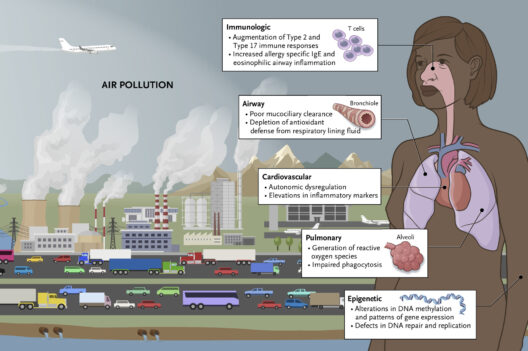
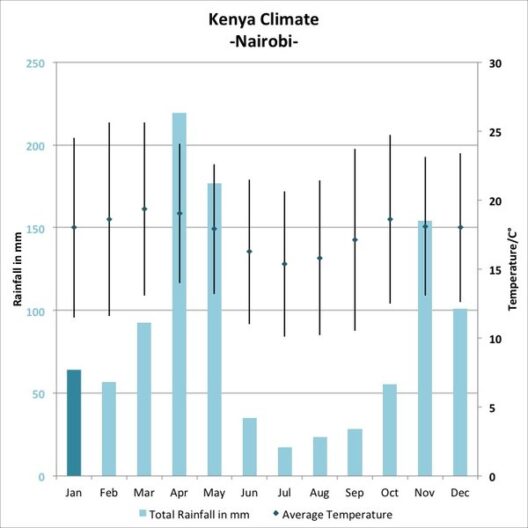
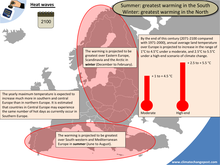
Indonesia, a vast archipelago comprising over 17,000 islands, stands at a critical juncture in its quest for economic progress amid the pressing realities of climate change. As one of the world’s most vulnerable nations to climate impacts—rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and biodiversity loss—Indonesia is compelled to revisit its economic strategies through a climate-centric lens. This transition necessitates the integration of sustainable practices, innovative technologies, and proactive policies to secure a resilient economic future.
The Indonesian economy, historically reliant on natural resources, is heavily influenced by agriculture, forestry, and fisheries, sectors that face existential threats due to climate change. Increasing temperatures and erratic rainfall patterns jeopardize agricultural yields, diminishing food security and threatening livelihoods. To counter this, an agrarian revolution beckons, prioritizing sustainable agricultural practices such as agroforestry, organic farming, and crop diversification. These innovations not only enhance productivity but also contribute to carbon sequestration, addressing climate goals while fostering economic stability.
Furthermore, the energy sector in Indonesia remains a core component of its economic framework, predominantly powered by fossil fuels. However, with global momentum shifting towards renewable energy, the Indonesian government is under increasing pressure to decarbonize its energy portfolio. Indonesia possesses immense potential for renewable sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal energy. Investing in these alternatives can create job opportunities, stimulate local economies, and reduce reliance on imported fuels, fortifying the nation’s economic independence.
Transforming Indonesia’s economic landscape also involves advancing its industrial sectors. The manufacturing and processing industries can play a pivotal role in adopting greener practices. Circular economy principles—where materials are reused, remanufactured, or recycled—can be integrated to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency. These practices not only mitigate environmental degradation but can also enhance competitiveness in international markets increasingly favoring environmentally responsible products.
The role of policy frameworks cannot be overstated in this transformative journey. The Indonesian government has made strides toward sustainable development by ratifying international agreements and setting ambitious targets for emissions reductions. However, stringent enforcement measures and the establishment of incentives for sustainable practices are essential to catalyze genuine change. Regulatory mechanisms that incorporate environmental accountability into corporate practices will compel businesses to prioritize sustainability, thus aligning economic growth with climate resilience.
In addition to policy and industry reforms, fostering a culture of innovation remains crucial. Indonesia’s burgeoning tech scene presents an opportunity to develop cutting-edge solutions to address climate challenges. Startups focusing on climate technology, such as water conservation systems, precision agriculture tools, and energy efficiency solutions, can spur economic growth while enhancing environmental stewardship. By nurturing a vibrant ecosystem for innovation, Indonesia can position itself as a leader in the green technology sector in Southeast Asia.
Moreover, the importance of community engagement in climate adaptation efforts cannot be overlooked. Grassroots movements and local communities have invaluable knowledge regarding their ecosystems and environmental challenges. Empowering these groups through funding and resources will facilitate localized solutions that align with national objectives. Collaborative efforts between the government, businesses, and civil society can foster a unified approach to tackling climate change, ensuring that the voices of those most affected are heard and respected.
Education serves as a fundamental pillar in equipping future generations with the skills necessary to navigate a climate-impacted economy. Integrating climate education into school curricula will cultivate environmental awareness and instill a sense of responsibility towards sustainable practices. Higher education institutions can also play a key role by conducting research that informs policy and promotes innovation in climate adaptation strategies. An educated populace will be a significant asset in Indonesia’s transition towards a sustainable economy.
Indonesia’s economic future hinges on its ability to harmonize development with environmental stewardship. An industrious approach is paramount to ensure that economic growth does not come at the expense of ecological balance. The integration of sustainable practices across all sectors, propelled by informed policy decisions and community involvement, will enable Indonesia to forge a path towards resilience in the face of climate change.
As Indonesia endeavors to chart this course, it is imperative to recognize that climate change is not merely a challenge; it is also an opportunity for rejuvenation and innovation. Embracing sustainability can unlock new economic avenues, enhance competitiveness, and improve the quality of life for millions. The road ahead requires bold leadership, collaboration, and an unwavering commitment to protecting the natural environment while securing economic prosperity. Only by interweaving these elements can Indonesia achieve a sustainable economic future that safeguards the well-being of its citizens and the integrity of its diverse ecosystems.