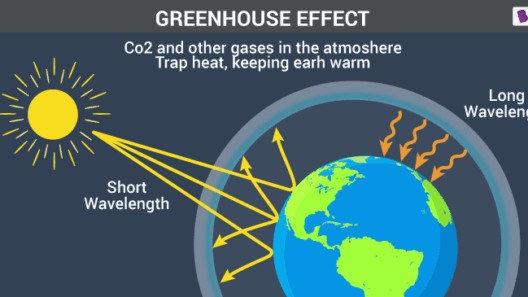
Climate change represents an unprecedented challenge, one that necessitates urgent and comprehensive action across all societal spectrums. The greenhouse effect, a natural phenomenon that has been exacerbated by human activities, is a primary culprit in this global crisis. Understanding actionable strategies to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions is essential. The following discourse examines potent tactics that can contribute to ameliorating climate change.
Understanding the Greenhouse Effect: A Two-Edged Sword
The greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring process where certain gases in Earth’s atmosphere trap heat, thereby maintaining a temperature conducive to life. However, anthropogenic activities—such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial practices—have intensified this effect. The gaseous culprits include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, among others. As these emissions accumulate, they create an insidious barrier that exacerbates global warming, leading to severe climatic disruptions. The question then arises: how can we effectively mitigate these emissions?
Embrace Renewable Energy: A Shift from Fossils to Renewables
Transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources is paramount in tackling greenhouse emissions. Solar panels, wind turbines, and hydropower installations offer cleaner alternatives that can significantly reduce reliance on carbon-intensive energy sources. Governments and organizations can encourage this transition by providing financial incentives for renewable energy investments, promoting research and development, and creating public policies that favor sustainable practices.
Furthermore, individual households can contribute by installing solar panels or investing in green energy options provided by utility companies. Embracing renewable energy is not merely an option; it is an obligation for a sustainable future. By gradually reducing fossil fuel dependence, we pave the way for a cleaner, more resilient planet.
Energy Efficiency: The Power of Conservation
Energy efficiency emerges as another critical strategy in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. From upgrading appliances to choosing energy-efficient lighting, every action contributes to lowering energy consumption. Implementing smart home technologies can also optimize energy use, ensuring that power is consumed judiciously.
Commercial sectors play a pivotal role as well. Employing advanced technologies and practices in manufacturing and logistics can dramatically attenuate emissions. For instance, energy audits can identify inefficiencies, allowing businesses to minimize waste and cut costs. As organizations embrace sustainability, they not only contribute positively to the environment but also enhance their public perception and profitability.
Transportation Solutions: Redefining Mobility
Transportation is one of the largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. Therefore, reevaluating our mobility habits can result in significant reductions. Promoting public transit systems, carpooling, and cycling can alleviate the over-reliance on individual cars. As urban centers expand, integrating pedestrian walkways and cycling lanes fosters healthier and more sustainable communities.
The electrification of vehicles is another burgeoning solution. Electric cars, powered by renewable energy, promise a stark reduction in emissions from conventional vehicles. Governments can also incentivize the production of electric vehicle charging infrastructure, thus enabling a smoother transition towards greener automotive technology.
Waste Reduction: From Landfills to Compost
An often-overlooked aspect of greenhouse gas emissions stems from waste. Decomposing organic waste in landfills produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Strategies to combat this include promoting composting initiatives and encouraging consumers to reduce, reuse, and recycle. Educational campaigns can raise awareness about the importance of waste management and its direct impact on climate change.
Moreover, businesses can integrate circular economy principles to minimize waste output and extend product lifecycles. By reimagining product design and employing sustainable materials, companies can contribute to a significant decrease in landfill contributions and greenhouse gas emissions.
Forestry and Land Use: Carbon Sinks in Action
Forest ecosystems serve as natural carbon sinks, sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. However, deforestation, primarily for agriculture and urban development, diminishes this capacity. Protecting existing forests and restoring degraded areas are essential strategies in combating climate change. Afforestation projects not only restore biodiversity but also enhance the carbon sequestration potential of landscapes.
Agroforestry practices, which integrate trees and agriculture, exemplify a holistic approach to land use. By implementing these practices, farmers can improve soil health, increase crop yields, and mitigate greenhouse gas emissions simultaneously. Sustainable land management practices are crucial in the broader endeavor to restore ecological balance.
Incentivizing Change: Policy and Community Engagement
Finally, the role of policy cannot be understated. Governmental entities should enact stringent regulations aimed at mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. Establishing carbon pricing or cap-and-trade systems encourages businesses to internalize environmental costs. Public investment in clean technology and infrastructure is vital to facilitating a sustainable transition.
Moreover, community engagement plays a fundamental role in driving behavioral change. Grassroots movements and local organizations can galvanize public support and larger-scale initiatives. By fostering open dialogues and advocating for sustainable practices in everyday life, communities can champion a robust response to climate change.
In conclusion, the reduction of the greenhouse effect hinges on a multi-faceted approach involving renewable energy, efficiency, innovative transportation solutions, waste management, forestry, and supportive policies. Each individual’s actions, when accumulated, can create a collective impact—making it imperative that everyone contributes to the fight against climate change. Only through cooperative efforts can a sustainable future be realized.