Global warming, a sinister phenomenon gradually unfurling over decades, poses a profound challenge to humanity. As temperatures rise, a myriad of questions arise, compelling us to explore the consequences of this climatic upheaval. How does global warming impact humans on Earth? Beyond the obvious alterations to weather patterns, the ramifications are extensive, affecting health, ecosystems, and socio-economic structures. This investigation reveals the multifaceted nature of global warming’s impact, urging humanity to reflect on its role as stewards of the planet.
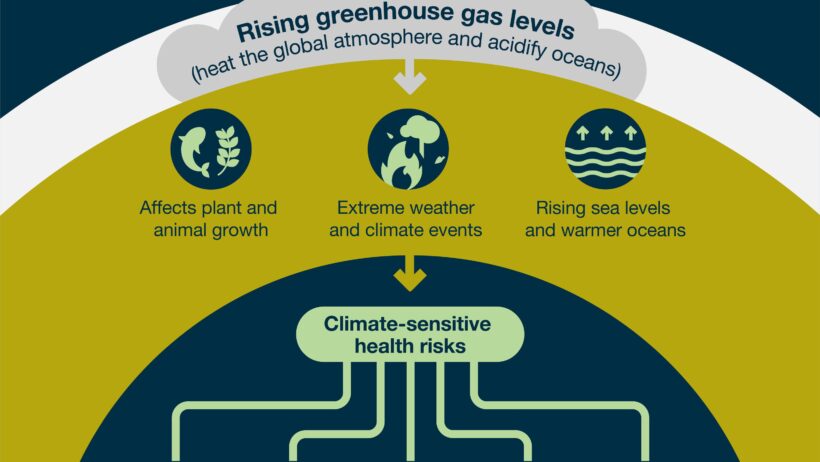
The most immediate concerns regarding global warming relate to the alteration of weather patterns. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves, are becoming more frequent and intense. This unpredictability disrupts agricultural practices, leading to food insecurity. Imagine a scenario where entire crops fail due to unprecedented heat or unexpected floods, leading to potential famines in vulnerable regions. The implications extend far beyond mere inconvenience; they threaten the very fabric of societal stability.
As temperatures rise, it is not just the environment that suffers; human health is intrinsically linked to climatic conditions. Heat-related illnesses, such as heat exhaustion and heatstroke, become more prevalent during scorching summers. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions, are at especially high risk. The exacerbation of respiratory diseases, particularly among populations exposed to increased pollution, is another pressing health concern. As air quality deteriorates, the prevalence of asthma and other chronic respiratory issues escalates, affecting millions worldwide.
Furthermore, the emergence of vector-borne diseases is a ticking time bomb in the era of global warming. Warmer temperatures expand the habitats of mosquitoes and ticks, which transmit diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Lyme disease. The geographical distribution of these vectors is shifting, meaning regions previously untouched by such illnesses may now face outbreaks, challenging public health systems to respond effectively. With global connectivity, even a localized health crisis can quickly morph into a global pandemic, as increasingly mobile populations traverse borders.
But let’s shift our focus for a moment—what if, instead of viewing these changes solely as threats, we reimagined them as opportunities for innovation? The challenges posed by global warming could catalyze advancements in healthcare, technology, and community resilience. For instance, the surge in telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated how ingenuity could lead to improved access to healthcare. As climate change exacerbates health crises, there may be a burgeoning demand for innovative healthcare solutions, combining technology with environmental consciousness.
Addressing issues of mental health is equally crucial in the discourse surrounding global warming. The phenomenon not only entails physical health risks but also induces psychological stress. Anxiety and depression related to climate change, commonly termed eco-anxiety, are emerging as significant public health challenges. The sense of inevitability regarding the planet’s trajectory results in distress, particularly among younger generations who often grapple with a perceived loss of future opportunities—an unsettling reality that should stimulate discourse and action around mental health services.
The socio-economic ramifications of global warming present a formidable challenge as well. Climate change disproportionately affects marginalized communities, exacerbating existing inequalities. Regions with limited resources often rely on climate-sensitive sectors, such as agriculture or fisheries, for their livelihoods. As climate conditions worsen, the wealthy may be able to adapt—investing in climate-resilient infrastructure or technologies—while the disadvantaged are left vulnerable, often with catastrophic consequences. This divide not only persists within nations but also between them, igniting tensions over resources like water and arable land.
Environmental policy becomes an essential tool in navigating these turbulent waters. Globally coordinated efforts to mitigate climate change and adapt to its impacts are paramount. The Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global temperature rise, exemplifies international acknowledgment of the urgency surrounding climate issues. Nevertheless, the commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions necessitates robust domestic policies, equitable resource distribution, and investment in renewable energy sources. Transitioning to sustainable practices demands a collective effort from individuals, corporations, and governments.
Investing in renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, not only curtails our carbon footprint but also generates jobs. This dual benefit presents an enticing opportunity—prompting a fundamental shift in the labor market as a green economy emerges. Pioneering technologies in carbon capture, battery storage, and sustainable agriculture present avenues for innovation, stimulating economic growth while combating climate change. Adapting educational curricula to include environmental science and sustainability initiatives can equip future generations with the tools required to tackle these pressing issues.
In conclusion, the outline of global warming’s impact on humanity is intricate and multifaceted. From health challenges and socio-economic disparities to increased mental health concerns and technological opportunities, the spectrum of consequences is vast. The interplay between these factors necessitates a holistic approach to address the crisis effectively. Collaboration across various sectors, international cooperation, and community engagement are vital in combating the pressing challenge posed by global warming. As we grapple with the reality of these changes, we must also embrace the creative solutions that arise from adversity, fostering a resilient society prepared for both current challenges and future uncertainties.