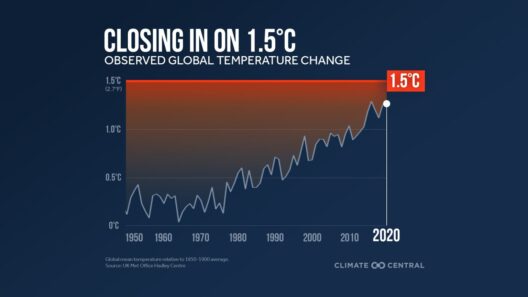
As the urgency to combat climate change escalates, the spotlight on sustainable architecture intensifies. Green buildings are heralded as a crucial solution for reducing energy consumption and mitigating environmental impact. This article explores how much energy is conserved by green buildings, offering a wealth of statistics and facts that paint a compelling picture of their efficacy, particularly for the year 2025.
By definition, green buildings are structures that are designed, constructed, and operated in ways that enhance environmental performance. This encompasses energy efficiency, use of sustainable materials, water conservation, and enhanced indoor air quality. Each component contributes significantly to a building’s overall energy conservation profile.
One of the most striking aspects of green buildings is their energy efficiency. In the United States, buildings are responsible for approximately 39% of total energy use. However, green building practices can reduce energy consumption by as much as 30% to 50% compared to conventional buildings. This remarkable decrease is primarily attributed to advanced technologies, innovative design strategies, and the integration of renewable energy sources.
Renewable energy systems such as solar panels and wind turbines are commonly incorporated into green buildings. These systems not only offset energy consumption but also contribute to energy generation. By 2025, it is expected that solar energy will become increasingly prevalent in these structures. Projections indicate that solar photovoltaic systems can produce around 10 to 12% of the total energy consumed by large-scale commercial green buildings. The shift towards these renewable energy technologies is particularly relevant, as they significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Another key contributor to energy conservation in green buildings is the use of energy-efficient appliances and systems. Standard appliances may consume excessive energy, while Energy Star-rated products utilize advanced technology that minimizes energy use. The adoption of high-efficiency heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems can lead to energy savings of 20% to 30%. It is anticipated that the market for energy-efficient products will burgeon, especially as more consumers demand sustainable options.
Beyond appliances, the design and orientation of buildings play a pivotal role in energy conservation. For instance, optimizing natural daylight through strategic window placement reduces the need for artificial lighting, which can account for up to 25% of a building’s energy use. The use of high-performance glazing and reflective roofing materials can further enhance thermal performance, leading to additional savings. In 2025, it’s predicted that more architects will embrace passive design principles, which harmonize buildings with their surrounding environment to maximize energy efficiency.
The insulation quality of a building is also paramount in energy conservation. Properly insulated buildings can significantly reduce heating and cooling needs, leading to annual energy savings of 10% to 30%. As building codes evolve, the mandate for superior insulation in green buildings will likely become the standard, bolstering energy conservation efforts across the board.
Water conservation is intertwined with the energy-saving narrative of green buildings. Traditional water heating systems consume a vast amount of energy. However, green buildings often employ tankless water heaters and greywater recycling systems that can reduce water-related energy consumption by up to 50%. This dual focus on water and energy conservation is increasingly recognized as crucial in the fight against climate change.
In addition to the tangible energy savings, green buildings contribute to a myriad of environmental benefits. Enhanced indoor air quality resulting from better ventilation systems not only promotes occupant health but can also lead to increased productivity. Studies have shown that companies that operate in green buildings experience reductions in absenteeism, leading to higher overall workforce efficiency.
As we look toward 2025, it is essential to consider the economic implications tied to green building practices. While initial investment in green technologies may deter some builders, the long-term financial benefits often outweigh the upfront costs. Life cycle assessments reveal that green buildings can lead to reduced operational costs of approximately 20% to 30%, thanks to their energy-saving design. This translates into substantial savings over time, encouraging more builders to adopt eco-friendly practices.
Moreover, the demand for green buildings is poised to rise, influencing property values positively. Many studies show that properties with sustainable certifications command higher prices and quicker sales. This trend reflects a growing consumer preference for environmentally responsible living and working spaces. As sustainability becomes more ingrained in societal values, the appeal of green buildings will only intensify.
Data predicts that the global green building market will reach significant milestones by 2025, with an increasing number of structures seeking green certification. This momentum is driven by policy changes, investor preferences, and broader public awareness of environmental issues. Consequently, the effectiveness of green buildings in conserving energy and reducing the carbon footprint will become even more pronounced.
In conclusion, green buildings represent a formidable strategy towards energy conservation, offering numerous benefits that extend beyond mere statistics. The integration of renewable energy, energy-efficient systems, sustainable design, and water conservation techniques synergizes to create a potent force against climate change. The commitment to sustainable practices within construction and architecture is not simply an aspect of compliance but a vital step towards a resilient and sustainable future. As we approach 2025, the momentum behind green buildings will undoubtedly shape the landscape of construction, crafting environments conducive to both human wellbeing and ecological preservation.