Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our time, and it is widely recognized that human activities play a pivotal role in driving this phenomenon. The relationship between human behavior and global warming is complex, permeating through various facets of daily life, industrial operations, and even the policies governing our societies. From the mundane choices individuals make to the colossal emissions generated by industries, the impact of human activities on the climate is profound and multifaceted.
At the grassroots level, the choices made by individuals can have a cumulative effect on environmental degradation. Daily decisions regarding transportation, consumption, and energy use reflect a lifestyle heavily reliant on fossil fuels. For instance, opting for personal vehicles over public transportation contributes significantly to carbon emissions. According to recent studies, transportation accounts for approximately 29% of total greenhouse gas emissions in the United States. This figure underscores a dramatic truth: the personal convenience of driving, while appealing, comes at a substantial environmental cost.
Moreover, the food choices we make can exacerbate the situation. The modern consumer culture promotes a diet high in meat and dairy, which has a disproportionately large carbon footprint compared to plant-based diets. Livestock farming is responsible for about 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, primarily through methane production during digestion and nitrous oxide emissions from manure. Individuals have the power to mitigate these emissions by reducing meat consumption and embracing more sustainable dietary practices. The movement towards vegetarianism or veganism is gaining momentum as awareness grows about the environmental impacts of food production.
Energy consumption, particularly in residential settings, represents another critical area where individual actions can drive global warming. The reliance on electricity generated from fossil fuels, such as coal and natural gas, propels emissions into the atmosphere. In many regions, homes are heated and cooled in ways that are inefficient and environmentally detrimental. Simple measures, such as improving insulation and adopting renewable energy sources like solar or wind, can significantly reduce a household’s carbon footprint. The increasing affordability and accessibility of renewable technologies have empowered consumers to make choices that directly combat climate change.
Transitioning to industrial practices reveals a more systemic challenge. The industrial sector is one of the largest contributors to global greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for around 21% of total emissions worldwide. Businesses, particularly those engaged in manufacturing and production, often prioritize short-term profits over sustainability. This choice culminates in practices such as deforestation for raw materials, excessive energy consumption, and wasteful water usage. The pressure to produce at a rapid pace often results in the neglect of sustainable methodologies. Despite the alarming figures, there is hope, as innovative companies are beginning to adopt greener practices. The shift towards circular economies, where waste is minimized, and materials are reused, reflects a paradigm shift in industrial relationships with the environment.
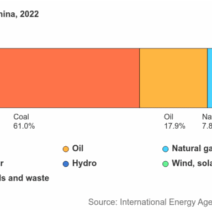
The energy sector is particularly noteworthy regarding its evolution and impact on global warming. Fossil fuels—coal, oil, and natural gas—are largely responsible for the release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. The extraction, refining, and combustion processes are not only energy-intensive but also contribute to ecological devastation, such as oil spills and habitat destruction. Governments and corporations face mounting pressure to transition to renewable energy sources. Solar, wind, and geothermal energy present viable alternatives that promise to lessen the burden on the environment. As technology advances, the feasibility of large-scale implementation of these alternatives becomes more realistic.
Despite the alarming trends, governmental policies play an instrumental role in shaping the relationship between human activities and climate change. Legislative frameworks that encourage or discourage certain behaviors essentially dictate the extent of environmental degradation. Subsidies for fossil fuels provide no incentive for companies to pursue greener practices, perpetuating a cycle of dependence on non-renewable resources. Conversely, policies advocating for reduced emissions, carbon pricing, and support for renewables can catalyze a meaningful transition towards sustainability. International accords, like the Paris Agreement, signify collective awareness and commitment, yet the challenge remains to convert these agreements into actionable change.
One can also examine the role of technology and innovation in addressing these challenges. The advent of smart technologies and IoT (Internet of Things) allows for improved efficiency in energy consumption and resource management. Smart grids, for instance, can optimize electricity distribution, minimizing waste and maximizing the use of renewable sources. Furthermore, advancements in carbon capture and storage technologies provide a means to reduce emissions from fossil fuel sources, albeit as a temporary measure rather than a permanent solution.
In summary, the evidence is irrefutable: human activities are a significant driver of global warming. From individual choices like transportation and dietary habits to large-scale industrial processes and governance, there exists a continuum of contributors to climate change. While the situation is undoubtedly critical, it also offers a plethora of opportunities for change. Each of us possesses the agency to make informed choices that can collectively steer our planet towards a more sustainable future. It is imperative that we recognize our role in this intricate web of influence and become proactive participants in combating one of humanity’s greatest challenges. As we move forward, fostering awareness, advocacy, and action remains crucial in the fight against global warming.