The Law of Conservation of Energy is a fundamental principle in physics and a cornerstone of our understanding of the universe. It posits that energy cannot be created or destroyed; instead, it can only be transformed from one form to another. This concept not only resonates within the realms of science but also reverberates throughout various aspects of life, leading to profound implications for our environment and energy consumption. To grasp this concept fully, it is essential to cover several facets that illuminate its importance and relevance.
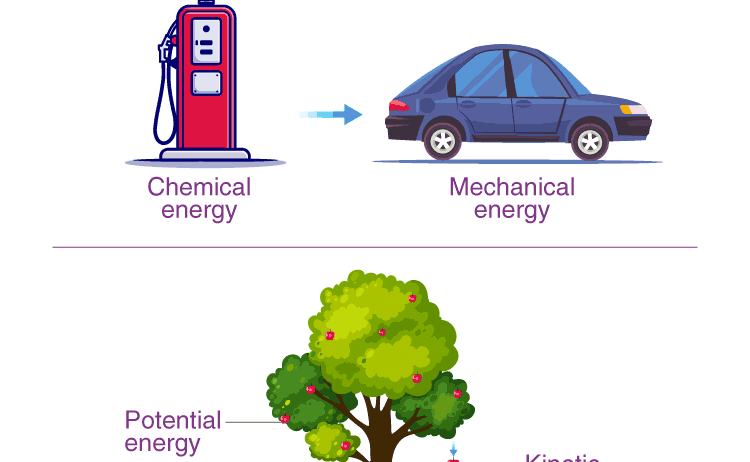
At its core, the Law of Conservation of Energy tells us that the total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant over time. This means that while energy can take different shapes — such as kinetic energy in moving objects, potential energy in stored states, thermal energy as heat, or chemical energy in bonds — the sum of these forms is invariant. For instance, when a ball is thrown into the air, its kinetic energy diminishes as it ascends and is transferred into potential energy; at the peak of its trajectory, all the kinetic energy is converted into potential energy. Upon descending, potential energy reverts back into kinetic energy. This cyclical transformation is a quintessential illustration of conservation in action.
The implications of this law stretch far beyond theoretical physics. Consider the electricity we consume daily. The power generated in a hydroelectric plant transcends gravitational potential energy stored in elevated water to kinetic energy as the water wheels turn turbines, creating electrical energy. When we flip a switch to light up a room, we benefit from a cascade of energy transformations initiated by the gravitational pull of flowing water and ending in the luminescence of our light bulbs. This intricate dance of energy conversion exemplifies conservation principles while simultaneously emphasizing the critical relationship between energy systems and their environmental impact.
Fascination with the Law of Conservation of Energy also fosters deeper inquiries into sustainable practices. In an era defined by climate change, reliance on fossil fuels is becoming increasingly untenable. As humanity grapples with the dire repercussions of carbon emissions, understanding energy conservation becomes pivotal. Renewables like solar and wind power offer tantalizing prospects for sustainable energy generation, illustrating not only the conversion of natural forces into usable energy but also highlighting the need for innovative technologies to harness these processes efficiently.
Yet, despite the seemingly straightforward nature of the law, misconceptions abound. Many individuals perceive energy consumption as a linear equation, where utilizing energy equates to its generation. However, the reality is more nuanced. The persistent struggle against wasteful practices — illustrated by the infamous ‘vampire energy’ phenomenon where devices consume power even when switched off — serves as a reminder that energies continuously oscillate between potential and kinetic states, often eluding our grasp.
In an educational context, simplifying the Law of Conservation of Energy can be advantageous for promoting comprehension. Visual aids, practical experiments, and relatable analogies can facilitate understanding. For instance, engaging students with a pendulum experiment demonstrates energy transformation simply: at the peak of its swing, the pendulum possesses maximum potential energy; as it arcs downward, this energy transitions into kinetic energy. Such tangible examples not only clarify concepts but also engage curious minds in fundamental physics.
Moreover, when discussing energy conservation, it is vital to impart a sense of responsibility towards conserving resources. Individuals can contribute to energy conservation in their daily lives through actions such as reducing water and electricity consumption, utilizing energy-efficient appliances, and adopting renewable energy practices. Every small step nudges the community toward broader environmental sustainability, culminating in a long-lasting pool of collective responsibility that can mitigate climate change.
It is pertinent to broaden the discussion to the implications of energy conservation on global scales. Nations worldwide will need to reconsider their energy strategies. For developed nations, transitioning to greener technologies while developing infrastructures that support sustainable energy practices is a necessity. Developing nations, on the other hand, face the dual challenges of advancing economically and adopting clean energy technologies without depleting their natural resources disproportionately. This complex interplay of economics, technology, and environmental stewardship underlines the multifaceted nature of the Law of Conservation of Energy.
Furthermore, embracing the law cultivates a spirit of innovation. Continuous research into energy-efficient solutions fuels technological advancements that can enhance energy conversion processes. From smart grids that optimize energy distribution to innovative battery technologies that increase storage capacities for renewable resources, the journey towards achieving comprehensive energy conservation depends heavily on our ability to engage with, and understand, these natural principles.
Moreover, the philosophical implications surrounding the Law of Conservation of Energy suggest an interconnected universe where every action reverberates through time and space. Thus, in every exchange of energy, there is a burgeoning awareness that we are part of something much larger than ourselves — a collective existence where each contribution either moves us towards sustainability or further exacerbates our environmental crises. This awareness prompts proactive engagement, revealing that the challenges we face today are indeed opportunities for tomorrow.
In conclusion, explaining the Law of Conservation of Energy requires integrating scientific principles with environmental ethics and personal accountability. It is more than a mere formula; it serves as a guiding philosophy applicable to individual behaviors, institutional practices, and global policies. By fostering an understanding of how energy operates, we can cultivate a culture of conservation that not only respects our natural world but also promotes sustainable innovations for generations to come.