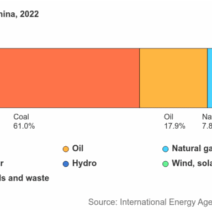
Space heating is an imperative aspect of maintaining thermal comfort in residential and commercial settings. However, it often accounts for a significant portion of energy consumption, particularly during the colder months. Conserving energy used for space heating not only mitigates costs but also plays a pivotal role in combating climate change. This discourse delves into effective strategies for warming up efficiently while minimizing energy expenditure.
To commence, it is essential to understand the various methods of space heating. Common modalities include central heating systems, such as furnaces and boilers, as well as localized solutions like space heaters. Each heating system has its own energy conservation tactics, which can be improved through a variety of techniques.
One of the primary methods of conserving energy involves the retrofitting and optimizing of existing heating systems. Ensuring that these systems operate at peak efficiency is crucial for reducing waste. Regular maintenance, such as changing filters, cleaning air ducts, and checking the thermostat functions, can substantially enhance performance. Furthermore, installing programmable thermostats allows users to regulate temperatures based on occupancy, decreasing energy use when spaces are unoccupied.
Moreover, insulating a building is of utmost importance in defending against heat loss. Insulation acts as a barrier to heat transfer, meaning that less energy is needed to maintain comfortable temperatures. Various insulation materials, including fibreglass, cellulose, and spray foam, can be applied to attics, walls, and floors. Attention should also be paid to sealing air leaks around windows and doors; caulking and weatherstripping can drastically diminish drafts and elevate energy conservation.
In addition to improving insulation, utilizing passive solar heating is an innovative approach to enhance energy efficiency in heating systems. This technique harnesses sunlight through south-facing windows, allowing for significant natural warmth during daylight. Strategic placement of overhangs or eaves can maximize solar gain in the winter while providing shade in the summer. To further leverage this method, consider incorporating thermal mass materials, such as concrete or brick, which absorb desiring heat and release it slowly, sustaining warmth even after the sun sets.
Transitioning to high-efficiency heating systems is another integral stride toward energy conservation. Modern advancements in technology have presented numerous energy-efficient options, like condensing boilers and heat pumps. These systems are designed to extract maximum energy from fuel sources, delivering more heat while consuming less energy. For instance, air-source heat pumps operate by transferring heat from outside sources, rendering them remarkably efficient in milder climates.
Moreover, the utilization of renewable energy sources can significantly curtail reliance on fossil fuels for heating purposes. Solar thermal systems, for example, can be integrated into residential heating systems to provide supplementary warmth. By collecting heat via solar panels, households can harness a renewable energy source that drastically reduces operational costs. Wind energy too, although less common for direct space heating, can power electric heating solutions, minimizing carbon footprints associated with conventional heating methods.
Besides mechanical and physical systems, behavioral modification is crucial for optimizing energy conservation. Educating occupants on energy-saving practices fosters a collective responsibility toward reduced consumption. Simple actions—such as wearing warm clothing indoors, utilizing blankets, and keeping doors closed—can have a profound impact on overall heating efficiency. Establishing communal goals around energy conservation can also instil pride and motivate community members to engage in sustainable heating practices.
In the realm of technological integration, smart home automation presents advantages in energy management. Smart thermostats learn user patterns, adjusting temperatures automatically to optimize comfort while minimizing waste. Integration with mobile applications allows for remote temperature adjustments, ensuring that heating systems are not operating in an inefficient manner while residents are away. Home automation systems can further connect various appliances and lighting to facilitate energy recovery during peak heating demands, demonstrating the potential for comprehensive sustainability through technology.
Addressing the most frequently overlooked aspect, the importance of policy and regulations cannot be understated. Incentives for energy-efficient renovations, tax credits for adopting renewable energy systems, and energies’ involvement can stimulate widespread changes in energy consumption behaviors. Moreover, building codes should reflect an emphasis on thermal performance, enforcing standards to lead the construction industry towards sustainable building practices.
Nevertheless, adopting energy-conserving practices requires an investment of time, effort, and sometimes financial resources. Setting realistic goals and seeking professional advice can assist in transitioning towards a more efficient heating strategy seamlessly. Encouragingly, the long-term savings on energy bills and the positive environmental impact make these investments worthwhile.
In summation, conserving energy used for space heating necessitates a multidimensional strategy encompassing system optimization, insulation enhancements, technological advancements, and behavioral modifications. While individual actions may seem small, when aggregated, they yield significant benefits for our environment and economy alike. As global temperatures continue to rise, the urgency for efficient heating solutions becomes increasingly evident. Fostering an energy-conscious culture can pave the way for a more sustainable future, reaffirming that efficient warming is not merely a personal choice but a collective responsibility.