The vast, icy expanses of the Arctic and Antarctic regions, with their majestic icebergs drifting languidly in the ocean, evoke a sense of wonder and splendor. However, beneath this striking beauty lies a grim reality — the melting of these icy giants and their consequential role in elevating global sea levels. Understanding how icebergs contribute to rising sea levels is imperative in grasping the broader implications of climate change. As the world warms, these titanic structures transform from ethereal sculptures of frozen water into harbingers of impending ecological upheaval.
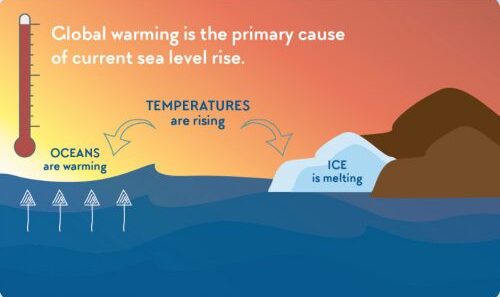
Icebergs are fascinating phenomena, born from glaciers and massive land ice sheets. These magnificent formations fracture, calving off from their parent ice bodies, creating floating masses of fresh water. Under normal conditions, the frozen water residing in these structures would take eons to evaporate into the atmosphere. However, as global temperatures escalate due to climate change, the dynamics surrounding icebergs shift dramatically. Their melting not only disrupts the ethereal beauty of polar landscapes but also contributes significantly to the overall rise in sea levels.
Understanding the physics of melting icebergs offers insight into their contribution to rising oceans. When icebergs drift into warmer waters, they begin to melt, a process driven by the delicate balance of freshwater and saltwater interactions. As the iceberg loses mass, the freshwater has an immediate effect on sea levels. The melting iceberg contributes directly to sea level rise, while simultaneously altering oceanic circulation patterns. This interplay between ice melt and ocean dynamics creates a cascading effect that exacerbates the trajectory of sea level increase.
In the grand tapestry of Earth’s climate systems, icebergs serve as both indicators and influencers. Their melting presents a dual narrative; at once, it reveals the warming temperatures afflicting our planet, while also contributing to the very peril they illustrate. The story of icebergs is an ongoing saga marked by interdependence between climate change and rising seas, grounded in the physics of fluid dynamics.
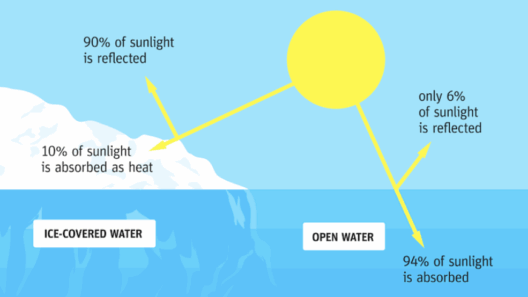
A closer examination of polar regions unveils a narrative of stark contrasts. Glaciers, the progenitors of icebergs, have long been stable features of our planet’s geography. However, recent satellite measurements have indicated alarming trends. Massive ice sheets, such as those found in Greenland and Antarctica, are disintegrating at an unprecedented rate, releasing vast quantities of freshwater into the oceans. This phenomenon is akin to opening floodgates, where the unrelenting flow of freshwater accelerates the upward trajectory of sea levels, encroaching on coastlines worldwide.
Furthermore, the melting of icebergs exacerbates thermal expansion — a secondary driver of rising sea levels. As ocean temperatures rise, water expands, adding another layer to the complex equation of global sea level rise. Simply put, the confluence of melting icebergs and thermal expansion creates a perfect storm, wherein one aspect amplifies the other. This synergy serves as a clarion call, urging action towards a sustainable and climate-responsive future.
Coastal communities stand at the precipice of this rising tide, facing a dual threat: encroaching waters from melting icebergs and the inevitable transformation of their environments. Urban planners and environmentalists alike labor to create strategies to mitigate the impacts of this burgeoning crisis. The infrastructure along coastlines must adapt, evolve, and reinforce against the relentless advance of rising oceans.
But beyond immediate existential threats, the melting of icebergs influences global climate systems. As freshwater from icebergs pours into the ocean, it disrupts the salinity balance critical for ocean currents. Ocean currents are the lifeblood of planetary climate, governing weather patterns and precipitation zones. Disruptions to these currents can lead to erratic weather, unpredictable storms, and altered agricultural zones, thus impacting food security and habitat integrity worldwide.
While the dialogue surrounding icebergs and sea levels often focuses on quantitative measures, it is essential to address the qualitative aspects of these changes. The majestic beauty of icebergs has inspired generations, from artists to scientists, yet their rapid decline signifies a poignant cultural loss. The metaphor of icebergs as “giants of the sea” encapsulates their role not only as ecological entities but also as reservoirs of history, culture, and identity — all threatened by modernity’s excesses.
Considering the repercussions of melting icebergs transcends mere scientific inquiry; it is a clarion call to reflect upon our stewardship of the planet. Each iceberg lost is not merely a statistic but a step toward a future characterized by uncertainty and instability. Consequentially, it encapsulates a deliberate moment in history where human activity has driven nature to the brink.
As we navigate the complexities of this existential threat, concerted efforts aimed at addressing climate change are paramount. Policies centered around reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting renewable energy, and fostering sustainable practices can curtail the escalating crisis linked to melting icebergs. The clarion call of the icebergs must echo in our collective consciousness, urging us to recognize the fragility of our climate and the interconnectedness of all life on Earth.
In conclusion, the melting of icebergs is a multifaceted phenomenon with profound implications for rising sea levels. Their existence serves both as a solemn reminder of our warming planet and a challenge to our collective will to effect change. We must heed the warning signs, shift our actions, and embrace a sustainable future, preserving not just the awe-inspiring beauty of icebergs but also the delicate equilibrium of our ecosystems.