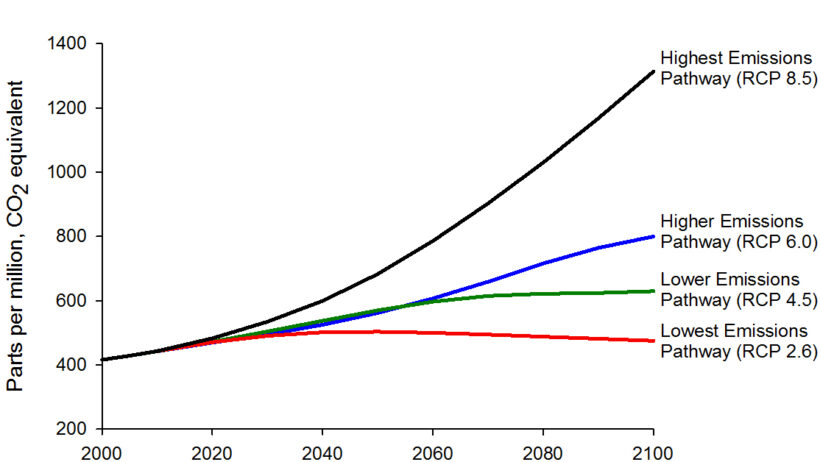
Global warming is no longer a distant concern; it is a pressing reality that poses profound implications for both our economy and environment. As greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise, the average global temperature increases, leading to a cascade of consequences that will shape our future. Understanding these ramifications is crucial for informed decision-making and effective policy formulation. This analysis delves into how global warming could influence various facets of our economy and environment moving forward.
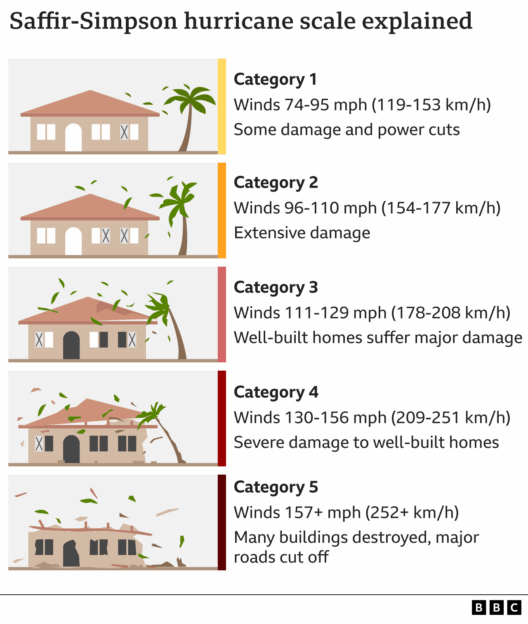
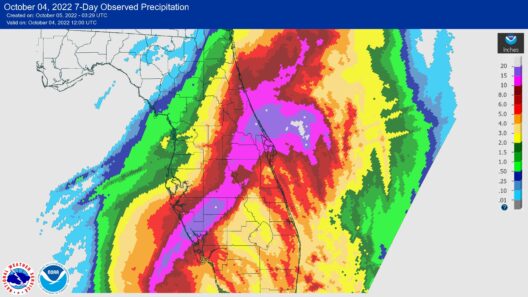
Firstly, one of the most immediate consequences of global warming is the alteration of weather patterns. Increased temperatures result in more frequent and severe weather events, including hurricanes, droughts, and floods. These extreme weather phenomena can devastate infrastructure, disrupt supply chains, and lead to significant economic losses. In agricultural sectors, unpredictable weather can wreak havoc on crop yields, jeopardizing food security. The agricultural losses could lead to fluctuations in food prices, ultimately affecting global markets and exacerbating economic inequality.
Moreover, the increased frequency of extreme weather events may compel governments and businesses to allocate substantial resources for disaster preparedness and recovery. This diversion of funds could stifle economic growth in other areas, such as education and healthcare. As communities grapple with the aftermath of natural disasters, long-term investment in infrastructure becomes paramount. However, the resources required for such endeavors may become strained, revealing the economic double-edged sword of climate change.
In addition to affecting weather patterns, global warming will likely exacerbate water scarcity issues. The melting of glaciers and polar ice caps threatens freshwater supplies for many regions globally. Areas dependent on glacial meltwater, such as parts of India and Central Asia, face severe challenges as these vital water sources dwindle. With water scarcity will come an increase in conflicts and competition over limited resources, straining geopolitical relations and fostering instability.
Conversely, some regions may benefit economically from climate change, albeit in a limited manner. For example, the warming climate could open new shipping routes in the Arctic, facilitating trade and commerce. Nations like Russia are already exploring opportunities presented by the melting ice. However, such advantages are overshadowed by the broader implications of global warming, reminding us that short-term economic gains do not justify long-term environmental degradation.
Shifting to the power sector, global warming is propelling the transition from traditional fossil fuels toward renewable energy sources. This transition is essential, not only to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions but also to create new economic opportunities. The renewable sector is burgeoning, with investments in solar, wind, and hydropower paving the way for job creation. However, the economic implications are multifaceted. Workforce transitions are necessary, as workers from fossil fuel industries may face job loss and retraining needs. While renewable energy presents growth potential, equitable solutions must be implemented to support affected communities.
A critical aspect of the economic impacts of global warming lies in its effect on health. Higher temperatures correlate with increased incidences of heat-related illnesses, respiratory issues from poor air quality, and the proliferation of vector-borne diseases. As healthcare costs mount in response to these health challenges, economic productivity may decline. A less healthy workforce translates to higher absenteeism rates and diminished productivity. This, in turn, can create a feedback loop of economic vulnerability, particularly in low-income communities that may lack adequate healthcare access.
Furthermore, rising sea levels, a direct consequence of global warming, pose an existential threat to coastal economies. Cities like Miami, New Orleans, and New York are grappling with flooding risks that jeopardize infrastructure and public safety. The property market faces potential collapse as homeowners and investors begin to recognize the risks associated with flood-prone areas. Insurers are also becoming increasingly wary, adjusting their policies and raising premiums, which could create an economic ripple effect across various sectors.
While some might view global warming merely through an environmental lens, it is essential to recognize its interconnectedness with economic stability. Sustainable practices and climate-resilient infrastructure have become paramount to mitigate the impending chaos wrought by climate change. Investment in green technology and pollution reduction can create a robust economic framework that fosters innovation while preserving our planet.
In conclusion, global warming will invariably shape both our economy and environment, leading to significant transformations across numerous sectors. The increasing frequency of extreme weather events, shifts in agricultural productivity, water scarcity issues, and health implications intertwine in complex ways that require comprehensive strategic planning. It is imperative for businesses, governments, and communities to adopt climate-conscious approaches and prioritize sustainability to foster resilience. The future may be uncertain, but proactive measures can pave the way for an adaptive economy that strives for both prosperity and environmental stewardship.