The intricate web of our ecosystem is profoundly affected by human activities, particularly through the production and disposal of waste. One of the most effective methods to mitigate our impact on climate change is recycling. This process not only reduces the volume of waste sent to landfills but also contributes significantly to decreasing greenhouse gas emissions. Let us delve into the multifaceted ways in which recycling influences the environment and serves as a powerful tool in combating climate change.
Understanding the Environmental Footprint of Waste
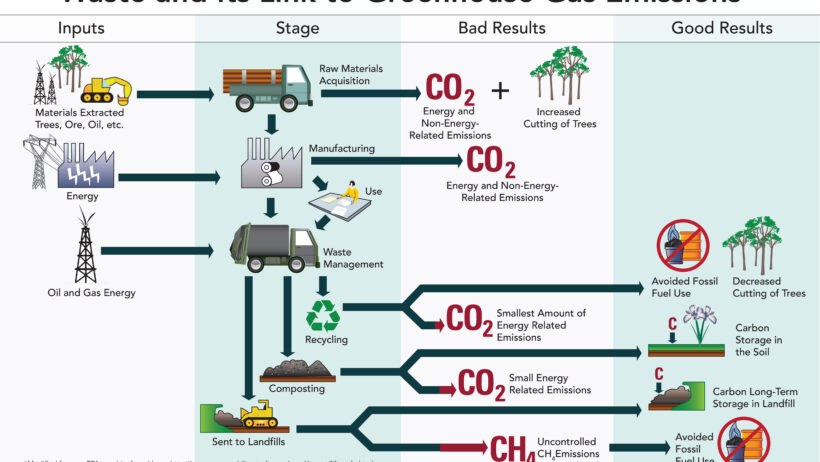
The modern consumer society produces an astonishing amount of waste. Each year, millions of tons of materials, including plastics, metals, and paper products, are discarded, contributing to environmental degradation. When waste is deposited in landfills, it undergoes anaerobic decomposition, which emits methane—a potent greenhouse gas that is significantly more harmful than carbon dioxide in the short term. Hence, recycling emerges as a salient solution to curtail this phenomenon.
Recycling diverts waste from landfills, thereby reducing overall methane emissions. More importantly, it conserves natural resources and energy. The extraction, processing, and transportation of virgin materials require substantial energy inputs and often result in harmful emissions. Conversely, recycling materials such as aluminum or glass consumes considerably less energy and translates into lower carbon emissions. In this way, recycling acts as a critical bridge connecting waste management and climate change mitigation.
Transforming Production Processes: The Circular Economy
Recycling not only conserves resources but also encourages the development of a circular economy—a system that minimizes waste and maximizes resource usage. In a circular economy, products are designed with their end-of-life in mind, facilitating ease of recycling and reuse. This shift in production paradigms promotes sustainability, reducing the reliance on new raw materials and lowering the overall carbon footprint of industries.
For example, consider the production of aluminum. The recycling of aluminum saves up to 95% of the energy required to produce it from raw bauxite ore. This energy conservation translates into a dramatic reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, the process of recycling aluminum also diminishes the need for mining activities that disrupt ecosystems and contribute to biodiversity loss. The circular economy thus champions a regenerative approach, where recycling plays a pivotal role in reducing both production impacts and climate change effects.
The Role of Renewable Resources
Another significant aspect of recycling’s impact on climate change lies in the conservation of renewable resources. By recycling, we conserve trees, water, and minerals, which are often overexploited through traditional manufacturing processes. For instance, recycling paper reduces the need for logging, which results in fewer carbon sinks being destroyed. Trees play a crucial role in sequestering carbon dioxide, and their removal exacerbates climate change. So, by utilizing recycled paper, we not only preserve forests but also help maintain the balance of our planet’s carbon cycle.
The influence of recycling on climate change extends beyond the tangible benefits; it also fosters a culture of environmental stewardship. The act of recycling empowers individuals and communities to engage actively in sustainable practices, thus creating a ripple effect. When people become aware of the emissions mitigated through recycling, they are more likely to adopt other environmentally friendly habits, such as reducing waste or choosing sustainable products.
Potential Obstacles: Misconceptions and Challenges
Despite the compelling evidence supporting recycling’s benefits, misconceptions abound. Many individuals mistakenly believe that recycling is a finish line rather than a means to an end. While recycling is undeniably important, it should not replace other critical actions such as reducing consumption and reusing items. A holistic approach to environmental responsibility requires a multifaceted strategy that prioritizes waste reduction at its source.
The efficacy of recycling programs can also be hindered by inadequate infrastructure or lack of public awareness. Communities may lack the necessary facilities to recycle efficiently, leading to contamination of recyclable materials and diminishing their effectiveness. Investing in comprehensive recycling programs, education about proper recycling practices, and community engagement can significantly enhance recycling rates and ultimately strengthen local economies.
Conclusion: A Collective Effort Towards Sustainability
As we grapple with the realities of climate change, the importance of recycling cannot be overstated. By understanding its profound effects on emissions reduction, resource conservation, and fostering a circular economy, we can appreciate recycling not merely as an individual action, but as a communal responsibility. Every bottle recycled, every paper saved, and every metal reused contributes to our collective fight against climate change. Embracing recycling as a crucial component of our societal framework fosters an integrated approach to sustainability, one that engenders hope for a healthier planet.
In conclusion, recycling is an essential mechanism through which individuals, communities, and industries can combat climate change. It connects the dots between waste reduction, resource conservation, and environmental protection, thereby reinforcing the urgent need for sustainable practices in an increasingly resource-constrained world. The path towards a more sustainable future is paved with our commitment to recycle and promote a culture of resilience and stewardship for the Earth.