As we traverse through our modern world, we often hear about climate change. But have you ever pondered the intricacies of how climate change transpires? It’s a complex narrative that unfolds over time and involves a myriad of factors, both natural and anthropogenic (human-induced). What if you could grasp the various mechanisms underlying this monumental phenomenon? Grab your metaphorical magnifying glass as we embark on a journey through the steps that delineate how climate change occurs.
Understanding climate change necessitates diving into the delicate interplay between the Earth’s systems and human activities. Let’s take a closer look.
Unveiling the Greenhouse Effect: A Natural Phenomenon
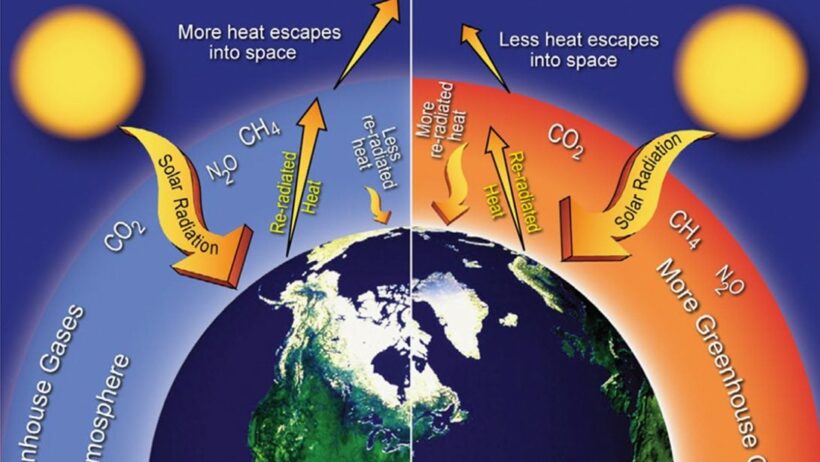
At the heart of climate change lies a process known as the greenhouse effect. But what exactly does this mean? Simply put, the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon whereby certain gases in our atmosphere trap heat, keeping our planet warm enough to sustain life. Without this effect, Earth would be a frozen wasteland.
When sunlight reaches the Earth, some of it is reflected back into space. However, a portion of this sunlight is absorbed by the Earth’s surface, converting solar energy into heat. This heat then radiates back toward space, but greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) absorb and re-radiate some of the outgoing heat, keeping the atmosphere snug and temperate. This layer of gases creates a sort of blanket around our planet.
Consider this: What would life on Earth look like without this protective blanket? A rather crisp existence, to say the least. While this natural effect is essential, the game becomes perilous when human actions amplify these greenhouse gases beyond natural levels.
Identifying Anthropogenic Contributions: The Human Footprint
Now that we’ve dug into the natural aspects of the greenhouse effect, let’s confront the specter of human influence. With rapid industrialization, urbanization, and socioeconomic activities, humans have began to contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. But how does this occur?
Firstly, the burning of fossil fuels for energy is a major culprit. Power plants, automobiles, ships, and planes rely heavily on coal, oil, and natural gas. As these fuels combust, they release significant amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, exacerbating the greenhouse effect. Additionally, industries that produce cement, plastics, and metals contribute further to emissions through energy consumption and chemical processes.
Furthermore, the agricultural sector plays a pivotal role. Livestock, particularly cows and sheep, generate substantial methane emissions through digestion and manure management. Fertilizers used in crop production release nitrous oxide, another potent greenhouse gas. Deforestation for agricultural expansion reduces the number of trees that can absorb CO2 and contributes to the emissions when forests are cleared.
What would happen to our atmosphere if these human activities ceased altogether? Perhaps a chance for rejuvenation, but the path to that point is neither immediate nor straightforward.
The Consequences: Unraveling the Impact
As anthropogenic greenhouse gases continue to rise, we witness a cascade of climatic consequences. But what does this entail for ecosystems and human societies? First and foremost, global temperatures are on a dramatic upward trajectory. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) provides alarming data showing that since the late 19th century, the Earth’s average temperature has risen approximately 1.2 degrees Celsius.
This warming leads to the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers, contributing to rising sea levels. Coastal regions are increasingly vulnerable, facing potential flooding and displacement of populations. Have you ever considered how many communities may become dystopian narratives as they are engulfed by the encroaching ocean?
Moreover, climate change catalyzes more frequent and severe weather events—think hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves. These variations disrupt ecosystems, alter species distributions, and even threaten biodiversity. The delicate balance that sustains life is thrown into turmoil, challenging the resilience of already stressed ecosystems.
Another notable consequence is the impact on agriculture and food security. Altered precipitation patterns create a gamble for crop yields. Increased heat can stunt growth or lead to crop failures, thus exacerbating hunger issues worldwide.
What can we do to emerge as architects of solutions rather than mere participants in this alarming circumstance? The landscape of climate action offers potential avenues for exploration.
Taking Action: The Road to Resilience
As global citizens, the onus is upon us to mitigate climate change and fortify our resilience against its effects. Strategies include transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydro while enhancing energy efficiency. Imagine a world where clean energy powers our homes, offices, and vehicles, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Additionally, investing in reforestation and afforestation initiatives is crucial. Trees are nature’s lungs, scrubbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Promoting sustainable agricultural practices can further mitigate emissions while ensuring food security.
The challenge is formidable, but collective action can spur monumental shifts in societal norms. Innovating policies aimed at reducing emissions and fostering sustainable practices can usher in a new age of ecological stewardship. Are you prepared to take part in this transformative journey?
In conclusion, understanding how climate change unfolds is imperative for anyone keen on rectifying its trajectory. By appreciating the mechanisms that drive climate change, we equip ourselves to combat its effects and safeguard the planet for future generations. Together, let us seize the challenge and advocate for sustainable practices that nurture the planet’s well-being.