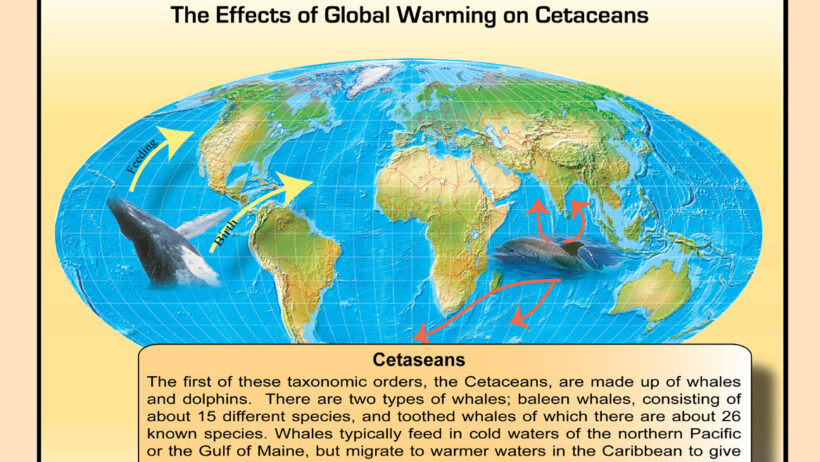
Global warming, a phenomenon characterized by an increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to greenhouse gas emissions, poses a significant threat to various ecological and atmospheric processes. Among these processes, one of the most critical is the global conveyor belt, also known as thermohaline circulation. This complex system of ocean currents plays an integral role in regulating climate patterns across the globe. Understanding how global warming impacts the global conveyor belt is essential, not only for predicting climatic shifts but also for grasping the overarching climate domino effect that follows.
At its core, the global conveyor belt consists of a vast network of ocean currents driven by differences in water temperature and salinity, also referred to as thermohaline factors. Surface waters, heated by the sun, are less dense and more buoyant, while cold, saline waters sink to the ocean’s depths. This interplay creates a continuous loop that transports warm water from the equator towards the poles and returns colder water towards the equator, thus facilitating energy transfer across the globe.
One point of contention lies in how global warming, ostensibly a steady rise in temperature, could disrupt this delicate equilibrium. As atmospheric temperatures rise, the polar ice caps and glaciers melt at an unprecedented rate, injecting vast quantities of freshwater into the salty oceans. This alteration in salinity can interfere with the sinking of cold water—a critical component of thermohaline circulation. The far-reaching implications of this disruption could be likened to a domino effect, where one shift precipitates a cascade of changes, affecting weather patterns, sea levels, and marine ecosystems.
One immediate consequence of a weakened global conveyor belt could manifest as altered weather patterns. Regions that depend on milder climates, particularly in Western Europe, could experience harsher winters as the warm Gulf Stream weakens. The absence of warm water circulation would lead to an overall decrease in regional temperatures, potentially echoing significant climate shifts reminiscent of the Little Ice Age in the 17th century. This chilling effect represents just one strand in the climate domino tapestry; further disarray could emerge as ecosystems fail to adapt to rapid environmental changes.
The cascading effects extend beyond terrestrial climates. Alterations in ocean currents influence marine biodiversity and fisheries. Many marine species depend on predictable currents for migration, breeding, and feeding. If these currents are altered, it could lead to habitat loss and declines in fish stocks, threatening food security for millions reliant on seafood. This underscores an undeniable link between global warming, ocean health, and human economic stability.
Moreover, a weakened conveyor belt can exacerbate extreme weather events, as changes in ocean temperatures influence storm patterns. An intensified Gulf Stream creates conditions for more severe hurricanes and tropical storms. The resulting economic burden from property damage, displacement, and loss of life would elevate climate change as an unmanageable crisis, requiring vigilant action and readiness from policymakers around the globe.
Another area where the effects of disrupted thermohaline circulation manifest itself is in global sea level rise. As glaciers melt and contribute freshwater to the oceans, the resultant alteration in salinity prompts changes in water density. This can lead to localized increases in sea levels in some regions while causing decreases in others. Such variations complicate coastal management and heighten the risks for vulnerable coastal communities, potentially leading to increased flooding, erosion, and loss of habitat.
While the scientific community increases its understanding of these interconnections, a critical aspect remains the role of policymakers and global cooperation in mitigation efforts. Combating the adverse effects of global warming necessitates a multifaceted approach. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, fostering sustainability in agriculture, and investing in carbon capture technologies are paramount steps. This proactive stance seeks to limit emissions, thereby preserving not just the global conveyor belt, but the overall health of the planet.
The climate domino effect initiated by global warming extends into numerous realms: from socio-economic impacts to geopolitical conflicts over dwindling resources. As nations grapple with the reality of climate-induced migration and food security, the interplay between global warming and the conveyor belt becomes a crucial focal point in discussions on international agreements, such as the Paris Agreement. Collaborative frameworks to address these exigencies are more vital than ever.
Simultaneously, public awareness and education play pivotal roles in mobilizing collective action. Environmental advocacy, grassroots movements, and community-level adaptations are essential in fostering a culture of sustainability. By spreading awareness about the intricacies of climate systems, including the crucial functions of the global conveyor belt, individuals can be encouraged to embrace conservation efforts and advocate for robust climate policies. Every effort, no matter how small, contributes to the larger battle against climate change.
In conclusion, the implications of global warming on the global conveyor belt underscore a complex system interwoven with the fabric of our planet’s ecosystem. As the hydrologic cycle and ocean currents undergo unprecedented changes, the cascading effects challenge not only environmental stability but also human survival. The domino effect, initiated by shifts in oceanic systems, illustrates how alterations in one area can propagate through food systems, weather patterns, and socio-economic structures. Addressing the threats posed by global warming requires an integrative, global approach encompassing ecological awareness, innovation in sustainability, and urgent action on climate policy, emphasizing the significance of preserving the delicate balance of our world’s vital ocean currents.