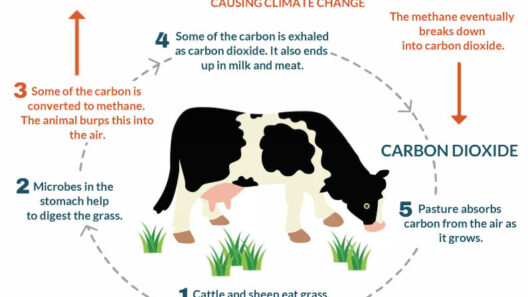
The climate crisis is an ever-looming specter that haunts our collective conscience. As extreme weather events become more frequent and devastating, the urgency to take action mounts. This phenomenon is not merely a fleeting concern; it represents a monumental shift in the very dynamics of our planet. When experts gather to address this pressing issue, their dialogues resonate deeply with a common observation: our intrinsic connection to the Earth is both profound and precarious. Yet, care must be taken to examine not only the symptoms but also the underlying causes that contribute to our current predicament.
At the crux of the climate dilemma lies the notion that climate change is principally a derivative of human behavior. The extensive reliance on fossil fuels, deforestation, overconsumption, and industrial agriculture has led to unsustainable practices that exacerbate the situation. Scientists observe a pattern; emissions from these activities have significantly increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels. Consequently, global temperatures continue to rise, triggering a cascade of catastrophic ecological consequences. Thus, it becomes vital to scrutinize our collective modus operandi and seek transformative pathways toward sustainability.
Transitioning to renewable energy sources is a pivotal solution. Experts advocate for solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy as viable alternatives to fossil fuel dependence. The advancements in technology have considerably reduced the costs associated with harnessing these energy sources. More importantly, they offer a cleaner and sustainable means of powering our societies. By promoting policies that incentivize renewable energy investments, nations can mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. This shift fosters not only environmental benefits but also job creation, ultimately sparking economic revitalization within communities.
However, as we pivot toward cleaner energy, it is essential to recognize the intricacies of systemic change. Simply substituting one form of energy for another does not automatically yield positive outcomes. The circular economy emerges as a transformative concept—proposing that resources should be reused, repaired, and recycled, thus extending their lifecycle. By rejecting the linear model of “take, make, dispose,” individuals and businesses can contribute to a sustainable ecosystem. Emphasizing conscientious consumption, therefore, becomes invaluable in cultivating a culture of responsibility toward our planet.
Furthermore, regenerative agriculture is gaining traction as an essential component of climate action. Unlike conventional agricultural practices that deplete soil health, regenerative techniques prioritize ecological balance. Crop rotation, cover cropping, and agroforestry not only enhance soil fertility but also sequester carbon dioxide back into the earth. This holistic approach to food production promotes biodiversity, supports local economies, and enhances food security. Hence, investing in regenerative practices aligns agricultural objectives with environmental imperatives, establishing a symbiotic relationship that is indispensable for long-term sustainability.
In addition, addressing climate change requires a comprehensive understanding of social equity. Vulnerable communities often bear the brunt of environmental degradation, facing disproportionate impacts from climate-related disasters. Therefore, climate justice needs to be part of the discourse surrounding climate action. Policymakers must ensure that marginalized populations are not only included in decision-making processes but are also equipped with resources and support to adapt to climate change. Bridging the gap between affluent and disadvantaged communities enhances resilience and catalyzes collective action.
The role of innovation cannot be understated in combating climate change. Technological advancements, such as carbon capture and storage, energy efficiency improvements, and sustainable urban planning, hold great potential in reducing our carbon footprint. Integrating artificial intelligence and big data into climate modeling, for instance, enables more accurate predictions and aids in developing targeted mitigation strategies. Encouraging public-private partnerships can facilitate the adoption of these innovations, allowing for impactful solutions to emerge from collaborative efforts.
Education is a crucial facet of fostering a culture that prioritizes environmental stewardship. As awareness of climate issues grows, educational institutions bear a responsibility to equip future generations with necessary knowledge and skills. Curricula that emphasize sustainability, ecology, and climate science will empower students to think critically about the world around them. Engaging young minds in solutions-focused initiatives nurtures a sense of agency, laying the groundwork for a more sustainable future.
Finally, individual actions, while seemingly small, contribute significantly to the collective effort against climate change. Simple choices, such as reducing meat consumption, utilizing public transportation, or minimizing plastic use, resonate far beyond personal habits. Each decision taken in favor of sustainability sends a ripple effect through communities, planting seeds for broader cultural shifts. Grassroots movements, such as local clean-up initiatives or tree-planting drives, serve as powerful reminders of the impact of communal engagement.
In conclusion, the multifaceted nature of the climate crisis necessitates a holistic approach encompassing energy transition, sustainable agriculture, environmental justice, innovation, education, and individual responsibility. It is this interconnected web of solutions that holds the potential to avert a climate disaster. By adhering to the lessons learned from experts and the wisdom imparted by the Earth itself, societies can forge a resilient path forward, one that honors both the well-being of the planet and the generations yet to come. The time to act is now; inaction only exacerbates the profound challenges we face. Together, through collaborative and informed efforts, a more sustainable future is attainable.