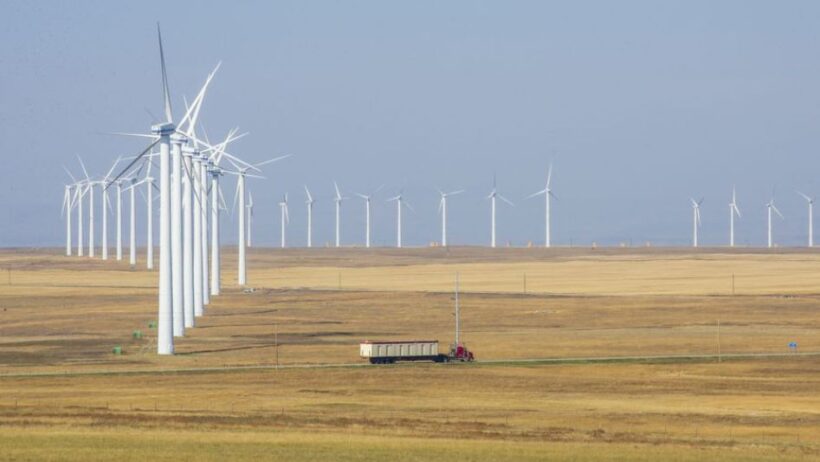
Wind energy has emerged as a pivotal component in the global transition towards renewable energy sources. As nations grapple with the exigencies of climate change, the adoption of wind power has proliferated across continents. In this discourse, we will delve into the extent of wind energy usage worldwide, exploring how many countries have embraced this sustainable resource and evaluating the implications for future energy landscapes.
Countless innovations have made wind energy more accessible and efficient, prompting a shift in how energy is generated. This change is not merely statistical; it signifies a collective awakening to the potential of wind as a clean, inexhaustible energy source. The ascent of wind power is a narrative rich with transformative potential, yet it is essential to understand the varying degrees of adoption and integration among different nations.
Countries Leading the Charge: A Global Overview of Wind Energy Adoption
The threshold for adopting wind energy varies significantly from one nation to another, framed by economic, geographic, and political constraints. As of now, countries such as the United States, Germany, Spain, and China are at the forefront of wind energy development. Notably, China has solidified its position as the world leader in wind power capacity, boasting substantial investments and advancements in technology.
In the United States, wind energy has burgeoned into one of the most significant sources of renewable electricity. The Wind Energy Association reports increasing wind capacity installations across various states, with Texas leading the charge. Meanwhile, European nations like Germany and Denmark have made substantial strides in harnessing wind energy. Denmark, for instance, derives a remarkable percentage of its electricity from wind, showcasing the efficiency of integrated renewable energy systems.
Beyond the traditional powerhouses, many developing countries are also exploring wind energy as a viable resource. Nations in South America, Africa, and Asia are gradually recognizing the benefits of wind power. For instance, countries like Brazil and India have invested substantially in wind farms, reflecting a keen interest in diversifying their energy portfolios. This growing trend signifies a robust global interest in adopting cleaner energy solutions, pushing the boundaries of traditional energy practices.
The Mechanisms Driving Global Wind Energy Adoption
Several factors contribute to the global adoption of wind energy. These factors encompass technological advancements, governmental policies, and economic considerations. The escalation in wind turbine efficiency has rendered wind power more economically attractive. Enhanced storage solutions and advancements in grid integration have facilitated the seamless incorporation of wind energy into existing power infrastructure.
Government initiatives play a pivotal role in determining how nations capitalize on wind energy. Policies such as renewable energy incentives, tax breaks, and government funding for research and development have proven crucial in propelling wind installations. Moreover, international agreements aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions have catalyzed countries to invest in renewable energy sources, including wind. The Paris Agreement, for example, has set ambitious targets for nations to bolster their energy strategies, thereby fostering an environment conducive to wind energy growth.
The growing awareness of climate change impacts has also heightened public and corporate sentiment toward renewable energy. Businesses are increasingly committing to sustainability practices, often requiring cleaner energy sources. This corporate social responsibility is a significant driver for nations to adopt and enhance their wind energy infrastructure. Consequently, the interplay between corporate demands and governmental policies has propelled the growth of wind energy across various nations.
Navigating Challenges: The Hurdles to Wind Energy Implementation
Despite the surging enthusiasm for wind energy, several challenges persist that can thwart its adoption in certain regions. Geographic limitations pose a significant barrier; not all countries possess the ideal terrain or wind conditions to deploy wind farms effectively. Urbanization and land use conflicts can complicate siting decisions, as suitable locations for wind turbines may be at odds with ongoing development.
Moreover, initial capital expenditure remains a crucial concern. The cost of manufacturing and installing wind turbines, along with necessary infrastructure adjustments, can deter investment, particularly in developing nations with constrained budgets. To overcome this, international financing mechanisms and partnerships have emerged, aiming to streamline investments in wind projects globally.
Finally, societal acceptance is vital for the successful establishment of wind farms. Public opposition can stem from concerns about noise, aesthetics, and environmental impacts, often necessitating comprehensive community engagement strategies to foster buy-in from local populations.
The Future of Wind Energy: A Vision Ahead
The future of wind energy appears bright, bolstered by the continuous expansion of technology and supportive policies. The International Energy Agency predicts that wind power will comprise an increasingly large share of the global energy mix. As more countries take definitive steps toward harnessing wind energy, the trajectory of this renewable resource looks promising.
Countries are progressively diversifying their energy sources, moving away from fossil fuel dependence. Wind energy stands out not only for its ecological benefits but also for its capacity to create jobs and stimulate economic growth. Through careful navigation of existing challenges and the fostering of innovation, the global community can undoubtedly enhance its reliance on wind energy, solidifying a sustainable and resilient energy future.
In summation, wind energy has transcended mere potential to become an essential asset in the quest for sustainable energy solutions. As myriad nations embark on this journey toward renewable resources, the implications for energy security, environmental stewardship, and economic prosperity are profound. By understanding the current state and challenges of wind energy adoption, stakeholders can facilitate a robust and equitable transition to a cleaner energy paradigm.