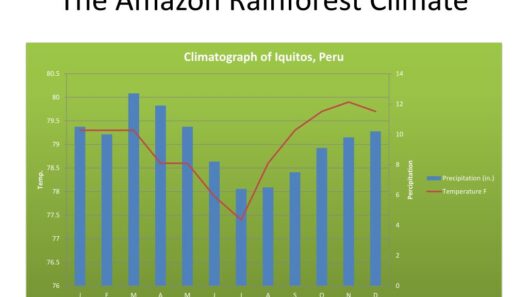
Climate change and global warming are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they embody distinct phenomena within the spectrum of environmental science. Understanding the nuances between these two terms is essential for grasping the complexities of our planet’s climate system and the challenges we face. This exploration delves into their definitions, causes, manifestations, and implications.
Definition of Global Warming
Global warming refers specifically to the increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). This phenomenon results from both natural processes and anthropogenic activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial emissions. The term commenced its use as public awareness of climate issues grew, particularly after the industrial revolution when human activity began to significantly alter the natural climate balance.
Definition of Climate Change
Climate change, while inclusive of global warming, encompasses a broader spectrum of changes to the Earth’s climate. This includes alterations in temperature, precipitation patterns, sea levels, and the frequency and intensity of weather events. Climate change is influenced by both natural processes — such as volcanic eruptions and solar variations — and human-induced factors. Thus, climate change embodies a more extensive range of environmental shifts, more than mere average temperature increases.
Causes of Global Warming
The primary catalyst for global warming is the greenhouse effect, which is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface. Human activities exacerbate this effect through increased emissions of greenhouse gases. Key contributors include:
- Fossil Fuel Combustion: The burning of coal, oil, and natural gas for energy leads to higher CO2 levels.
- Agricultural Practices: Livestock production releases methane, while certain fertilizers emit nitrous oxide.
- Deforestation: Trees absorb CO2, and their removal increases atmospheric levels.
Causes of Climate Change
Climate change results from a complex interplay of factors, some of which are long-term and some short-lived. While global warming is a significant driver, other elements include:
- Natural Climate Variabilities: Changes such as El Niño or La Niña influence weather patterns significantly.
- Land Use Changes: Urbanization and agricultural expansion alter the natural landscape and contribute to local climate shifts.
- Oceanic Changes: Oceans act as a climate regulator, but rising temperatures affect currents, leading to drastic changes.
Manifestations of Global Warming
As global temperatures rise, various observable effects arise, each with substantial implications:
- Glacial Melting: Acceleration in the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers contributes to rising sea levels.
- Ocean Heating: Warmer oceans disrupt marine ecosystems and lead to coral bleaching.
- Increased Weather Extremes: Rising temperatures correlate with more severe heatwaves, droughts, and heavy precipitation events.
Manifestations of Climate Change
The effects of climate change stretch far beyond temperature increases, affecting ecosystems, human health, and economies:
- Shifts in Biodiversity: Altered habitats may lead to species extinctions and biodiversity loss.
- Food Security: Changes in weather patterns can disrupt agricultural production, threatening food supplies.
- Human Displacement: Rising sea levels and extreme weather can force communities to relocate, leading to climate refugees.
Implications of Global Warming
The implications of global warming are profound and multifaceted. As temperatures rise, potential consequences include:
- Public Health Risks: Increased heat-related illnesses, respiratory issues from poor air quality, and the spread of vector-borne diseases.
- Economic Strain: Damage to infrastructure from extreme weather results in costly repairs and disrupts economies.
- Resource Scarcity: Water shortages and reduced agricultural yields may lead to conflicts and exacerbated inequality.
Implications of Climate Change
The broader impacts of climate change encompass a variety of societal shifts and environmental degradation:
- Socioeconomic Disparity: Vulnerable populations often face the greatest risks despite contributing the least to climate change.
- Global Security: Competition for dwindling resources can heighten tensions between nations.
- Natural Disasters: The increased frequency and severity of hurricanes, floods, and wildfires wreak havoc on communities.
Conclusion
In understanding the difference between climate change and global warming, one gains a more comprehensive view of environmental issues. While global warming focuses predominantly on increased temperatures due to greenhouse gas emissions, climate change encapsulates a broader array of alterations in our climate system. Addressing these challenges demands collective action, grounded in scientific understanding and proactive policies. By recognizing these distinctions, society can better navigate the complexities of climate dynamics and forge a sustainable path forward.