Indonesia, a sprawling archipelago of over 17,000 islands, presents a compelling canvas for economic growth tempered with the multitudinous challenges of climate change. With its burgeoning economy poised to become one of the largest in Southeast Asia, the dichotomy between economic expansion and environmental preservation has been starkly illuminated. The imperative for sustainable development emerges not only as a necessity for ecological protection but also as a fundamental pillar for future economic stability.
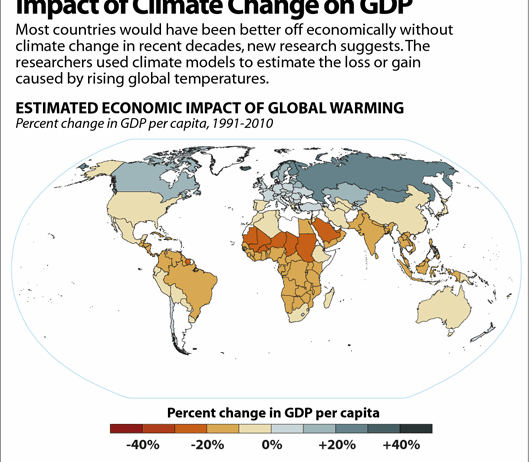
The conundrum faced by Indonesia is underscored by its significant reliance on natural resources, particularly in agriculture, fisheries, and forestry. These sectors, intrinsically linked to the health of the natural environment, are increasingly vulnerable to the repercussions of climate change. Rising sea levels threaten coastal communities and agricultural productivity, while extreme weather patterns wreak havoc on food security and livelihoods. Consequently, understanding the extent to which climate change will impact Indonesia’s economic future is crucial for devising effective policy responses.
Climate change is not merely an environmental issue; it is a multifaceted economic challenge. The agricultural sector, for instance, employs a substantial portion of Indonesia’s workforce and contributes significantly to GDP. However, changes in rainfall patterns, increased temperatures, and the prevalence of pests—all exacerbated by climate change—jeopardize food production. The vulnerability of these workers calls for structural adjustments in the economy to foster resilience and adaptability.
Moreover, Indonesia is one of the world’s largest emitters of greenhouse gases, primarily due to deforestation and land use changes. The country has faced international scrutiny for its accelerated deforestation rates, driven by palm oil production and timber extraction. While these industries have engendered economic growth and global trade, they also pose existential threats to Indonesia’s biodiversity and climate stability. The balance between leveraging natural resources for economic gain and conserving them for sustainability is delicate, necessitating innovative frameworks that prioritize long-term ecological and economic health.
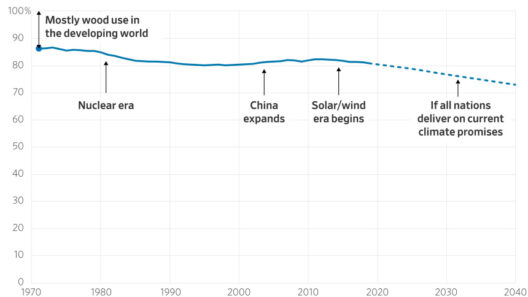
To navigate these tumultuous waters, Indonesia is increasingly looking towards green technologies and renewable energy sources. The government has set ambitious targets to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 29% by 2030, with an ultimate goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2060. Investments in solar, wind, and geothermal energy not only promise environmental benefits but also present significant opportunities for job creation and economic diversification. Transitioning to a green economy can alleviate reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate the risks associated with climate volatility.
However, realizing this vision of sustainable growth is fraught with challenges. Infrastructural constraints impede the expansion of renewable energy projects, while the costs associated with transitioning existing industries toward sustainable practices can be prohibitive. Aligning the interests of various stakeholders—including government agencies, local communities, and private enterprise—is vital for fostering a cohesive approach to climate resilience. This is where the role of education and awareness becomes paramount; empowering local populations through knowledge can cultivate a culture of sustainability that permeates economic activities.
The intersection of climate change and economic policy necessitates a recalibration of Indonesia’s developmental agenda. Emphasizing sustainable practices across all sectors is essential—not only to safeguard the environment but to enhance long-term economic prospects. Initiatives that promote eco-tourism, sustainable agriculture, and clean technology can stimulate economic growth while preserving the natural heritage that underpins Indonesia’s identity.
Additionally, fostering partnerships with international organizations and nations can facilitate knowledge transfer and resource allocation. Collaborative efforts in research and development can yield innovative solutions tailored to Indonesia’s unique climatic and geographical conditions. Harnessing regional and global expertise can accelerate the transition toward sustainability, positioning Indonesia as a leader in climate resilience in the Indo-Pacific region.
Moreover, the role of the private sector remains critical in this transformative journey. Corporations are increasingly recognizing the strategic value of embedding sustainability into their business models. Investing in sustainable supply chains, reducing carbon footprints, and engaging in corporate social responsibility are poignantly aligned with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible practices. By integrating sustainability into their core operations, businesses can not only enhance their competitiveness but also contribute to the broader goal of climate adaptation and mitigation.
Finally, addressing social equity is paramount as Indonesia ventures into a more sustainable economic paradigm. Vulnerable populations, often the most affected by climate change, must be included in decision-making processes. Ensuring equitable access to resources and opportunities is essential in fostering community resilience and garnering support for sustainable initiatives. As the nation gravitates toward inclusive growth, facilitating dialogue between marginalized groups and policymakers will be crucial in creating a participatory framework that champions equitable economic development.
In conclusion, Indonesia’s economic future hinges precariously on its ability to navigate the complexities of climate challenges. The path forward requires a holistic approach that harmonizes economic growth with environmental stewardship. By embracing sustainable practices, investing in renewable technologies, fostering international collaborations, and prioritizing social equity, Indonesia can carve a resilient pathway toward a prosperous and sustainable future. The forthcoming decades will be characterized by profound transformation, wherein the commitment to sustainability will ultimately dictate Indonesia’s economic trajectory on the global stage.