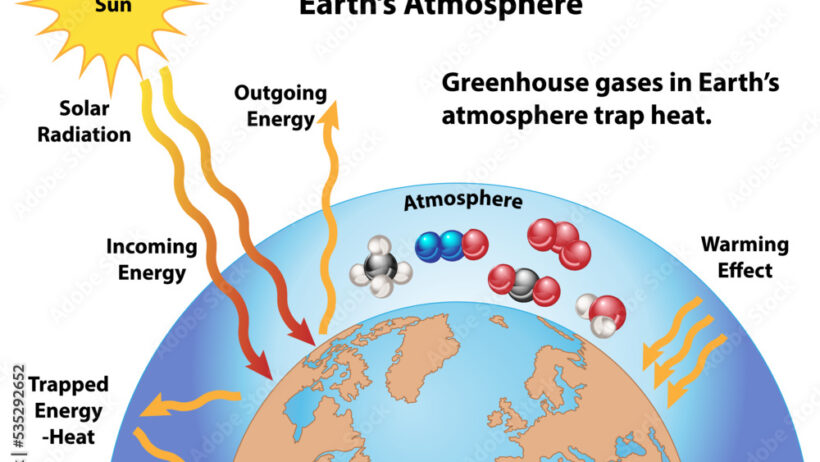
The greenhouse effect, an intricate ballet of gases within our atmosphere, could easily be likened to the embrace of a warm blanket on a chilly night. Pleasant at first, yet it can easily become stifling if too tight. Among the various players in this phenomenon, nitrous oxide (N2O) occupies an often overshadowed but nonetheless critical role. This colorless, non-flammable gas, though small in quantity, exuberantly influences our climate system, and its contribution to global warming deserves our attention and deep understanding.
To grasp how nitrous oxide contributes to the greenhouse effect, one must first navigate the labyrinth of its origins, properties, and the unique way it interacts with the atmosphere.
Consideration of Sources: Unveiling the Origins of Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous oxide is a compound born from both natural and anthropogenic sources. In the grand tapestry of the Earth’s nitrogen cycle, it emerges as a byproduct of soil microbial processes, particularly during nitrification and denitrification. Forests, oceans, and wetlands unknowingly produce this potent greenhouse gas, contributing roughly 30% of the total global emissions.
However, human activities exacerbate its prevalence. Fertilizers, particularly those rich in nitrogen, when applied to crops, unleash significant quantities of nitrous oxide into the atmosphere. Reports suggest that agricultural practices, including the application of animal waste and the tillage of soil, account for nearly 70% of the total anthropogenic emissions. These activities, while aimed at enhancing crop yields, inadvertently tighten the sheets of the greenhouse blanket wrapped around our planet.
The Unique Properties of Nitrous Oxide: More Than Meets the Eye
One might ponder why nitrous oxide should command our attention when carbon dioxide (CO2) is often the star of the climate change narrative. The intrigue lies in nitrous oxide’s radiative potency. Although it exists in much smaller concentrations compared to CO2, its global warming potential is staggering—approximately 298 times greater than CO2 over a century. This remarkable disparity underscores the significance of targeting nitrous oxide emissions in our climate strategies.
Moreover, nitrous oxide exhibits a long atmospheric lifespan, remaining suspended in the atmosphere for about 114 years. This longevity means that even slight upticks in concentration due to human activities can have lingering effects on global temperatures for generations. Such nuances paint a vivid picture of the intricate dynamics at play in Earth’s climate system. Like an elusive shadow that amplifies the chill of a room, nitrous oxide quietly contributes to the overarching atmosphere of warming.
The Mechanism of Warming: The Dance of Molecules
But how exactly does nitrous oxide exacerbate global warming? The answer lies in its interaction with sunlight and the overall energy balance of our planet. When sunlight enters the Earth’s atmosphere, it encounters a variety of gases, including nitrogen oxides, which absorb infrared radiation. In a manner akin to trapping heat in a greenhouse, nitrous oxide captures this energy, preventing it from escaping back into space.
This process is emblematic of the greenhouse effect and sparks a chain reaction—an elevation in global temperatures, creating a feedback loop. Warmer temperatures can lead to increased microbial activity in soils, generating even more nitrous oxide. Like a self-reinforcing cycle, the repercussions of warming fuel further warming, raising critical questions about the sustainability of our agricultural practices.
Consequences of Ignoring Nitrous Oxide: The Urgency of Action
Failing to address nitrous oxide emissions is akin to ignoring a slow leak in a boat—over time, the consequences can be catastrophic. The agricultural sector stands as a focal point where transformative action can yield substantial benefits. Implementing practices such as precision farming, crop rotation, and the adoption of cover crops can significantly reduce nitrous oxide emissions while simultaneously improving soil health and productivity. These actions create a win-win situation where the planet and its inhabitants emerge as beneficiaries.
Additionally, the importance of policy frameworks cannot be overstated. Comprehensive regulations and incentives are vital for steering agricultural practices toward lower emissions. The integration of sustainable land management techniques can prove to be the lifeline in mitigating the threat posed by increased greenhouse gas emissions.
Looking Ahead: A Call for Collective Action
As we gaze toward the horizon, the plight of our planet acts as a clarion call for collective action. Mitigating the impacts of nitrous oxide should not merely be an afterthought; rather, it warrants a central position in global climate policies. Collaboration among scientists, governments, and environmentalists can pave the way toward innovative solutions that embrace both sustainability and biodiversity.
Addressing the formidable challenge of climate change requires embracing the entire spectrum of greenhouse gases, with nitrous oxide being a pivotal player in this ongoing narrative. The stakes are high, and the time for proactive measures is now. By illuminating the hidden influences of nitrous oxide, we can embark on a journey toward a more sustainable and equitable world. Can we withstand the heat of inaction or will we act swiftly to ensure a cooler, sustainable future?
In conclusion, the role of nitrous oxide in the greenhouse effect is a vivid reminder of the complexities enveloping climate change. Understanding this less heralded gas equips us to engage effectively in meaningful dialogue and advocacy for the Earth. Every effort to curtail emissions, be it through innovative agricultural practices or robust policymaking, signifies a valuable step toward preserving our planet’s delicate balance for generations to come.