Global warming, a phenomenon marked by the gradual increase in Earth’s average surface temperature, is a crucial issue that reverberates through various ecological and socio-economic facets. The implications of this climatic shift extend far beyond mere statistics; they embody profound alterations in our environment. Understanding the intricate effects of global warming on our surroundings necessitates a closer examination of its impacts on ecosystems, weather patterns, flora and fauna, as well as human life.
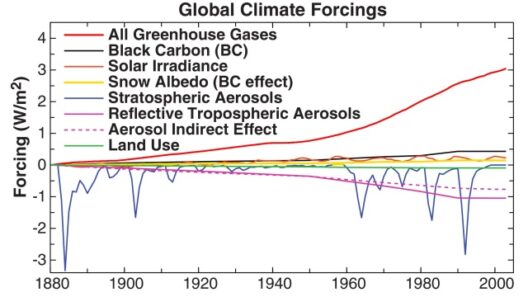
To commence this exploration, one must acknowledge that global warming is primarily driven by anthropogenic factors. The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes release greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane, into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to a cascade of environmental disturbances. As the greenhouse effect intensifies, we observe a rise in average global temperatures, which in turn catalyzes a series of alarming phenomena.
Polar ice caps and glaciers, those majestic sentinels of the planet’s climate history, are among the first to reflect the reality of climate change. With rising temperatures, these icy formations are succumbing to accelerated melting rates. According to recent studies, Arctic sea ice is diminishing at an unprecedented pace. This phenomenon not only contributes to rising sea levels but also disrupts marine ecosystems. As habitats for seals, polar bears, and various species of seabirds dwindle, the delicate balance of Arctic biodiversity is jeopardized. The loss of ice alters albedo— the reflection of solar radiation—and further exacerbates warming, creating a vicious cycle.
Another striking consequence of global warming manifests in the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. Hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves are becoming more prevalent, challenging the resilience of ecosystems and human communities alike. For instance, warmer ocean temperatures provide additional energy for storm systems, leading to more potent hurricanes, such as those witnessed in recent years. These storms wreak havoc on coastal ecosystems, eroding shorelines, destroying habitats, and contributing to the degradation of coral reefs. Such disruptions have both immediate and long-term repercussions, endangering marine biodiversity and jeopardizing the livelihoods of communities reliant on coastal resources.
The terrestrial environment is not immune to these changes. Fluctuations in temperature and precipitation patterns have initiated shifts in ecosystems around the world. Species migration patterns are being altered as flora and fauna struggle to adapt to their changing habitats. Some species are retreating to cooler altitudes or latitudes, while others face the grim prospect of extinction. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) warns that if current trends continue, an estimated one million species could be lost within decades. This alarming statistic underscores the urgency of our situation. Biodiversity loss diminishes the resilience of ecosystems, making them more susceptible to further changes and less able to recover from disturbances.
Additionally, terrestrial ecosystems face the ominous threat of altered growing conditions. Agricultural practices are directly impacted by changing climatic conditions. Crop yields are subject to the whims of unpredictable weather patterns, leading to potential food shortages. Flooding, droughts, and altered rainfall can drastically affect food production, challenging food security for populations worldwide. Furthermore, the nutritional quality of crops may be compromised as rising carbon dioxide levels influence the nutrient content of staples, such as wheat and rice. The complexity of these interactions demands innovative agricultural strategies and policies focused on enhancing resilience to climatic shifts.
Forests, often heralded as the lungs of the Earth, are equally vulnerable to the repercussions of global warming. As temperatures rise, forests face increased risks from pests and diseases. For instance, the mountain pine beetle has proliferated in response to warmer winters, decimating vast stretches of forest in North America. The resulting tree mortality not only reduces carbon storage capabilities but also heightens the risk of wildfires—a phenomenon becoming alarmingly widespread. These intense wildfires result in the release of stored carbon back into the atmosphere, perpetuating the cycle of warming.
Moreover, global warming has begun to infiltrate freshwater ecosystems, affecting lakes, rivers, and wetlands. Changes in water temperature and chemistry disrupt aquatic life, including fish populations and other species dependent on specific thermal habitats. Algal blooms, fueled by increased temperatures and nutrient runoff, threaten water quality and aquatic biodiversity. These changes have dire implications for human communities reliant on freshwater resources for drinking, recreation, and agriculture.
The socio-economic ramifications of global warming are profound and cannot be overlooked. As environmental conditions deteriorate, marginalized communities often bear the brunt of these changes. Climate-induced phenomena such as famine, displacement, and health crises exacerbate existing inequalities, leading to humanitarian challenges. Vulnerable populations may find themselves at the frontline of climate impacts, lacking the resources to adapt and recover from environmental shocks.
Ultimately, the question of how global warming affects our environment transcends mere analysis; it invites a moral imperative for action. As stewards of the planet, it is our responsibility to confront climate change with urgency and innovation. Mitigating carbon emissions, investing in renewable energy, and fostering sustainable practices can alter the trajectory of global warming. Furthermore, enhancing public awareness and engagement is paramount; fostering a more enlightened populace will position us to advocate for robust policies aimed at ecological preservation.
In conclusion, global warming represents a formidable threat to environmental integrity and human well-being. By understanding its multifaceted consequences, we can cultivate a deeper sense of responsibility towards our planet. Awareness translates into action, and together, we can pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient future. The time to act is now, and the stakes could not be higher.