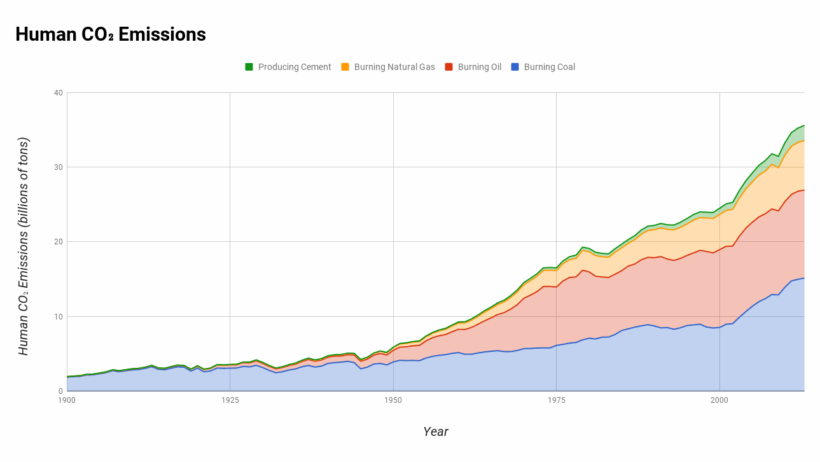
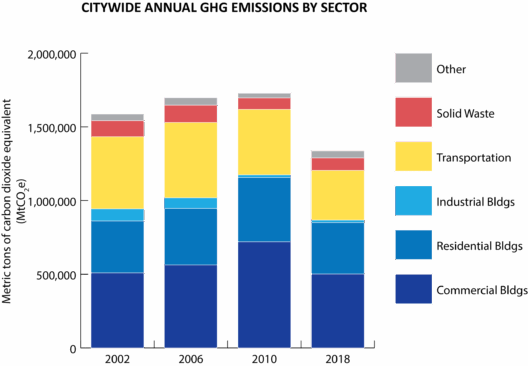
The planet we inhabit is undergoing a profound transformation, largely as a result of human activities. Global warming, one of the most pressing issues of our time, is primarily driven by the emissions of greenhouse gases, with carbon dioxide (CO2) being the most significant contributor. To grasp the intricacies of this challenge, it is imperative to understand how these emissions come about, their far-reaching consequences, and the urgent need for a paradigm shift in our approach to environmental stewardship.
At its core, global warming refers to the increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This phenomenon is not merely a theoretical concept but a tangible reality, as evidenced by increasingly frequent and severe weather events, rising sea levels, and diminishing ice caps. The main human activities responsible for elevated greenhouse gas emissions include transportation, industrial processes, agriculture, and energy production. Each of these sectors contributes uniquely to the overall emission footprint.
Transport is one of the most visible contributors to global warming. The internal combustion engine, commonly found in automobiles, releases substantial quantities of CO2 and other pollutants. As transportation networks proliferate, so does the consumption of fossil fuels, leading to increased emissions. A shift toward electric vehicles and improved public transit systems holds promise. However, the transition is slow, and the status quo remains largely due to socio-economic factors and infrastructural inertia.
Industrial processes further exacerbate the situation. Factories, manufacturing plants, and refineries emit not only carbon dioxide but also other greenhouse gases such as methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O). These emissions arise from the combustion of fossil fuels for energy and from various chemical reactions during production. While technological advancements have led to cleaner production methods, many industries still rely heavily on carbon-intensive processes. More rigorous regulations and incentives to adopt sustainable practices are crucial to mitigating this impact.
Agriculture, often overlooked, plays a pivotal role in global warming. Agricultural practices contribute to greenhouse gas emissions through livestock digestion processes, fertilizer application, and land-use changes such as deforestation. Livestock produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas with a far greater warming potential than CO2 in the short term. Moreover, the clearing of forests for agricultural expansion not only releases stored carbon but also diminishes the planet’s capacity to absorb existing CO2. Sustainable agricultural practices, such as regenerative farming and permaculture, present an opportunity to reduce emissions and enhance carbon sequestration.
Energy production is arguably the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions globally. The combustion of coal, oil, and natural gas for electricity and heat is responsible for a significant proportion of the CO2 released into the atmosphere. The reliance on fossil fuels is deeply embedded in modern society, presenting a formidable challenge in the quest for a sustainable future. Thought leaders in energy policy advocate for a transition to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. These alternatives not only reduce emissions but also promote energy independence and resilience against fluctuating fossil fuel markets.
The implications of unchecked global warming are staggering. As temperatures rise, ecosystems become destabilized, leading to a cascade of adverse effects. Coral reefs, often described as the “rainforests of the sea,” are particularly vulnerable to temperature increases, which cause coral bleaching and massive die-offs. Terrestrial ecosystems face similar threats, with altered precipitation patterns disrupting habitats and leading to species extinction. The loss of biodiversity diminishes ecosystem resilience, reducing the ability to adapt to climate changes.
Furthermore, human health is at stake. The direct consequences of heatwaves, increased air pollution, and heightened allergen exposure can lead to serious health problems. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions, are especially at risk. Moreover, the intersection between climate change and social inequities raises concerns about environmental justice. Marginalized communities often bear the brunt of climate-related consequences, lacking the resources to adapt or recover from adverse events.
The economic ramifications are equally dire. Infrastructure damage from extreme weather events, disruptions in food supply chains, and increased energy costs impose significant burdens on both developed and developing economies. Insurance costs rise as risks become less predictable, leading to an inevitable increase in premiums that further exacerbate socio-economic disparities.
Yet, amid the daunting challenges posed by global warming lie opportunities for innovation and transformation. The pursuit of sustainable practices is gaining momentum as individuals, businesses, and governments recognize the need for immediate action. Public awareness campaigns, grassroots movements, and international agreements underscore the collective resolve to combat climate change. The Paris Agreement exemplifies global commitment to limit temperature rise and facilitate collaborative efforts. Sustainable development goals pave the way for integrating environmental considerations into all aspects of life.
As societies evolve, the shift in perspective must be profound. Recognizing that our actions have consequences is the first step. Every choice, from the transportation we use to the products we consume, influences our planetary health. A commitment to sustainability transcends individual behavior and demands systemic change. Policymakers must legislate for a greener economy, businesses must innovate for reduced environmental impact, and communities must unite in advocacy. The immediacy of the climate crisis necessitates a collective response, grounded in shared values and a vision for a sustainable future.
In conclusion, understanding the intricate ways human activities influence global warming is crucial for initiating substantive change. A combination of technological innovation, legislative action, and societal commitment can chart a course toward sustainability. The pressing issue of climate change calls for a determined and collaborative response. Addressing it will require an amalgamation of our intellect, creativity, and altruism. The time to act is now; the planet depends on it.