The phenomenon of global warming has become a central topic in contemporary discourse surrounding environmental issues. It signifies more than just a gradual uptick in temperatures; it embodies a profound alteration in the delicate equilibrium that sustains diverse ecosystems across the globe. The intricacies of these ecosystems are remarkable. They encompass the interdependent relationships between organisms and their environments, where even minor shifts can cascade into significant consequences. Hence, addressing how global warming affects ecosystems is imperative to foster a deeper understanding of our planet’s health and the well-being of its inhabitants.
Global warming stems chiefly from the increase of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere—most notably carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide—largely as a result of human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and agricultural practices. This accumulation creates a blanket that traps heat, consequently elevating global temperatures. As this systemic warming unfolds, it generates a plethora of repercussions felt across various ecosystems—from the polar ice caps to tropical rainforests.
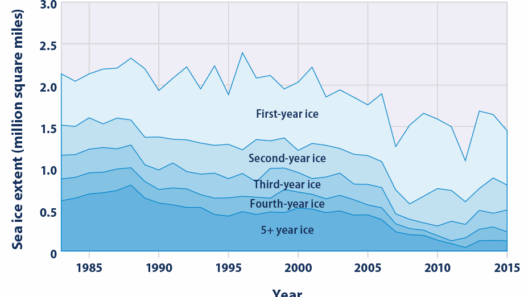
Perhaps the most visible manifestation of rising temperatures is the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers. As these ice masses recede, the natural habitats of species such as polar bears, seals, and various seabirds are irrevocably altered. The loss of this critical habitat not only threatens the survival of these animals but also disrupts the intricate food webs they are part of. When apex predators, like polar bears, struggle to find food, the entire community of prey species is affected, highlighting the interdependent nature of ecosystem dynamics.
Moreover, the phenomenon of ocean acidification cannot be understated. As ocean temperatures rise, the ocean absorbs a significant amount of atmospheric CO2, which leads to changes in water chemistry. This increased acidity can devastate coral reefs—often dubbed the “rainforests of the sea”—which provide essential services such as habitat for countless marine species. Coral bleaching, resulting from heightened sea temperatures, leads to extensive coral mortality and a subsequent reduction in biodiversity. The ramifications extend beyond marine life; coral reefs serve as natural barriers protecting coastlines from storm surge and erosion, thus impacting human communities as well.
Terrestrial ecosystems are not immune to these shifts either. For instance, changes in climate patterns result in altered precipitation cycles, influencing plant growth and distribution. Certain plant species, especially those adapted to specific climate conditions, may become obsolete if temperatures continue to rise. As habitats shift poleward or to higher altitudes, it places stress on native flora and fauna unable to adapt quickly enough. This phenomenon, known as ‘range shift,’ poses significant risks to biodiversity, as displaced species may compete with local populations, potentially leading to extinction.
The intricacies of these dynamics highlight the concept of phenology—the study of how climate affects the timing of life cycle events in organisms. For many species, global warming has resulted in mismatches between the timing of food availability and reproductive cycles. For example, if insects emerge earlier due to warmer temperatures but migratory birds that feed on them do not adjust their arrival times, the birds may face food scarcity. Such mismatches can result in population declines, which, again, reverberate through the entire ecosystem.
In addition to these biological impacts, it’s essential to consider the socio-economic implications of global warming on ecosystems. Human communities, especially those in developing nations, often rely heavily on natural ecosystems for their livelihoods. Fishing, agriculture, and tourism—industries that depend on healthy ecosystems—are becoming increasingly precarious as climate change progresses. The resulting economic strain can exacerbate existing vulnerabilities, making adaptation more urgent than ever.
The balance of ecosystems is not merely a scientific concern; it is crucial for preserving biodiversity, which in turn safeguards the ecosystem services that humanity relies upon. Biodiversity serves as a buffer, enhancing resilience to climate shifts. When ecosystems are diversified, they can better withstand adverse changes, thus underscoring the importance of conservation efforts in the age of global warming. Protecting biodiversity through the establishment of protected areas, restoration of degraded lands, and sustainable resource management practices is essential for creating resilient ecosystems capable of adapting to changing climates.
While the challenges posed by global warming to ecosystems are daunting, there exists a nascent hope borne from public awareness and advocacy. Collective action can drive policy changes and spark a cultural shift toward sustainable practices. Commitment to reducing carbon footprints, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and advocating for systemic change can set the stage for a new paradigm of coexistence between humanity and nature.
Thus, the conversation surrounding global warming’s impact on ecosystems invites reflection and re-evaluation. By recognizing the intricate interconnections within ecosystems and the fragility of their balance, we can ignite curiosity and commitment to a sustainable future. The path forward hinges on collective action—an acknowledgement that the health of ecosystems is intrinsically linked to our survival. As stewards of the planet, it is imperative that we advocate for the protection of these delicate and vital communities—only then can we hope to restore balance in a warming world.