The ubiquitous presence of wind energy in our daily lives is often overlooked. Yet, its applications permeate a wide array of sectors, from electricity generation to transportation. Understanding the practical uses of wind power can elucidate how this renewable resource contributes to a sustainable future while complementing our routines. This exploration provides insights into the multifaceted roles that wind energy plays in contemporary society.
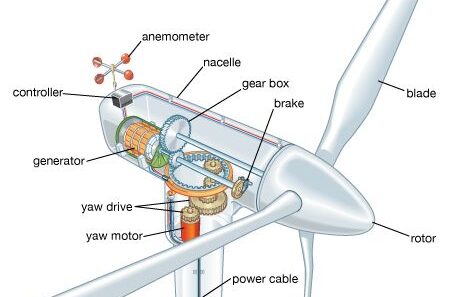
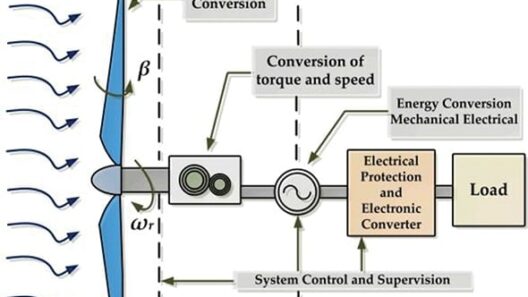
Wind energy is harnessed through wind turbines, which convert kinetic energy from wind into electrical energy. Throughout the globe, wind farms dot the landscape, capturing natural wind currents to deliver power to communities. This overview of wind energy applications illustrates its significance and interconnectedness with our daily lives.
Among the most prominent applications of wind energy is its contribution to grid electricity. As wind turbines proliferate in both onshore and offshore locations, they enable electric utility companies to incorporate clean energy into their power mix. The growing trend towards renewable sources has paved the way for wind-generated electricity to meet consumer demands without exacerbating greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, modern advancements in technology have enhanced the efficiency and efficacy of wind power. The development of larger turbines with extended rotor diameters has allowed for greater energy capture, making wind a more viable alternative to fossil fuels. This innovation is crucial as it aligns with the global imperative to transition towards renewable energy sources.
Wind energy’s contribution to electricity does not merely terminate at the generation stage. It plays a significant role in sustainable practices across various industries, including agriculture. Wind-powered systems, such as those for grain milling or water pumping, enable farmers to harness renewable energy for their operations. This reduces reliance on fossil fuels, subsequently promoting ecological integrity by minimizing carbon footprints and operational costs.
Another critical area where wind energy proves invaluable is in the transportation sector. As electric vehicles gain traction, many manufacturers are beginning to utilize wind-generated electricity to charge their batteries. Wind power not only reduces dependency on non-renewable energy sources but also supports advancements in the charging architecture necessary for widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
In urban landscapes, wind energy further finds its calling through the integration of microturbines. These smaller units can be installed on rooftops or as part of community energy systems, providing localized wind power that contributes to a building’s overall energy consumption. Such installations manifest an innovative approach to energy management, allowing residential and commercial properties to harness wind energy more directly.
Wind energy also extends its reach beyond conventional applications. Innovative designs, such as vertical-axis wind turbines, have emerged for urban and suburban environments. These structures often feature unique aesthetics while serving to generate power in areas where standard horizontal-axis turbines might be prohibitive due to space constraints or zoning issues.
Another fascinating aspect of wind energy’s role in daily life is its intersection with energy storage systems. In tandem with batteries and other storage solutions, wind energy can provide a steady power supply even when wind speeds fluctuate. By storing excess wind-generated electricity during peak production hours, communities can ensure that they have access to this renewable resource during periods of low wind, establishing reliability in the energy grid.
Moreover, the utilization of wind energy is not merely about the immediate benefits of reduced emissions. Long-term sustainability hinges upon the economic opportunities that arise from investing in wind energy. Expanding wind power projects creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, thus stimulating local economies. Cities and towns that embrace wind energy see not only an environmentally beneficial outcome, but they also experience a resurgence in economic activity.
The burgeoning awareness and acceptance of social responsibility have also spurred the integration of wind energy into corporate strategies. Many businesses are choosing to power their operations with renewable energy sources, including wind, to enhance their sustainability profiles. By tapping into wind energy, companies realize not just cost savings but also the capability to project their commitment to environmental stewardship, thereby elevating brand equity among increasingly eco-conscious consumers.
Wind energy’s versatility is an essential hallmark of its integration into our daily lives. From large-scale projects that feed energy into the national grid to small turbines that power individual homes or businesses, the applications are boundless. This renewable resource represents a paradigm shift—redefining traditional power paradigms while encouraging communities and individuals to actively participate in a more sustainable future.
In conclusion, as modern society grapples with the pressing challenges of climate change, the practical applications of wind energy emerge not only as innovative solutions but as essential components of a resilient energy future. By embracing wind power in our daily lives, we take strides toward a greener tomorrow, integrating sustainability into the very fabric of our existence.