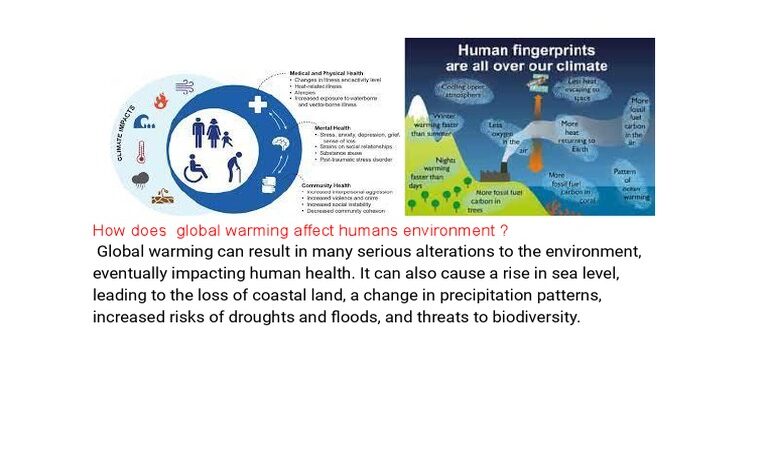
Global warming is a pressing issue that has captured the attention of scientists, policymakers, and the general public. It refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to human activities. Understanding how humans are orchestrating this monumental shift is crucial in combating climate change. Several key factors drive this phenomenon, which can be categorized into various sectors, including energy production, transportation, agriculture, and industrial processes.
Energy Production
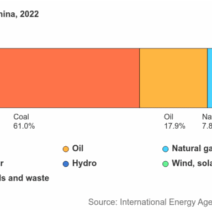
One of the primary culprits of global warming is the combustion of fossil fuels for energy production. Power plants, predominantly coal, oil, and natural gas-based, are significant sources of greenhouse gas emissions. When fossil fuels are burned, they release carbon dioxide (CO2) and other pollutants into the atmosphere. The abundance of these emissions enhances the greenhouse effect, leading to atmospheric warming. Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power present alternatives that can mitigate these effects, but adoption rates remain insufficient to combat the immediate threat of climate change.
Transportation
The transportation sector is another major contributor, responsible for nearly a quarter of global greenhouse gas emissions. Automobiles, airplanes, ships, and trucks primarily rely on gasoline and diesel, which release significant amounts of CO2 and other emissions as byproducts of fuel combustion. The increase in global vehicle ownership, compounded by urbanization and the expansion of road networks, exacerbates these emissions. Transitioning to electric vehicles (EVs), optimizing public transport systems, and encouraging alternatives like biking and walking can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with this sector.
Agriculture
Agriculture also plays a pivotal role in exacerbating climate change. Practices such as deforestation, methane emissions from livestock, and nitrous oxide emissions from fertilizers contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. The conversion of forests into agricultural land releases stored carbon, while livestock produce methane—a gas potent in its ability to trap heat in the atmosphere. Furthermore, excessive fertilizer application can lead to nitrous oxide emissions. Sustainable farming practices, including crop rotation, improved manure management, and organic farming, are essential in curtailing the agricultural sector’s impact on global warming.
Industrial Processes
The industrial sector, which encompasses the manufacturing of goods, is also responsible for a considerable fraction of greenhouse gas emissions. Industries such as cement, steel, and chemical manufacturing emit substantial amounts of CO2 through energy-intensive processes. Moreover, certain industrial activities release potent greenhouse gases like hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which, although less common, can have much greater warming potentials than CO2. Implementing energy-efficient technologies, adopting cleaner production methods, and pursuing carbon capture and storage (CCS) can alleviate the environmental toll associated with industrial production.
Waste Management
Human activity generates a staggering amount of waste, which significantly contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Landfills produce methane as organic waste decomposes anaerobically. The inefficacy of many current waste management practices means that these emissions remain unchecked. Additionally, the incineration of waste releases CO2 and other harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. Enhancing recycling initiatives, promoting composting, and minimizing waste generation are critical components of a comprehensive strategy to tackle emissions from this sector.
Land Use Change
Another crucial aspect of human impact on climate is land use change, particularly deforestation. The clearing of forests for agriculture, urban development, and resource extraction exacerbates CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere. Trees act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 during photosynthesis and storing carbon in their biomass. The destruction of these vital ecosystems not only releases stored carbon but also diminishes the planet’s capacity to absorb CO2. Conservation efforts and reforestation projects play an essential role in sequestering carbon and restoring biodiversity.
Consumer Behavior
The collective actions of individuals also contribute to global warming. Consumer choices related to energy consumption, product purchases, and lifestyle habits influence demand for high-emission goods and services. The culture of convenience, coupled with a penchant for fast fashion and processed foods, exacerbates resource depletion and increases carbon emissions. Educating consumers about sustainable practices, encouraging responsible consumption, and promoting eco-friendly products can empower individuals to make choices that align with climate action.
The Role of Policy and Advocacy
Finally, governmental policies and international agreements play a critical role in addressing the human causes of global warming. Global cooperation is vital; climate change knows no borders. Frameworks such as the Paris Agreement aim to unite countries in their effort to limit temperature rise and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, real change requires stringent regulations, incentives for renewable energy, and the promotion of green technologies, along with grassroots advocacy and public awareness initiatives.
In conclusion, humans are integral to both the cause of and potential solutions to global warming. By comprehensively understanding the various ways in which our activities contribute to climate change—from energy production to consumer behavior—we can enact meaningful changes that benefit the planet. Collective awareness and action, coupled with innovative strategies and global cooperation, are essential to curb the escalating impacts of climate change and steer our planet towards a more sustainable future.