The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that plays a critical role in maintaining the Earth’s climate. It is the process by which certain gases in our atmosphere trap heat, keeping the planet warm and conducive to life. Understanding how this complex mechanism operates is essential not only for grasping fundamental environmental science but also for recognizing the broader implications of human activities on our climate.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the greenhouse effect, beginning with the essential components involved in heat retention, followed by an exploration of the human impact on this natural process, and concluding with the urgent need for collective action to mitigate its adverse effects.
The Components of the Greenhouse Effect
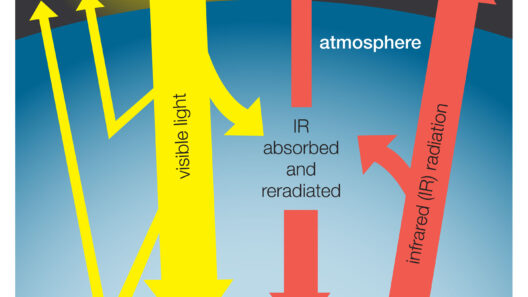
At the core of the greenhouse effect are greenhouse gases, or GHGs, which include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor. These gases function much like the glass panels of a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to enter while preventing some of that heat from escaping back into space. When sunlight reaches the Earth, some of it is reflected back, while the rest is absorbed by land, oceans, and vegetation. This absorbed energy is then re-radiated as infrared radiation, a form of heat.
As this infrared radiation attempts to escape the Earth’s surface, greenhouse gases efficiently absorb and re-emit the radiated energy in all directions, including back towards the surface. This process results in the warming of the lower atmosphere and ultimately keeps the planet’s temperature at a level suitable for life. Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth would be inhospitable, with average temperatures plummeting to around -18 degrees Celsius (0 degrees Fahrenheit). The presence of these gases keeps Earth’s average temperature at approximately 15 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit).
The Role of the Sun: An Indispensable Energy Source
The Sun serves as our primary energy source, emitting energy through a process known as nuclear fusion. This energy travels to Earth in the form of visible light and other types of radiation. Upon reaching the planet, the surface absorbs a significant portion of this energy. However, the Earth does not operate in isolation. The delicate balance between the energy that enters the atmosphere and the energy that escapes back into space is crucial. Various factors can influence this energy balance, including variations in solar output, cloud cover, and human-induced changes in atmospheric composition.
Perturbations in this balance can lead to climate change, showcasing just how interconnected the elements of the greenhouse effect are.
The Human Factor: Amplifying the Greenhouse Effect
While the greenhouse effect is a natural and necessary phenomenon, human activities have drastically altered its dynamics. The combustion of fossil fuels for energy, deforestation, and industrial processes release excessive amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. This anthropogenic augmentation of GHG concentrations leads to enhanced greenhouse effects, commonly referred to as global warming.
Carbon dioxide emissions from vehicles, power plants, and various industrial activities are especially concerning. In addition, methane, a gas with a global warming potential many times greater than that of CO2, is released from agricultural practices, waste management, and the extraction and transportation of fossil fuels. The persistent build-up of these gases traps more heat, leading to an increase in global temperatures.
Scientific Consensus: The Impacts of Climate Change
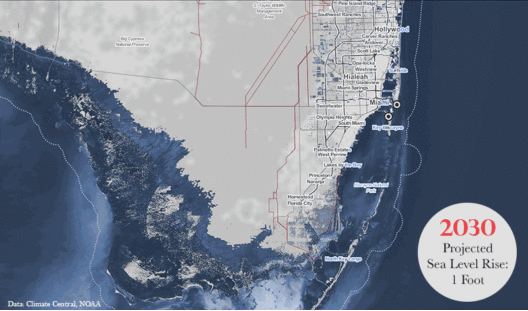
Research indicates that human-induced climate change has resulted in a range of consequences, from rising sea levels and increasingly severe weather patterns to alterations in biodiversity and agriculture. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has warned that if greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise unchecked, we could witness an increase of 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels as early as 2030. This temperature threshold is critical, as it marks a turning point beyond which the risks of irreversible impacts become severely heightened.
The urgency is real. Communities worldwide are already feeling the effects, manifested in more frequent and intense heatwaves, wildfires, hurricanes, and flooding. Addressing these challenges requires an understanding that the greenhouse effect, while vital for sustaining life, necessitates a responsible approach towards mitigating its intensification.
Collective Action: Transformation and Responsibility
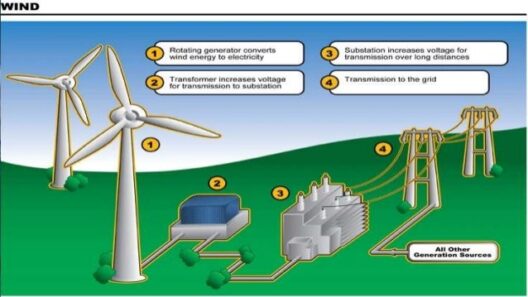
To address the looming threat of climate change, comprehensive strategies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions are essential. Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, enhancing energy efficiency, and safeguarding our forests and natural carbon sinks are just a few avenues through which society can combat the adverse impacts of the greenhouse effect. It is imperative that policymakers, businesses, and individuals work synergistically to effect change.
For instance, adopting sustainable agricultural practices, investing in carbon capture technologies, and promoting public transportation can significantly curtail emissions. Moreover, raising awareness, educating communities about the greenhouse effect, and advocating for change can empower individuals to contribute positively to environmental sustainability.
Conclusion: Awareness and Action for Sustainable Futures
The greenhouse effect is a cornerstone of Earth’s climate system, significantly influencing weather patterns, ecosystems, and overall planetary health. However, when human activities disrupt this natural balance, the implications can be catastrophic. Acknowledging the consequences of our actions and committing to sustainable practices is essential for ensuring the well-being of future generations.
Understanding the greenhouse effect is not an isolated scientific inquiry; it’s a pressing moral responsibility of our era. The time to act is now, and engaging in informed dialogues and sustainable actions will pave the way towards a more balanced coexistence with our planet.