Increased droughts have emerged as a stark emblem of the broader metamorphosis occurring in our planet’s climate. As global temperatures rise, the frequency and severity of droughts have exacerbated, threatening ecosystems, agriculture, and human livelihoods. Understanding the parched reality of a warming world requires delving into the multifaceted phenomena underlying this environmental crisis.
Drought, fundamentally, denotes a prolonged period of abnormally low rainfall. However, its repercussions ripple outward, affecting not only precipitation levels but also the intricate web of ecological and human systems dependent on timely water availability. Historically, droughts have been natural occurrences; nevertheless, the latest patterns signal an alarming transformation in their behavior, intensifying in both duration and intensity. This implies a pivotal relationship between human-induced climate change and the hydrological cycles that govern life on Earth.
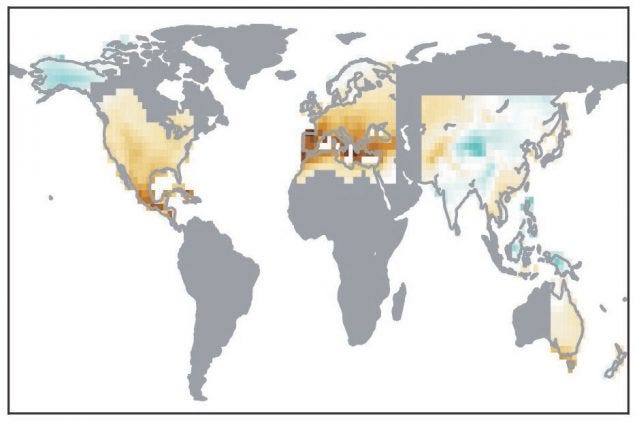
The correlation between increasing atmospheric temperatures and burgeoning drought conditions is evidentially clear. With each increment of warming, the atmosphere’s capacity to hold moisture escalates, resulting in heightened evaporation rates. As a consequence, areas already suffering from limited water resources experience exacerbated aridity. This searing combination of increased evaporation and diminished precipitation culminates in an intensified fandango of drought conditions.
Geographically, the hotspots of drought are shifting. Regions predisposed to arid climates, such as the southwestern United States, eastern Africa, and parts of Australia, are experiencing unprecedented dry spells. Yet, even temperate zones are not immune; areas historically characterized by sufficient rainfall are now grappling with increased occurrences of drought. This phenomena is a glaring reminder that climate change is not merely a distant specter; it is an immediate reality affecting communities worldwide.
A significant component of the drought narrative is the role of land management practices. Deforestation, unsustainable agricultural practices, and urbanization contribute to alterations in local and regional hydrology. The removal of forests disrupts the natural water cycle, as trees play an instrumental role in transpiration—returning moisture to the atmosphere. Furthermore, intensive agricultural practices often escalate soil degradation, diminishing its capacity to retain water. These anthropogenic pressures compound the challenges posed by climate change, leading to a detrimental feedback loop that aggravates drought conditions.
Moreover, the socio-economic ramifications of droughts cannot be overstated. As water scarcity becomes an insurmountable challenge, agricultural production dwindles, directly impacting food security. Crops fail under relentless sun and dry conditions, exacerbating the vulnerability of communities that depend on agriculture for their sustenance and economic stability. The specter of hunger looms larger as prices for basic food items spiral upward, leading to social unrest and increased migration as people flee inhospitable areas in search of better prospects.
Environmental ecosystems, too, bear the brunt of prolonged dry spells. Aquatic habitats suffer as water levels in rivers and lakes recede, leading to increased salinity and disrupting the balance of these delicate ecosystems. Terrestrial flora and fauna experience stress; flora may die off, altering habitats permanently and diminishing biodiversity. As species struggle to adapt to the altered climatic conditions, the risk of extinction rises, threatening the very fabric of ecological integrity.
In the face of escalating drought conditions, adaptation and mitigation strategies are paramount. Resilience must become the cornerstone of water management policies. Communities must embrace sustainable practices, introducing crop varieties that are drought-resistant and championing techniques such as rainwater harvesting and efficient irrigation methods. Furthermore, policies aimed at reforesting degraded areas can help restore the hydrological balance essential for maintaining moisture levels.
Beyond local and regional measures lies the global imperative to address climate change holistically. International cooperation and commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions are crucial for curbing the relentless rise in global temperatures. The Paris Agreement serves as a framework for nations to unite toward the common goal of limiting warming to below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. Meeting this objective is essential not only to mitigate drought conditions but also to ensure the sustainability of our planet for future generations.
Public awareness and education also play a pivotal role in combating the challenges posed by drought. Individuals and communities must understand the interconnectedness of their actions and their broader environmental impact. Encouraging water conservation initiatives, grassroots activism, and sustainable lifestyle choices can empower citizens to contribute meaningfully to the collective effort against climate change.
In conclusion, the increased frequency and intensity of droughts epitomize the harsh realities of a warming world. This phenomenon transcends mere statistics; it embodies a complex interplay of climatic, ecological, and socio-economic factors. Addressing this pressing issue demands a paradigm shift in how we perceive and manage water resources, alongside a steadfast commitment to combating climate change. As stewards of the Earth, it is incumbent upon us to safeguard the delicate balance of our environment, ensuring that future generations can thrive in a world that is resilient, sustainable, and capable of withstanding the trials of a changing climate.