Understanding how prevailing winds shape our climate is pivotal in demystifying the complex interplay of atmospheric phenomena. Among the various constituents of wind systems, the jet stream emerges as a significant player, weaving dynamically across the globe and influencing weather patterns, climate variability, and even ecological shifts. In this exploration, we delve into the mechanics, implications, and overarching narrative encapsulated in the story of the jet stream.
The Jet Stream: What Is It?
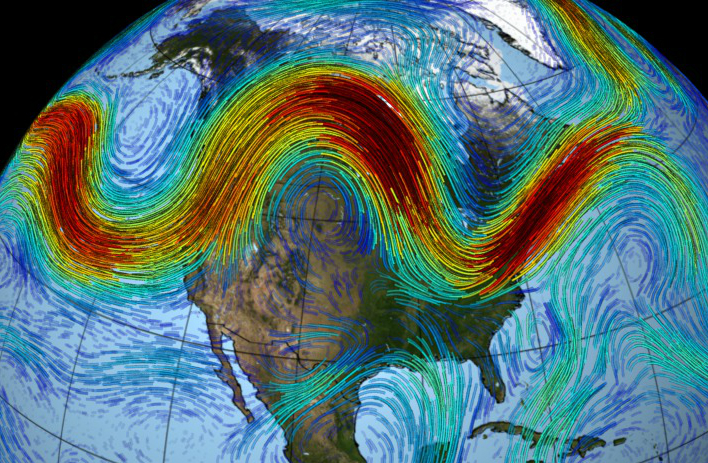
The jet stream is a narrow band of fast-moving air located high in the atmosphere, usually at altitudes of about 30,000 feet. This powerful current flows from west to east and plays a critical role in steering weather systems and regulating temperatures across continents. It exists due to the temperature differences between the equatorial and polar regions, creating pressure gradients that induce immense wind speeds. Understanding this atmospheric river is crucial, as it is intricately linked with climate phenomena.
The Mechanics of the Jet Stream
The formation of the jet stream is a product of Earth’s rotation and the uneven distribution of solar energy. The Coriolis effect, a consequence of the Earth’s rotation, causes winds to curve rather than travel in straight lines. This curvature transforms the straightforward air movement into a wavy pathway. As warm air rises near the equator and cold air descends near the poles, a dynamic balance arises. However, this balance is not static; it is influenced by various factors, including geographical features, ocean currents, and climate change.
Temperature differentials act as the primary force propelling the jet stream’s trajectory. For instance, during winter months, polar air masses are colder and denser, resulting in a more pronounced jet stream. This pronounced jet stream can fluctuate in amplitude, leading to significant weather events such as cold snaps or heat waves. Conversely, a weaker jet stream can allow for warmer air to seep into traditionally cooler regions, thus altering seasonal expectations.
Climate Impact of the Jet Stream
The consequences of jet stream behavior are far-reaching. A strong, stable jet stream can maintain consistent weather patterns, facilitating predictable climates in various regions. However, fluctuations can lead to extreme weather events, such as prolonged droughts in one area while floods ravage another. In this sense, the jet stream acts like a conductor of an orchestra, coordinating the various climatic instruments to create harmony—or discord—in weather patterns.
For instance, in regions such as North America, the meandering jet stream can lead to phenomena like the “Polar Vortex.” This term describes the swirling pool of cold air trapped over the Arctic, which, when disrupted, can plunge southward, causing drastic temperature drops in mid-latitude regions. Such occurrences underscore how a single atmospheric current can precipitate significant climatic anomalies.
Influence of Climate Change on the Jet Stream
As global temperatures rise due to anthropogenic influences, the implications for the jet stream are profound. Climate change is altering the temperature gradients that drive jet stream mechanics. Specifically, the Arctic is warming more rapidly than other regions, which reduces the temperature contrast between the Arctic and temperate zones. This change can potentially weaken the jet stream, leading to more pronounced meanders or “stuck” patterns.
Consequently, these alterations present a paradox: while average temperatures globally may rise, local climates can experience more severe weather variability. This phenomenon raises crucial questions regarding agricultural practices, water resources, and even human settlements, as communities grapple with unpredictable microclimates.
Ecological Repercussions
The implications of jet stream alterations extend beyond human contingencies; they reverberate through ecosystems. Many species rely on predictable climate cues for migration, breeding, and foraging. Irregular weather patterns disrupt these cycles, threatening biodiversity. For example, a shift in the timing of seasonal cues can lead to mismatches between pollinators and plants, impacting food webs and ecological interdependencies.
Furthermore, as the jet stream continues to evolve due to climate shifts, the alteration of habitats may push some species to extinction while allowing others to thrive in new environments. The subtle but significant influence of the jet stream on ecological integrity serves as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of our planet’s systems.
Conclusion: A New Perspective on Climate Systems
As we peal back the layers surrounding prevailing winds, particularly the jet stream, we are compelled to reassess our understanding of climate dynamics. No longer can we view weather as isolated events; the jet stream’s narrative is a reminder of the intricate tapestry woven by the Earth’s atmospheric conditions. With climate change looming large, it is crucial to continue monitoring these phenomena to prepare for, mitigate, and adapt to the ever-evolving climate landscape.
In the final analysis, the jet stream encapsulates the complexity of weather systems and climate variability. It underscores the importance of a global perspective in understanding local environmental changes. Embracing this narrative invites curiosity, demanding our attention as stewards of the planet. The challenge ahead lies not just in academic analysis but in actionable steps to address the implications of these shifts; together, we may mitigate their effects and forge a sustainable future.