Have you ever gazed up at the sky and wondered how something as invisible as air could be causing such dramatic changes in our planet’s climate? The greenhouse effect, while a natural phenomenon, transforms into a formidable adversary when human activities amplify its intensity, leading to global warming. Let’s dive into this complex yet essential topic.
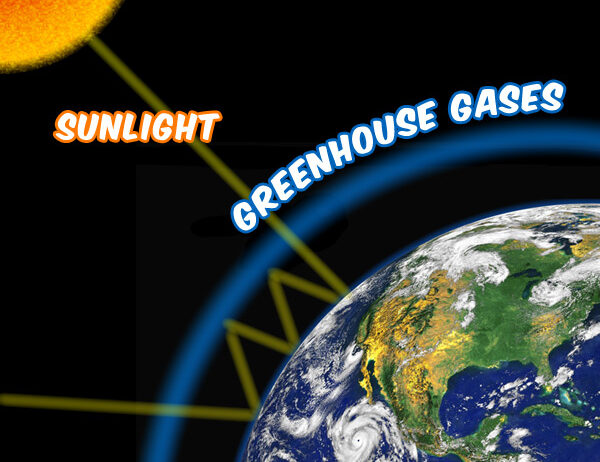
The greenhouse effect is a scientific occurrence where specific gases in the Earth’s atmosphere trap heat. But how does this process work? In simple terms, solar energy from the sun travels through the atmosphere and warms the surface of the Earth. This thermal energy is then radiated back toward space. However, certain gases—commonly known as greenhouse gases—absorb some of this outgoing heat, preventing it from escaping into space. These gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor.
The primary player in this intricate dance is carbon dioxide. Its levels have surged alarmingly due to various anthropogenic activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. Each time fossil fuels are combusted, CO2 is released into the atmosphere. This is where the challenge arises: as CO2 levels rise, so does the planet’s ability to retain heat.
Now, let’s pose a question: what would happen if we could see these greenhouse gases? Imagine a thick, warm blanket wrapped around the Earth, providing comfort but also suffocating all the life beneath it. As it becomes increasingly clear that CO2 does indeed function as this type of atmospheric blanket, we must ask ourselves how we can minimize this hazardous insulation effect.
The impact of the greenhouse effect extends beyond simply warming our planet; it initiates a cascade of ecological consequences. One of the most alarming effects of global warming is the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers. This melting not only contributes to rising sea levels but also disrupts habitats for various species, leading to biodiversity loss. Indeed, the very existence of certain ecosystems hangs in the balance.
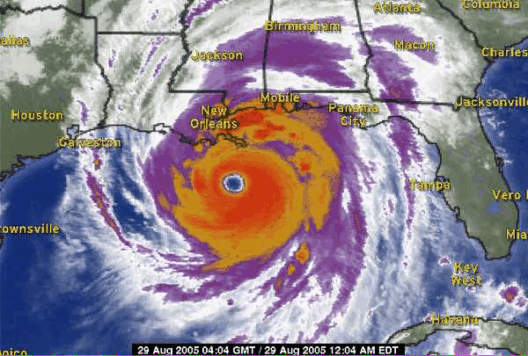
Moreover, global warming intensifies extreme weather events. Hurricanes, droughts, floods, and wildfires become more frequent and severe. These events result in not only destruction of infrastructure but also long-lasting economic ramifications. Communities, particularly those already vulnerable, find themselves grappling with the aftermath. The interplay of heat and moisture in the atmosphere alters precipitation patterns, posing a formidable challenge for agriculture, water supply, and overall human health.
As we dissect the dynamics behind the greenhouse effect, it’s also crucial to acknowledge the role of methane. While it exists in smaller quantities compared to CO2, methane is significantly more potent at trapping heat—approximately 25 times more effective over a century. Produced during the decomposition of organic matter in landfills, as well as from livestock digestion, addressing methane emissions is pivotal in our fight against global warming. Mitigating these emissions is not merely an afterthought; it is imperative for a balanced ecological future.
What about nitrous oxide? This gas, often released through agricultural practices and the burning of fossil fuels, contributes to global warming as well. While it may not dominate the narrative like CO2 or methane, its potency in terms of heat retention is noteworthy. Thus, sustainable agricultural practices become essential not just for food security but also for reducing nitrous oxide contributions to the greenhouse effect.
Now that we understand the intricacies of greenhouse gases, the next question on our minds might be: what can we do to mitigate these effects? The transition to renewable energy sources is paramount. Solar, wind, and hydropower offer sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels, drastically reducing carbon emissions. Embracing energy efficiency in our homes and businesses, optimizing the use of public transportation, and advocating for policies that prioritize sustainability can also make a significant difference.
Moreover, reforestation initiatives provide a dual benefit: trees absorb CO2, acting as natural carbon sinks, while also restoring habitats for wildlife. Similarly, shifting our diets to incorporate more plant-based foods can significantly decrease the demand for methane-producing cattle farming. Each of these steps, while they may appear small on the surface, holds the potential for monumental impact when adopted broadly.
Education plays a vital role in combating climate change. Understanding the science behind the greenhouse effect empowers individuals and communities to make informed choices. Children, too, must learn the importance of environmental stewardship. Future generations will bear the consequences of our actions, and they should be equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to effect meaningful change.
As we contemplate our relationship with our planet, we must recognize that the greenhouse effect is not an isolated phenomenon. It encompasses a broad spectrum of interactions, each interconnected and influential. By embracing sustainable practices, advocating for policy reform, and fostering an environmental ethos, we confront the global warming challenge head-on. So, what steps will you take today to contribute to a livable future for our planet?