Electric cars have surged to the forefront of discussions surrounding sustainable transportation. The increasing ubiquity of electric vehicles (EVs) reflects not only a shift in consumer preference but also a deeper commitment to mitigating the impacts of climate change. Among the plethora of benefits they offer, one standout aspect is their potential to significantly reduce global warming. This examination delves into the mechanics of how electric cars contribute to a cleaner environment, the underlying technologies that enhance their efficiency, and the broader implications of adopting electric vehicles as the cornerstone of future transportation.
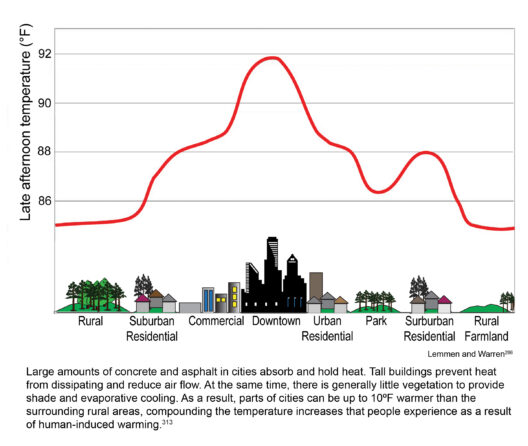
First and foremost, electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, a fundamental attribute distinguishing them from their internal combustion engine (ICE) counterparts. Traditional gasoline and diesel vehicles emit carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases that are detrimental to the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect and, subsequently, global warming. In contrast, an electric car relies on electricity stored in batteries, which means its direct emissions are non-existent. The reduction of these on-road emissions is critical, particularly in urban areas where air pollution poses immediate health risks.
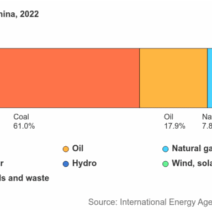
However, to fully comprehend the climate benefits of electric vehicles, one must also consider the electricity generation mix that powers them. Approximately 60% of the electricity produced in the United States comes from fossil fuels. While this might seem contradictory to the idea of EVs being environmentally friendly, the carbon footprint of electric cars can still be significantly lower than that of conventional vehicles. As the energy grid increasingly incorporates renewable sources such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, the emissions associated with electric vehicle charging are projected to diminish. Therefore, the overall environmental footprint of electric cars will continue on a downward trajectory in alignment with advancements in clean energy technologies.
Additionally, technological innovations within electric vehicles contribute to their efficiency and overall sustainability. Modern electric cars are equipped with regenerative braking systems that recapture kinetic energy, converting it back into stored energy in the battery during deceleration. This remarkable engineering not only enhances the driving range of electric vehicles but also reduces the overall energy consumption, making them an even more viable option for environmentally conscious consumers.
Electric vehicles also showcase remarkable advancements in battery technology. Lithium-ion batteries, the prevalent choice for EVs, have seen continual improvements in energy density, lifespan, and overall performance. Innovations such as solid-state batteries promise further enhancements, potentially offering higher capacity and faster charging times while mitigating safety concerns associated with traditional batteries. As these technologies evolve, the electricity required per mile driven will reduce, amplifying the environmental benefits electric vehicles offer.
An often-overlooked advantage of electric cars is their potential for reducing dependence on fossil fuels. The transportation sector is one of the largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions globally, primarily due to its reliance on oil. By adopting electric vehicles, societies can transition away from fossil fuels, thereby decreasing the demand for oil extraction, transportation, and refinement, processes notorious for their detrimental environmental impacts. This transition serves not only to address climate change but also fosters energy independence, allowing countries to harness their indigenous renewable energy sources.
Furthermore, the integration of electric vehicles into smart grids represents another layer of potential environmental benefit. Smart grids facilitate real-time communication between energy suppliers and consumers, optimizing electricity distribution and consumption. When electric vehicles are plugged into the grid, they can act as distributed energy storage, providing ancillary services such as load-balancing during peak demand. This ability can stabilize the grid and optimize renewable energy usage, ensuring that the energy generated from clean sources is utilized efficiently.
Public perception and policy play substantial roles in the proliferation of electric vehicles. Governments worldwide are implementing regulations, incentives, and infrastructure investments aimed at fostering cleaner transportation alternatives. Policies that promote electric vehicles, such as tax rebates and zero-emission vehicle mandates, serve to enhance their affordability and accessibility for consumers. Additionally, the expansion of charging infrastructure is vital, alleviating range anxiety that has historically deterred potential electric vehicle buyers. The smooth transition to a fleet of electric cars hinges upon public acceptance and policy frameworks that encourage widespread adoption.
Despite the myriad advantages, it is important to acknowledge the challenges facing the electric vehicle market. Concerns regarding battery production, resource extraction, and end-of-life battery disposal must be addressed. The extraction of lithium, cobalt, and other minerals needed for batteries often results in significant environmental degradation and ethical concerns surrounding labor practices. Thus, the future of electric vehicles must encompass sustainable practices throughout their lifecycle—from responsible sourcing to recycling programs. Failure to address these factors could undermine the overall sustainability narrative of electric cars.
In summation, electric vehicles stand at a pivotal juncture in the quest for sustainable transport solutions. Their capacity to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, combined with advancements in technology and grid integration, heralds a promising future for motorists and the planet alike. As society navigates the complexities of climate change, electric cars provide a tangible action point for consumers and policymakers. By prioritizing electric vehicle adoption, we can collectively move towards a future with cleaner air, healthier communities, and a more stable climate. It is imperative to embrace this transformative shift, ensuring that the path to sustainable mobility is accessible and equitable for all.