Indonesia’s tapestry of islands, sprawling across both sides of the equator, presents a myriad of cultural, ecological, and economic complexities that are inextricably linked to the broader challenges of climate change. As a nation that stands as a microcosm of diverse ecosystems, Indonesia’s approach to mitigating climate challenges is both critical and compelling. The country’s biodiverse landscapes, significant carbon sinks, and growing urban environments encapsulate a nation at a crossroads, where the choices made today will resonate through generations.
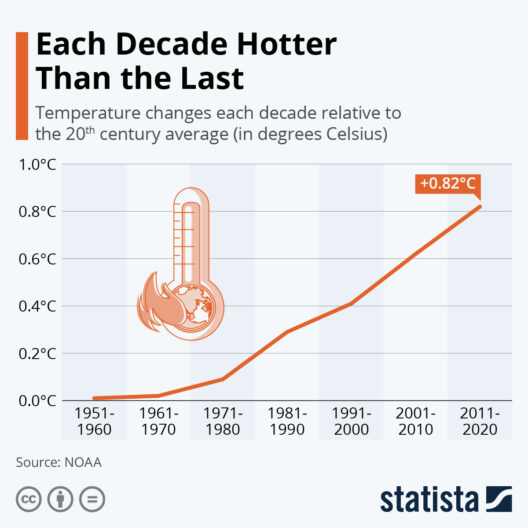
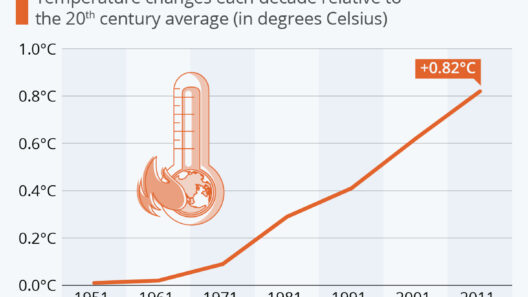
One of the most pressing issues Indonesia faces is deforestation, predominantly driven by agriculture, mining, and urban expansion. The country harbors some of the world’s largest tropical rainforests, which serve as vital carbon reservoirs. However, relentless logging and land conversion for palm oil plantations have decimated vast tracts of these forests. The statistics are alarming: Indonesia is one of the largest contributors to carbon emissions globally, primarily due to forest loss. Curbing deforestation is not merely an environmental imperative; it is a cornerstone of Indonesia’s commitment to international climate agreements, such as the Paris Agreement. The nation’s strategies for forest rehabilitation and sustainable land management are imperative components in the quest for a sustainable future.
In addressing these environmental predicaments, one cannot overlook Indonesia’s rich marine biodiversity. Home to the Coral Triangle, the nation possesses a staggering array of marine life. However, the oceans are under siege from pollution, overfishing, and climate change-induced coral bleaching. The degradation of marine ecosystems not only threatens biodiversity but also jeopardizes the livelihoods of millions of Indonesians who rely on fisheries. Sustainable ocean governance, including comprehensive marine protected areas and community-based fisheries management, can bolster resilience against climate impacts while preserving the natural heritage. By prioritizing the health of marine environments, Indonesia can secure its food sources and enhance its economic stability.
Moreover, Indonesia’s urban centers are experiencing rapid growth, often characterized by inadequate infrastructure and a lack of urban planning. As cities expand without consideration for sustainability, the ramifications are profound. Jakarta, for instance, grapples with catastrophic flooding exacerbated by climate change, rising sea levels, and rampant land subsidence. Urban resilience strategies must be embraced, integrating nature-based solutions and green infrastructure to mitigate risks. Investing in sustainable urban transport, energy-efficient buildings, and smart city technologies can catalyze change, steering Indonesia towards a low-carbon urban future.
However, technological advancements alone will not suffice. Engaging communities is equally essential. Local and indigenous knowledge offers invaluable insights into sustainable practices and ecosystem management. Empowering communities through education, capacity building, and participatory decision-making fosters resilience and cultivates a culture of environmental stewardship. Indigenous practices that have been honed over centuries can provide robust frameworks for sustainable resource management. Recognizing and integrating local wisdom into national policies is crucial for ensuring that development is both people-centric and ecologically sound.
Moreover, the energy sector presents both challenges and opportunities. Indonesia, with its substantial fossil fuel reserves, must navigate the delicate balance between energy security and environmental sustainability. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and geothermal, is not just a viable path—it is a necessity. Indonesia is endowed with abundant renewable resources, yet the current energy mix remains predominantly reliant on coal. Investment in renewable energy infrastructure, coupled with government incentives for clean technologies, can accelerate this transition. By championing renewables, Indonesia has the potential to meet its growing energy demands while reducing its carbon footprint.
Economically, Indonesia is at a critical juncture. The potential for green economy initiatives can lead to job creation, technological innovations, and improved quality of life. Green finance mechanisms, including green bonds and sustainable investment frameworks, can finance projects that contribute to environmental sustainability while bolstering Indonesia’s economy. This transformation, however, requires an unwavering commitment from both the government and the private sector to prioritize sustainable practices. Collaborative partnerships among stakeholders can drive the green agenda and catalyze systemic change throughout the economy.
Yet, systemic change requires robust policy frameworks at all levels of governance. Indonesia has made commendable strides in advancing climate policies, yet enforcement and accountability remain challenges. Transparent governance mechanisms can ensure that environmental regulations are adhered to, reinforcing the credibility of climate action. Inclusive policy dialogues that engage a breadth of stakeholders will be essential in crafting coherent strategies that benefit both the environment and society. Transparent, participatory governance structures will enhance public trust and cooperation, vital for the country’s ambitious climate goals.
As one looks toward the future, Indonesia stands as a beacon of both vulnerability and opportunity in the face of climate change. Navigating these challenges will require a multi-faceted approach that marries conservation with development, indigenous wisdom with technology, and local action with global awareness. By forging a sustainable path forward, Indonesia can emerge not only as a leader in climate action but also as a steward of its rich natural heritage, ensuring a flourishing environment for future generations.
In conclusion, Indonesia’s journey toward a sustainable tomorrow hinges on the concerted efforts of government, private sector, communities, and individuals. The road ahead may be fraught with challenges; however, the rich tapestry of Indonesia’s culture and ecosystems holds the promise of enduring resilience. As the world watches, the choices made today in Indonesia will lay the groundwork for a more sustainable and equitable future.