As we gaze out over the endless expanse of the ocean, one might wonder: is the sea level rising? If so, what could possibly be driving this phenomenon? The reality is, the oceans are indeed swelling, influenced by a myriad of factors, and this escalation prompts both curiosity and concern. Understanding the intricacies of sea level rise is crucial, as it holds significant implications for coastal communities, ecosystems, and the global climate.
What exactly causes the seas to rise? Let’s dive into the underlying mechanisms that contribute to this alarming trend.
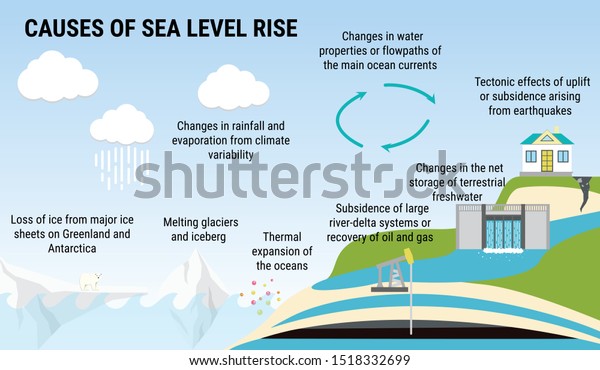
The two principal factors behind rising sea levels are thermal expansion and the melting of ice. Each plays a distinct yet interrelated role in contributing to the increase in ocean levels.
Warm water expands. It is a principle of physics that cannot be overlooked. As global temperatures climb due to climate change, the oceans absorb most of this excess heat, leading to thermal expansion. When water warms, its molecules move apart, causing the water to occupy more space. This phenomenon contributes to a substantial portion of observed sea level rise, as the Earth’s oceans have already observed an increase in temperature averaging about 1.5 degrees Celsius since the late 19th century.
However, the effects of global warming do not stop there. The melting of polar ice caps and glaciers adds yet another layer to this complex issue. Regions such as Greenland and Antarctica are experiencing accelerated ice loss. For example, researchers have indicated that Greenland’s ice sheet is undergoing a dramatic decline, losing approximately 280 billion tons of ice annually. The consequences of these melting glaciers are profound; as these colossal masses of ice disintegrate into the oceans, they contribute billions of gallons of water to the sea, further exacerbating the rise in sea levels.
Climate change’s cold arithmetic doesn’t end with these two factors; land subsidence and groundwater extraction also play significant roles. Many urban areas situated along coastlines are sinking due to the natural settling of the ground or the extraction of groundwater for human use. This makes the impact of rising sea levels even more pronounced in those regions. While cities like New Orleans and Jakarta grapple with this dilemma, they serve as stark reminders of the potential future for many coastal areas.
Let’s zoom out and appreciate the broader effects of rising sea levels. The ramifications extend beyond the immediate threat of inundation; they touch upon ecosystems, weather patterns, and human settlement.
First and foremost, coastal ecosystems face unprecedented challenges. Mangroves, salt marshes, and coral reefs, which serve as buffers against storm surges and provide critical habitats for diverse marine life, are increasingly threatened. As sea levels rise, saline intrusion becomes a pressing concern, where saltwater infiltrates freshwater systems. Aquatic flora and fauna struggle to adapt, leading to shifts in biodiversity. For instance, coral reefs, already stressed by warming waters, are further compromised by rising sea levels, which can diminish their health and resilience.
The sociocultural impact should not be underestimated. Coastal communities, many of which are densely populated, will face displacement due to rising tides. A startling prediction suggests that by 2050, upwards of 150 million people could find themselves as climate refugees, forced to relocate inland. This movement could lead to social strife, economic burdens, and an increase in competition for resources. When we think about future generations, the challenge becomes stark: how do we ensure a livable world for them?
In addition to these dire predictions, the increase of extreme weather events serves as an additional complication. The rising seas can amplify storm surges during cyclones and hurricanes, resulting in catastrophic flooding. Cities along the U.S. Gulf Coast and Eastern Seaboard have already experienced heightened vulnerability to such occurrences. Furthermore, meteorologists have established a connection between sea level rise and the increased frequency of major storms. As oceans warm, they generate more powerful storms, creating a vicious cycle of destruction.
So, the pressing question arises: what can be done to combat these concerning trends? The answer lies in a multi-faceted approach that encompasses mitigation, adaptation, and education.
Mitigation is crucial in addressing the root causes of climate change. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions through renewable energy sources, sustainable practices, and efficient technology can significantly impact this crisis. Governments must commit to international agreements aimed at curbing emissions, and industries must adopt sustainable practices that prioritize the environment.
Adaptation strategies are equally vital. Coastal communities will need to develop infrastructure that can withstand rising waters, such as sea walls or elevated buildings. Restoration projects for coastal ecosystems may also bolster resilience against flooding. These efforts will not only help safeguard human settlements but also restore natural habitats that serve as crucial buffers against storms.
Education plays an essential role as well. Raising awareness about the seriousness of sea level rise fosters community involvement and encourages individuals to advocate for sustainable policies. Empowering the public with knowledge informs better choices on both personal and governmental levels.
As we ponder the question of rising sea levels and the collective future of our planet, the imperative becomes clear. It is essential to confront this challenge head-on, fostering awareness, conceptualizing adaptive solutions, and advocating for effective policies. In understanding the causes and effects of rising oceans, we not only grasp the gravity of the situation but also begin to explore the actions necessary to safeguard both our shores and our future.