The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that plays a critical role in regulating Earth’s temperature. However, human activities have intensified this effect, leading to significant environmental consequences. Understanding the mechanics of the greenhouse effect is essential for grasping the current climate crisis. This article delves into how the greenhouse effect occurs and its implications for our planet.
The Earth operates within a delicate balance of energy, receiving warmth from the Sun and releasing heat back into space. The greenhouse effect is an integral part of this energy exchange. To fully comprehend this intricate system, it’s crucial to explore the components involved in the greenhouse effect, the processes that facilitate heat retention, and the broader implications of increased greenhouse gas concentrations.
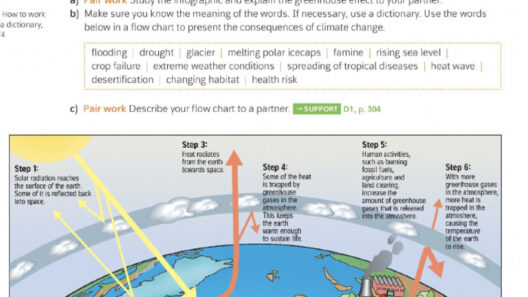
At its core, the greenhouse effect hinges on the interaction between solar radiation and Earth’s atmosphere. When sunlight reaches our planet, it is either absorbed by the Earth’s surface or reflected back into space. Approximately 30% of incoming solar energy is reflected, mainly by clouds and ice, while 70% is absorbed, leading to the warming of land, water, and vegetation. This absorbed energy is vital for sustaining life, as it drives weather patterns, ocean currents, and ecosystems.
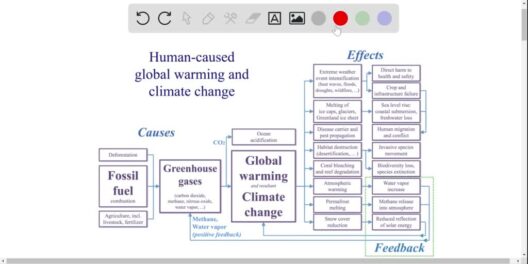
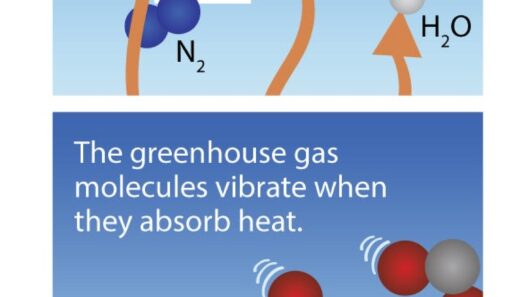
The next phase of the greenhouse effect involves the re-radiation of this energy. As the Earth warms, it emits energy back into the atmosphere in the form of infrared radiation. However, not all of this heat escapes seamlessly. Greenhouse gases, which include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), absorb and re-radiate some of this infrared energy back towards the Earth. This process is akin to a thermal blanket enveloping the planet, thereby helping to maintain a stable temperature conducive to life.
An integral aspect of the greenhouse effect is the composition of the atmosphere. Natural levels of greenhouse gases are crucial for maintaining a habitable climate. However, anthropogenic activities, such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes, have drastically increased the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere. Historical data shows that CO2 levels have surged over the past century, primarily due to human intervention.
As greenhouse gas concentrations rise, the heat-trapping capability of the atmosphere also escalates. This intensification results in an altered climate system, leading to phenomena such as global warming, extreme weather events, and ocean acidification. These changes not only threaten biodiversity but also pose significant challenges to food security, water resources, and human health.
With an increased understanding of the greenhouse effect, it’s essential to shed light on the ramifications of climate change. The rise in global temperatures has already manifested in various forms. Glacial retreat, sea-level rise, and shifts in agricultural zones exemplify how climate change disrupts natural ecosystems and human societies. Certain regions are becoming more susceptible to droughts, while others experience deluges, thereby jeopardizing food production and freshwater supplies.
Individuals and communities can take proactive measures to mitigate these effects by reducing their carbon footprint. Key strategies include adopting renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, practicing sustainable agriculture, and promoting reforestation efforts. However, addressing the effects of the greenhouse effect fundamentally necessitates collective action from governments, industries, and individuals alike.
Concurrently, international initiatives such as the Paris Agreement aim to unify nations in the global fight against climate change. By striving to limit temperature rises to below 2 degrees Celsius, countries pledge to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition to sustainable practices. Such commitments underscore the urgency of collective accountability in combating the greenhouse effect.
Moreover, raising public awareness about the greenhouse effect and its consequences is vital. Educational programs can empower individuals to make informed choices about their energy consumption, transportation options, and general lifestyle. With understanding comes responsibility, and by fostering a culture of environmental stewardship, individuals can contribute to the larger goal of climate stabilization.
In summary, the greenhouse effect is a complex interplay of natural processes amplified by human activity. As greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise, the consequences for our climate and ecosystems become increasingly severe. It is paramount that we understand this phenomenon and take tangible steps towards a more sustainable future. The call to action is clear: by mitigating our impact on the environment and advocating for responsible policies, we can work collaboratively to combat climate change and safeguard the planet for future generations.