Energy conservation in the workplace has garnered increasing attention as organizations grapple with escalating energy costs and a mounting responsibility to mitigate climate change. While some may perceive this focus as merely an economic imperative, it is also a pivotal aspect of sustainable practice. The quest for energy efficiency transcends mere savings; it embodies an ethos of stewardship, presenting an opportunity for businesses to lead by example in ecological responsibility.
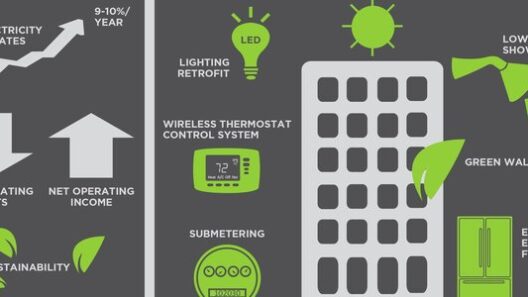
To cultivate a culture of energy conservation, organizations must begin by conducting a comprehensive energy audit. This process involves assessing current energy consumption patterns, identifying inefficiencies, and pinpointing potential improvements. Often, workplaces are rife with overlooked opportunities for energy savings. Outdated lighting, inefficient appliances, and poor insulation can dramatically increase energy expenditures. By implementing sophisticated monitoring solutions and utilizing smart meters, organizations can glean insights that drive informed decision-making.
Once inefficiencies are identified, the next step is to prioritize energy-efficient upgrades. Transitioning to LED lighting epitomizes one of the most accessible enhancements. Unlike conventional incandescent bulbs, LEDs consume significantly less power and have a longer lifespan. This transformation not only reduces electricity bills but also minimizes the frequency of replacements, thereby decreasing waste. Moreover, the implementation of daylight sensors and timers can further optimize lighting use based on occupancy and natural light availability.
Beyond lighting, the adaptation of Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems is crucial. HVAC systems are notorious for their energy consumption, often accounting for a substantial portion of a building’s overall energy usage. Regular maintenance, including filter changes and system checks, ensures that these systems operate at peak efficiency. Furthermore, integrating programmable thermostats allows for the automation of temperature controls based on occupancy patterns, thereby conserving energy during unoccupied hours.
Employees themselves play a critical role in the pursuit of energy efficiency. Raising awareness and fostering a culture of conservation is paramount. This can be achieved through training sessions that elucidate the importance of energy conservation and provide practical tips for daily practices. Simple actions—such as turning off computers and lights when not in use—can collectively lead to significant energy savings. Gamification techniques can further enhance participation, encouraging teams to engage in energy-saving competitions with rewards for the most conscientious departments.
In addition, remote work and flexible arrangements represent a growing trend that inadvertently promotes energy conservation. By enabling employees to work from home, organizations can reduce energy demands in the office, thereby lowering operational costs. However, it is essential to discuss sustainable home practices as well. Employees should be encouraged to consider energy-efficient appliances, smart home devices, and sustainable power sources—such as solar panels—if feasible. This holistic approach not only benefits the organization but also empowers employees to adopt environmentally conscious habits at home.
Implementing strategies for energy conservation extends to the procurement of energy-efficient office equipment. Investing in ENERGY STAR rated devices can yield substantial savings over time. By opting for energy-efficient printers, computers, and other essential machinery, businesses can drastically reduce their energy footprint. Furthermore, establishing a policy for minimal electronic waste, advocating for the recycling of old equipment, reflects an organization’s commitment to sustainability.
Another integral element of energy conservation is the utilization of natural resources. Strategically placing desks near windows can maximize natural light, reducing the reliance on artificial lighting. Additionally, incorporating indoor plants can improve air quality and reduce the need for mechanical ventilation. These biophilic principles not only create a more pleasant working environment but also bolster employees’ well-being and productivity.
Additionally, companies may explore renewable energy options, such as solar panels or wind turbines, to power their operations sustainably. While the upfront investment may be considerable, these technologies can yield long-term financial and environmental benefits. Furthermore, businesses that can substantiate their commitment to renewable energy can leverage this as part of their marketing strategy, appealing to an increasingly eco-conscious consumer base.
Establishing an energy management plan is a systematic approach that incorporates all of these strategies into a cohesive framework. This plan can delineate short-term and long-term energy reduction goals, outline responsibilities among personnel, and set measurable benchmarks for accountability. Transparency in energy reporting will also illuminate progress and facilitate adjustments as necessary, ensuring that the workplace remains adaptive to changing conditions.
Ultimately, the journey toward energy conservation in the workplace is more than just a series of tactical implementations; it is a comprehensive mindset shift that promotes sustainable practices across all facets of the organization. By recognizing the myriad benefits associated with energy efficiency—ranging from reduced operating costs to an enhanced company reputation—businesses can harness the collective action required to foster a more sustainable future. As climate change continues to pose critical challenges, the onus is on organizations to lead the charge in implementing pragmatic solutions that yield tangible benefits for both their bottom line and the planet.
In conclusion, the pathway to achieving energy efficiency in the workplace is multifaceted, requiring commitment and engagement at all levels. Through meticulous energy audits, employee involvement, and strategic upgrades, organizations can make significant strides in reducing energy consumption and costs. As they do so, they become not only more fiscally responsible but also champions of environmental stewardship, setting a precedent for others to follow.