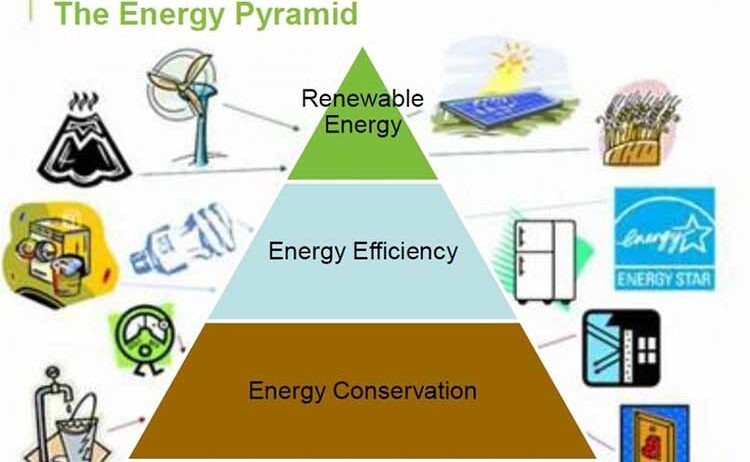
Energy conservation is not merely a buzzword in today’s ecological discourse; it is an imperative response to the escalating concerns surrounding climate change and resource depletion. The clarity of this concept resides in its intrinsic link to efficiency and sustainable management practices. Hence, bolstering energy conservation techniques can serve as a powerful catalyst for enhancing overall effectiveness, all while minimizing the negative environmental impacts associated with energy consumption.
At the heart of energy conservation lies the deliberate choice to use less energy while achieving the same output. A common observation is that many homes and businesses are rife with inefficiencies that can lead to substantial energy waste. This often stems from outdated practices, negligence, or a simple lack of awareness about efficient alternatives. Addressing these inefficiencies requires both an analytical mindset and a commitment to implementing progressive changes.
To embark on this journey, one must first understand the significance of energy audits. Conducting a thorough energy audit can unveil numerous opportunities for improvement. By assessing areas such as insulation, heating and cooling systems, and lighting, individuals and organizations can pinpoint wasteful practices. Tracking energy usage through established benchmarks also helps organizations understand patterns and enables targeted energy-saving interventions.
In residential settings, the reliance on fossil fuels for heating is a prevalent concern. The installation of high-efficiency heating systems, such as condensing boilers or heat pumps, presents a practical solution. These appliances are designed to extract maximum heat while using minimal energy. Furthermore, the integration of smart thermostats can enable homeowners to schedule heating and cooling systems according to their usage patterns, thus optimizing energy expenditure.
Moreover, upgrading insulation in buildings cannot be overstated. Proper insulation can drastically mitigate heat loss in winter and keep interiors cooler in summer, resulting in decreased energy demand. By investing in quality insulation materials such as spray foam or cellulose, individuals can further augment their energy conservation efforts, leading to long-term cost savings.
Lighting is another arena ripe for enhancement. The transition from incandescent bulbs to compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) or light-emitting diodes (LEDs) yields considerable reductions in energy consumption. Such lighting technologies are not only more efficient but also boast longer lifespans, reducing both replacement frequency and landfill contributions.
In commercial spaces, energy management systems (EMS) provide a sophisticated means of overseeing energy consumption. These systems utilize advanced algorithms to analyze energy use patterns, thereby identifying inefficiencies and suggesting optimization strategies. Additionally, employee awareness campaigns can foster a culture of conscientious energy use, where individual actions—like turning off lights and unplugging unnecessary devices—accumulate to create significant savings.
The realm of energy conservation extends beyond mere technological upgrades; behavior change plays a pivotal role. Individuals often overlook the impact of their choices on energy consumption. Advocating for mindful habits can transform daily routines. For instance, encouraging a culture of energy saving within households or workplaces can inspire collective commitment to these ideals. Simple practices, such as setting computer power-saving modes and utilizing natural light whenever possible, can contribute to a noticeable decline in energy usage.
Additionally, renewable energy sources are becoming an increasingly feasible option for both residential and commercial settings. The adoption of solar panels not only reduces reliance on non-renewable energy but can also provide financial incentives through energy rebates or tax credits. By harnessing renewable energy, establishments foster a dual benefit: a decrease in energy costs and an elevation in their ecological stewardship.
Furthermore, the importance of community engagement in energy conservation should not be underestimated. Grassroots initiatives aimed at educational outreach can inform populations about the broader impact of energy consumption and provide practical strategies for improvement. Workshops, informational pamphlets, and community challenges can ignite a collaborative spirit focused on energy management.
Technology also plays a transformative role in enhancing energy conservation. The advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) facilitates innovative solutions to monitor and control energy usage in real-time. Smart appliances and meters allow users to visualize their consumption patterns and make informed adjustments, reinforcing a data-driven approach to energy conservation.
As organizations and individuals continue to adopt energy-saving practices, the potential for increased efficiency expands. Collaborating with energy consultants or environmental agencies can further streamline these efforts. Such partnerships often provide access to resources, case studies, and best practices tailored to specific contexts.
In summary, energy conservation is an essential component of combating climate change and fostering sustainable practices. The amalgamation of efficient technologies, behavioral changes, community initiatives, and technological advancements creates a holistic strategy for reducing energy waste. The journey towards enhanced energy efficiency may seem daunting; however, incremental changes can precipitate profound effects on both the environment and economic resources. By making conscientious decisions today, individuals and organizations can contribute to a more sustainable tomorrow.