Climate change represents one of the most formidable challenges of our time, demanding a multifaceted approach to mitigate its catastrophic effects. This article delves into three pivotal avenues: robust policy frameworks, technological innovations, and the crucial role of trees in sequestering carbon. Each of these components plays an integral role in forging a sustainable future and alleviating the adverse impacts of climate change.
Understanding Climate Change
Before exploring mitigation strategies, it is essential to grasp the fundamental mechanics of climate change. Primarily driven by anthropogenic activities, especially the combustion of fossil fuels, climate change leads to a rise in greenhouse gas concentrations within the atmosphere, culminating in global warming. Consequentially, erratic weather patterns, rising sea levels, and biodiversity loss threaten the integrity of ecosystems and human livelihoods alike.
1. Policy Frameworks: Foundational Pillars of Mitigation
A comprehensive and coherent policy framework is indispensable for mitigating climate change. Governments around the world must implement stringent regulations and incentives aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable practices. The Paris Agreement serves as a foundational international treaty, encouraging countries to commit to specific emissions reduction goals, thereby fostering a collective global effort.
Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) epitomize individual country commitments within this framework. By setting ambitious targets for reducing emissions, nations can strategically transition toward renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. Moreover, policies that promote energy efficiency in transportation and buildings can significantly curtail fossil fuel consumption.
Another critical aspect of effective climate policy is the integration of climate resilience strategies into urban planning. Cities must adapt to the inevitable consequences of climate change through infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather events. This may include flood defenses, green roofs, and urban green spaces, all of which can serve dual functions: mitigating climate impacts and enhancing urban livability.
2. Technological Innovations: Harnessing Modern Solutions
In conjunction with robust policy frameworks, technological innovations are paramount in combating climate change. A broad spectrum of technological advancements exists, from renewable energy technologies to carbon capture and storage systems, each contributing uniquely to emission reductions.
At the forefront of renewable energy advancements is solar technology. Photovoltaics have dramatically decreased in cost, making solar energy more accessible to consumers and businesses alike. Furthermore, energy storage solutions, such as advanced battery systems, enhance the reliability of renewable energy by addressing intermittency issues.
Wind energy is another significant advancement, with onshore and offshore wind farms proliferating globally. Innovations in turbine design have increased efficiency and energy output, rendering wind an increasingly competitive energy source.
In addition to renewable energies, carbon capture and utilization (CCU) technologies are gaining traction. These systems capture carbon dioxide emissions from industrial sources, preventing them from entering the atmosphere and allowing them to be repurposed for industrial processes or stored underground. Such technologies provide critical pathways to achieving net-zero emissions.
3. The Role of Trees: Nature’s Carbon Sinks
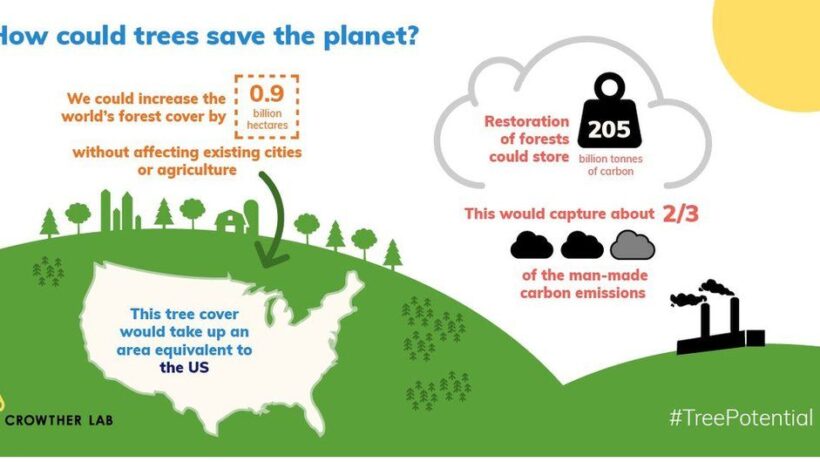
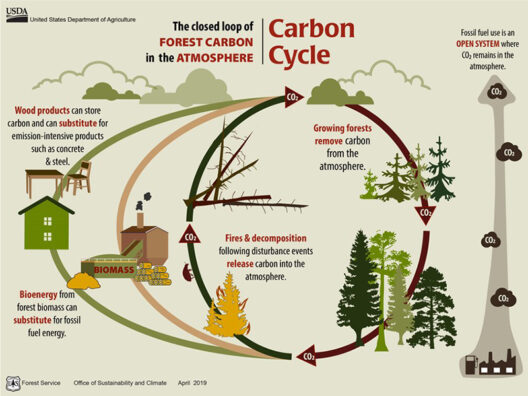
Among the most effective natural solutions for climate change mitigation is reforestation and afforestation. Trees act as natural carbon sinks, sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis. Their role goes beyond carbon storage; forests enhance biodiversity, maintain watershed health, and stabilize soil, all vital for ecosystem resilience.
Scientific studies underscore the significance of maintaining existing forests and restoring degraded ones. For instance, protecting primary forests is a cost-effective strategy that not only captures carbon but also conserves invaluable biodiversity. Initiatives like the Bonn Challenge aim to restore millions of hectares of deforested and degraded land, harnessing the power of trees to combat climate change while providing co-benefits to local communities.
Urban forestry emerges as another crucial strategy. Trees planted in urban environments can mitigate the urban heat island effect, improve air quality, and enhance mental health. Implementing tree canopy programs in cities not only counters carbon emissions but also fosters community engagement and education regarding environmental stewardship.
4. Integrated Approaches: Synergizing Strategies
The intersection of policy, technology, and natural solutions yields the most promising outcomes in climate change mitigation. A holistic approach entails leveraging technology to bolster policy initiatives and vice versa. For example, data-driven insights from technological advancements can inform policymakers about the most effective strategies for emissions reductions.
Moreover, public-private partnerships can facilitate investment in green technology while simultaneously supporting reforestation projects. By uniting corporate responsibility with environmental goals, companies can play a pivotal role in both reducing their carbon footprint and investing in natural climate solutions.
5. The Importance of Community Engagement
Effective climate change mitigation cannot be achieved in isolation. Community engagement is vital as it empowers individuals and local groups to partake actively in local climate initiatives. Education campaigns that emphasize sustainable practices, such as reducing waste and conserving energy, can significantly alter consumer behaviors.
Grassroots movements often foster a heightened sense of urgency and a call for action. Through community-led reforestation initiatives, local stakeholders can witness firsthand the tangible benefits of environmental restoration and stewardship.
In conclusion, mitigating climate change necessitates a tripartite approach that intertwines robust policy frameworks, innovative technologies, and the invaluable contributions of trees. While the challenges are immense, the potential for impactful action remains profound. By committing to these strategies collectively, society can cultivate a resilient future that honors both our environment and generations to come.