Global warming poses a significant challenge to our planet, foremost among its impacts being the rise in sea levels. This phenomenon is an alarming consequence of increased greenhouse gas emissions, which trap heat in the atmosphere and disrupt climate balances. As temperatures rise, two primary processes contribute to the increasing volume of our oceans: thermal expansion of seawater and the melting of glaciers and ice sheets. Understanding the nuances of how global warming influences rising sea levels is imperative for effective mitigation and adaptation strategies.
In this article, we delve into the intricate relationship between global warming and ocean expansion, exploring the mechanisms behind sea-level rise, its implications for coastal communities, and potential future scenarios.
The Mechanisms of Sea-Level Rise
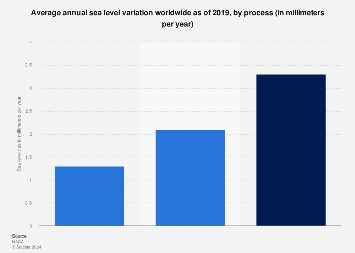
Thermal expansion and the melting of ice are the protagonists in the narrative of rising sea levels. As the planet warms, seawater absorbs heat, causing it to expand. This thermal expansion accounts for a significant portion of the observed rise in sea levels. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports that approximately half of the sea-level rise since the 1970s can be attributed to thermal expansion. The warmer the water, the more it expands, leading to a gradual yet relentless increase in ocean levels.
Additionally, terrestrial ice reservoirs—namely glaciers and the polar ice sheets of Greenland and Antarctica—are undergoing rapid melting due to elevated temperatures. The Greenland ice sheet is losing billions of tons of ice each year, contributing to rising sea levels. Similarly, Antarctica, with its massive ice formations, is experiencing accelerated ice loss. Recent studies show that the melting of these ice sheets is occurring at a pace faster than previously anticipated, primarily driven by warm ocean currents that undercut ice margins.
It is crucial to recognize that these processes are interconnected. As glaciers melt, freshwater is released into the oceans, contributing further to sea-level rise. Moreover, the feedback loops created by warming oceans and melting ice create a compounding effect that exacerbates the problem.
The Geopolitical and Societal Implications
The consequences of rising sea levels are far-reaching, presenting enormous challenges to society. Coastal communities around the world are at the forefront of this crisis. Nations with extensive coastlines—such as Bangladesh, the Netherlands, and various Pacific island nations—are facing existential threats due to encroaching tides and increased flooding. More than a billion people live in low-lying coastal areas, making them particularly vulnerable to the ramifications of rising waters.
As seawater intrudes on freshwater supplies, critical resources are compromised, leading to water scarcity and compromised ecosystems. The displacement of populations due to flooding and erosion not only creates humanitarian crises but also engenders geopolitical tensions. Migratory pressures may increase, leading to conflicts over dwindling resources, as communities are forced to abandon their homes in search of safer land.
Infrastructure also faces dire challenges. Transport networks, sewer systems, and homes are increasingly at risk from storm surges and regular flooding. The economic costs associated with damage to these infrastructures could reach staggering sums, necessitating investments in resilient engineering and adaptation measures. Governments are thus under pressure to revise zoning laws and invest in protective structures, such as sea walls, to safeguard vulnerable populations.
Future Scenarios: Navigating Uncertainty
Looking ahead, the trajectory of sea-level rise remains uncertain, contingent upon efforts to curtail greenhouse gas emissions and implement sustainable practices. Scientific models provide various scenarios, projecting potential increases ranging from one to several meters by the end of the century. These predictions are influenced by factors such as global temperature rises and ice sheet dynamics. Enhancing our understanding of these variables is crucial for accurate projections.
The scenarios are alarming; even a modest rise of just one meter could have profound impacts on global cities situated along coastlines, from New York to Mumbai. Increased flooding, loss of land, and economic disruption may become commonplace if preventive measures are not enacted. Climate change adaptation strategies involving managed retreat and reshaping urban landscapes will play essential roles in safeguarding humanity against the inevitable repercussions of warming.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
Understanding how global warming affects rising sea levels invites urgency and action. Policymakers, scientists, and the public must collaborate to foster an informed dialogue about climate change. There exists a pressing need to prioritize climate resilience, invest in renewable energy sources, and advocate for policies that mitigate emissions. It is imperative that as stewards of our planet, we not only acknowledge the threats posed by rising sea levels but also act decisively to address them.
The connection between global warming and ocean expansion is clear, and the implications are increasingly dire. It is a collective responsibility to educate ourselves about these dynamics, support sustainable practices, and contribute to global efforts aimed at combating climate change. Only then can we hope to secure a sustainable future for ourselves and generations to come.